-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 1
Multipart FileUpload
Uploading Files with Java Servlet Technology:
-
The Servlet 3.0 specification supports file upload out of the box, so any web container that implements the specification can parse multipart requests and make mime attachments available through the HttpServletRequest object.
-
A new annotation, javax.servlet.annotation.MultipartConfig, is used to indicate that the servlet on which it is declared expects requests to made using the multipart/form-data MIME type. Servlets that are annotated with @MultipartConfig can retrieve the Part components of a given multipart/form-data request by calling the request.getPart(String name) or request.getParts() method.
The @MultipartConfig Annotation:
The @MultipartConfig annotation supports the following optional attributes:
-
location: An absolute path to a directory on the file system. The location attribute does not support a path relative to the application context. This location is used to store files temporarily while the parts are processed or when the size of the file exceeds the specified fileSizeThreshold setting. The default location is "". -
fileSizeThreshold: The file size in bytes after which the file will be temporarily stored on disk. The default size is 0 bytes. -
MaxFileSize: The maximum size allowed for uploaded files, in bytes. If the size of any uploaded file is greater than this size, the web container will throw an exception (IllegalStateException). The default size is unlimited. -
maxRequestSize: The maximum size allowed for a multipart/form-data request, in bytes. The web container will throw an exception if the overall size of all uploaded files exceeds this threshold. The default size is unlimited.
For, example, the @MultipartConfig annotation could be constructed as follows:
@MultipartConfig(location="/tmp", fileSizeThreshold=1024*1024,
maxFileSize=1024*1024*5, maxRequestSize=1024*1024*5*5)Instead of using the @MultipartConfig annotation to hard-code these attributes in your file upload servlet, you could add the following as a child element of the servlet configuration element in the web.xml file.
<multipart-config>
<location>/tmp</location>
<max-file-size>20848820</max-file-size>
<max-request-size>418018841</max-request-size>
<file-size-threshold>1048576</file-size-threshold>
</multipart-config>- Interface Part: represents a part in a multipart/form-data request. This interface defines some methods for working with upload data (to name a few):
getInputStream(): returns an InputStream object which can be used to read content of the part.getSize(): returns the size of upload data, in bytes.write(String filename): this is the convenience method to save upload data to file on disk. The file is created relative to the location specified in the MultipartConfig annotation.
New methods introduced in HttpServletRequest interface:
-
getParts(): returns a collection of Part objects -
getPart(String name): retrieves an individual Part object with a given name.
Architecture of the Multipart FileUpload:
Some Program like JSP/Servlet raise the Multipart POST request, and other Program like Servlet consumes the request and save the Multipart data on to Server side Disk.
- FileUpload parses HTTP requests which conform to RFC 1867, "Form-based File Upload in HTML". That is, if an HTTP request is submitted using the POST method, and with a content type of "multipart/form-data", then FileUpload can parse that request, and make the results available in a manner easily used by the caller.
Two mandatory restrictions are applied to the form with input type file:
- The enctype attribute must be set to a value of multipart/form-data.
- Its method must be POST.
The simplest way to send a multipart/form-data request to a server is via a web form, i.e.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1">
<title>File Upload</title>
</head>
<body>
<center>
<h1>File Upload</h1>
<form method="post" action="UploadServlet" enctype="multipart/form-data">
File1: <input type="file" name="file1" size="60" /> <br/>
File2: <input type="file" name="file2" /> <br/>
<br/><input type="submit" value="Upload" />
</form>
</center>
</body>
</html>POST requests Message body:
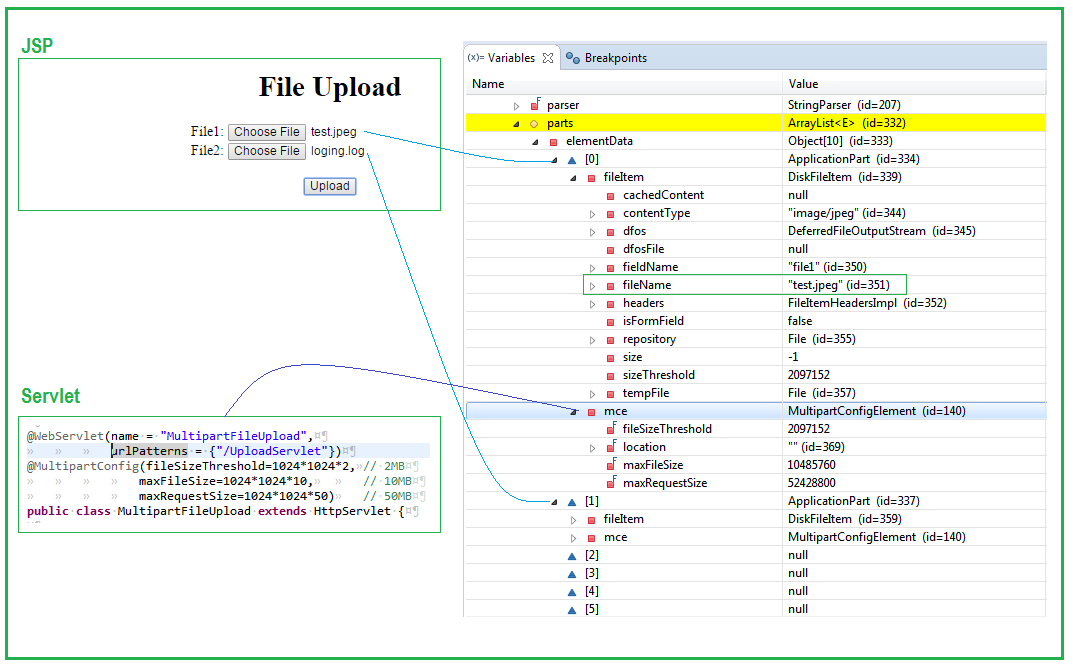
Example Servlet MultipartFileUpload.java
- The
@WebServletannotation uses the urlPatterns property to define servlet mappings.- The
@MultipartConfigannotation indicates that the servlet expects requests to made using the multipart/form-data MIME type.
@WebServlet(name = "MultipartFileUpload", urlPatterns = {"/UploadServlet"})
@MultipartConfig(fileSizeThreshold=1024*1024*2, // 2MB
maxFileSize=1024*1024*10, // 10MB
maxRequestSize=1024*1024*50) // 50MB
public class MultipartFileUpload extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("http://localhost:8080/UploadServlet30/upload.jsp");
File directoryPath = new File("E:\\");
for (Part part : request.getParts()) {
System.out.println("===== ----- Multipart Data ----- =====");
File tempFile = new File( extractFileName(part) );
int index = tempFile.getName().lastIndexOf('.');
String suffix = tempFile.getName().substring(index);
String fileName = tempFile.getName().substring(0, index);
System.out.format("File Name: %s, Extension: %s \n", fileName, suffix);
File file = File.createTempFile(fileName, suffix, directoryPath);
try ( InputStream input = part.getInputStream() ) {
Files.copy(input, file.toPath(), StandardCopyOption.REPLACE_EXISTING);
}
}
request.setAttribute("message", "Upload has been done successfully!");
getServletContext().getRequestDispatcher("/message.jsp").forward(request, response);
}
/**
* Extracts file name from HTTP header content-disposition
*
* <P> Content-Disposition: form-data; name="file"; filename="sample.txt"
*/
private String extractFileName(Part part) {
String contentDisp = part.getHeader("content-disposition");
String[] items = contentDisp.split(";");
for (String s : items) {
if (s.trim().startsWith("filename")) {
//return s.substring(s.indexOf("=") + 2, s.length()-1);
return s.substring(s.indexOf('=') + 1).trim().replace("\"", "");
}
}
return null;
}
}Required jars are: commons-fileupload-1.2.2.jar, commons-io-2.2.jar and WebService Example and Servlet2.5 Example
In a class-based object-oriented language, in general, state is carried by instances, methods are carried by classes, and inheritance is only of structure and behavior. Basic, Refactoring Techniques
Method signature: It consists of method name and parameter list (number/type/order of the parameters). methodName(parametersList y). An instance method in a subclass with the same signature and return type as an instance method in the super-class overrides the super-class's method.
Java OOP concepts
Class - Collection of a common features of a group of object [static/instance Fields, blocks and Methods]
Object - Instance of a class (instance fields)
Abstraction - Process of hiding complex info and providing required info like API, Marker Interfaces ...
Encapsulation(Security) - Class Binding up with data members(fields) and member functions.
Inheritance (Reusability by placing common code in single class)
1. Multilevel - {A -> B -> C} 2. Multiple - Diamond problem {A <- (B) -> C} [Java not supports] 3. Cyclic {A <-> B} [Java not supports]
* Is-A Relation - Class A extends B
* Hash-A Relation - Class A { B obj = new B(); } - (Composition/Aggregation)
Polymorphism (Flexibility) 1. Compile-Time Overloading 2. Runtime Overriding [Greek - "many forms"]
int[] arr = {1,2,3}; int arrLength = arr.length; // Fixed length of sequential blocks to hold same data type
String str = "Yash"; int strLength = str.length(); // Immutable Object value can't be changed.
List<?> collections = new ArrayList<String>(); int collectionGroupSize = collections.size();
Map<?, ?> mapEntry = new HashMap<String, String>();
Set<?> keySet = mapEntry.keySet(); // Set of Key's
Set<?> entrySet = mapEntry.entrySet(); // Set of Entries [Key, Value]
// Immutable Objects once created they can't be modified. final class Integer/String/Employee
Integer val = Integer.valueOf("100"); String str2 = String.valueOf(100); // Immutable classes
final class Employee { // All Wrapper classes, java.util.UUID, java.io.File ...
private final String empName; // Field as Final(values can be assigned only once) Only getter functions.
public Employee(String name) { this.empName = name; }
} Native Java Code for Hashtable.h, Hashtable.cpp
SQL API.
You can check your current JDK and JRE versions on your command prompt respectively,
- JDK
javac -version [C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_121\bin]o/p:javac 1.8.0_121 - JRE
java -version[C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_121\bin]o/P:java version "1.8.0_102"
JAVA_HOME - Must be set to JDK otherwise maven projects leads to compilation error. [ERROR] No compiler is provided in this environment. Perhaps you are running on a JRE rather than a JDK? C:\Softwares\OpenJDK\, 7-zip
Fatal error compiling: invalid target release: JRE and JDK must be of same version
1.8.0.XXX
Disable TLS 1.0 and 1.1
security-libs/javax.net.ssl: TLS 1.0 and 1.1 are versions of the TLS protocol that are no longer considered secure and have been superseded by more secure and modern versions (TLS 1.2 and 1.3).
Core Java
-
Java Programming Language Basics
- Object, Class, Encapsulation, Interface, Inheritance, Polymorphism (Method Overloading, Overriding)
- JVM Architecture, Memory Areas
- JVM Class Loader SubSystem
- Core Java Interview Questions & Programs
- Interview Concepts
Stack Posts
- Comparable vs Comparator
- Collections and Arrays
-
String, StringBuffer, and StringBuilder
- String reverse
- Remove single char
- File data to String
- Unicode equality check Spacing entities
- split(String regex, int limit)
- Longest String of an array
-
Object Serialization
- Interface's Serializable vs Externalizable
- Transient Keyword
-
implements Runnablevsextends Thread - JSON
- Files,
Logging API- Append text to Existing file
- Counting number of words in a file
- Properties
- Properties with reference key