-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 1
Collections vs Arrays
Array is of Fixed Size
Collection is a Re-sizable Array
The core collection interfaces encapsulate different types of collections, which are shown in the figure below. These interfaces allow collections to be manipulated independently of the details of their representation. Core collection interfaces are the foundation of the Java Collections Framework. As you can see in the following figure, the core collection interfaces form a hierarchy.
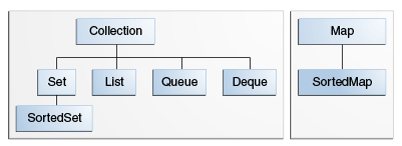
Collection — the root of the collection hierarchy. A collection represents a group of objects known as its elements. The Collection interface is the least common denominator that all collections implement and is used to pass collections around and to manipulate them when maximum generality is desired. Some types of collections allow duplicate elements, and others do not. Some are ordered and others are unordered. The Java platform doesn't provide any direct implementations of this interface but provides implementations of more specific subinterfaces, such as Set and List.
List — an ordered collection (sometimes called a sequence). Lists can contain duplicate elements. The user of a List generally has precise control over where in the list each element is inserted and can access elements by their integer index (position). If you've used Vector, you're familiar with the general flavor of List.
Integer[] elements = {25, 77 , 66};
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll( list, elements ); //Since:1.5
// List allows duplicates, Set contains unique values
List<Integer> distinctList = new ArrayList<>( new LinkedHashSet<>( list ) );
distinctList.add( 77 );-
add(Element);Make a new array of 's runtime type and coppies the prevous elements to new Array.<Object, Object> Object[] java.util.Arrays.copyOf(Object[] original, int newLength, Class<? extends Object[]> newType)
Copies the specified array, truncating or padding with nulls (if necessary)so the copy has the specified length.
-
add(index, Element);void java.lang.System.arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int destPos, int length)
Copies an array from the specified source array, beginning at the specified position, to the specified position of the destination array.A sub-sequence of array components are copied from the source array referenced by
srcto the destination array referenced bydest. The number of components copied is equal to the length argument.
To get the values from the List and display:
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); // DEFAULT_CAPACITY
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
list.add(i);
}
// Using Iterator Since 1.2
Iterator<Integer> iterator = list.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Integer integer = (Integer) iterator.next();
System.out.println(integer);
}
// Advanced for each Since 1.5
for (Integer integer : list) {
System.out.println(integer);
}
// Stream API - Lambda Expression Since 8
list.forEach(System.out::println);Because of Memory We go for ArrayList instead of Vector.
ArrayList<>(); // JDK1.2 Initial Capacity 10, Increase Capacity 50%
Vector<>(); // JDK1.0 Initial Capacity 10, Increase Capacity 100%, Theoretically Thread Safe.
Stack<>(); // JDK1.0 Initial Capacity 10, Increase Capacity 100%, Push(), Pop(), extera funcitons.
LinkedList<E>extends AbstractSequentialList
implements List, Deque, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
add(E e)
add(int index, E element)
addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)
addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c)
remove(Object o)
remove(int index)
get(int index)
set(int index, E element)
getFirst()
getLast()
removeFirst()
removeLast()
addFirst(E e)
addLast(E e)
contains(Object o)
size()
clear()
// Search Operations
indexOf(Object o)
lastIndexOf(Object o)
// Queue operations. @since 1.5
peek() - Retrieves, but does not remove, the head
element() - Retrieves, but does not remove, the head
@throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
poll() - Retrieves and removes the head
remove() - Retrieves and removes the head
offer(E e) - Adds the specified element as the tail
// Deque operations. @since 1.6
offerFirst(E e) - Inserts the specified element at the front
offerLast(E e) - Inserts the specified element at the end
peekFirst() - Retrieves, but does not remove, the first element
peekLast() - Retrieves, but does not remove, the last element
pollFirst() - Retrieves and removes the first element
pollLast() - Retrieves and removes the last element
push(E e) - Pushes an element onto the stack (front)
pop() - Pops an element from the stack (front)
removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) - when traversing the list from head to tail removes the first occred element
removeLastOccurrence(Object o) - when traversing the list from head to tail removes the last occred element
listIterator(int index)
descendingIterator() // @since 1.6
clone()
toArray()
toArray(T[] a)
spliterator() // @since 1.8
Set — a collection that cannot contain duplicate elements. This interface models the mathematical set abstraction and is used to represent sets, such as the cards comprising a poker hand, the courses making up a student's schedule, or the processes running on a machine.
Map — an object that maps keys to values. A Map cannot contain duplicate keys; each key can map to at most one value. If you've used Hashtable, you're already familiar with the basics of Map.
In a class-based object-oriented language, in general, state is carried by instances, methods are carried by classes, and inheritance is only of structure and behavior. Basic, Refactoring Techniques
Method signature: It consists of method name and parameter list (number/type/order of the parameters). methodName(parametersList y). An instance method in a subclass with the same signature and return type as an instance method in the super-class overrides the super-class's method.
Java OOP concepts
Class - Collection of a common features of a group of object [static/instance Fields, blocks and Methods]
Object - Instance of a class (instance fields)
Abstraction - Process of hiding complex info and providing required info like API, Marker Interfaces ...
Encapsulation(Security) - Class Binding up with data members(fields) and member functions.
Inheritance (Reusability by placing common code in single class)
1. Multilevel - {A -> B -> C} 2. Multiple - Diamond problem {A <- (B) -> C} [Java not supports] 3. Cyclic {A <-> B} [Java not supports]
* Is-A Relation - Class A extends B
* Hash-A Relation - Class A { B obj = new B(); } - (Composition/Aggregation)
Polymorphism (Flexibility) 1. Compile-Time Overloading 2. Runtime Overriding [Greek - "many forms"]
int[] arr = {1,2,3}; int arrLength = arr.length; // Fixed length of sequential blocks to hold same data type
String str = "Yash"; int strLength = str.length(); // Immutable Object value can't be changed.
List<?> collections = new ArrayList<String>(); int collectionGroupSize = collections.size();
Map<?, ?> mapEntry = new HashMap<String, String>();
Set<?> keySet = mapEntry.keySet(); // Set of Key's
Set<?> entrySet = mapEntry.entrySet(); // Set of Entries [Key, Value]
// Immutable Objects once created they can't be modified. final class Integer/String/Employee
Integer val = Integer.valueOf("100"); String str2 = String.valueOf(100); // Immutable classes
final class Employee { // All Wrapper classes, java.util.UUID, java.io.File ...
private final String empName; // Field as Final(values can be assigned only once) Only getter functions.
public Employee(String name) { this.empName = name; }
} Native Java Code for Hashtable.h, Hashtable.cpp
SQL API.
You can check your current JDK and JRE versions on your command prompt respectively,
- JDK
javac -version [C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_121\bin]o/p:javac 1.8.0_121 - JRE
java -version[C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_121\bin]o/P:java version "1.8.0_102"
JAVA_HOME - Must be set to JDK otherwise maven projects leads to compilation error. [ERROR] No compiler is provided in this environment. Perhaps you are running on a JRE rather than a JDK? C:\Softwares\OpenJDK\, 7-zip
Fatal error compiling: invalid target release: JRE and JDK must be of same version
1.8.0.XXX
Disable TLS 1.0 and 1.1
security-libs/javax.net.ssl: TLS 1.0 and 1.1 are versions of the TLS protocol that are no longer considered secure and have been superseded by more secure and modern versions (TLS 1.2 and 1.3).
Core Java
-
Java Programming Language Basics
- Object, Class, Encapsulation, Interface, Inheritance, Polymorphism (Method Overloading, Overriding)
- JVM Architecture, Memory Areas
- JVM Class Loader SubSystem
- Core Java Interview Questions & Programs
- Interview Concepts
Stack Posts
- Comparable vs Comparator
- Collections and Arrays
-
String, StringBuffer, and StringBuilder
- String reverse
- Remove single char
- File data to String
- Unicode equality check Spacing entities
- split(String regex, int limit)
- Longest String of an array
-
Object Serialization
- Interface's Serializable vs Externalizable
- Transient Keyword
-
implements Runnablevsextends Thread - JSON
- Files,
Logging API- Append text to Existing file
- Counting number of words in a file
- Properties
- Properties with reference key