-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 1
Install Guide
Riad Shash (Ray) edited this page May 9, 2023
·
22 revisions
Instrument Server was developed on MS Windows, so Windows is the only supported OS at this time. It is a Python Flask & QT application that uses lots of Python packages (like pyMeasure).
- Instrument Server was developed on Python
3.11.0, so any version of 3.11+ should work. - Python 3.11.0 Windows installer (64-bit)
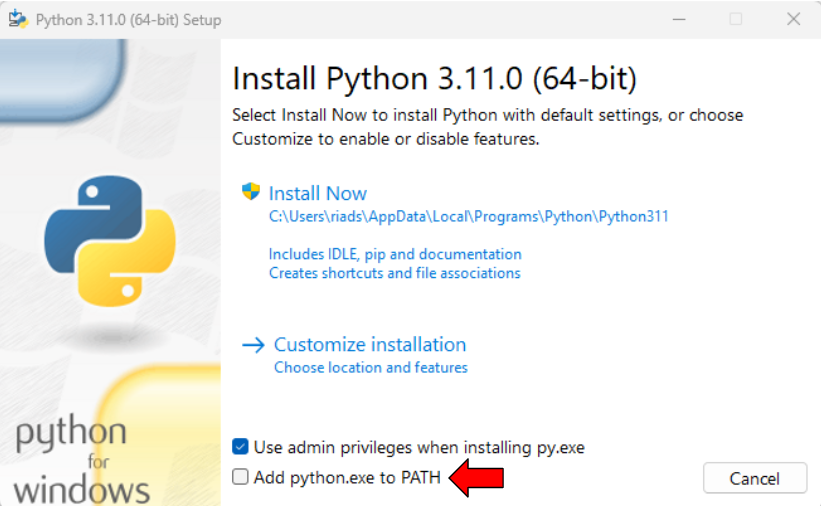
- Make sure to add
python.exeto your PATH
- Since Instrument Server uses
pyVISAto connect to VISA Instruments, a suitable host VISA backend is necessary. SincepyVISAwas tested to worked with National Instrument's (NI)NI-VISA, it to recommended to install this one. - NI-VISA
- Instrument server uses
picoscopePython package to connect to Picscope Instruments. Just like for VISA, it also needs a backend. - Download & Install the appropriate PicoScope Downloads backend & application from Pico Technology.
- Instrument Server uses
PostgreSQLDB for persistence. In order to easily facilitate easy deployment of DB with minimal effort, Instrument Server will connect to a containerized instance ofPostgreSQLrunning inside of a Docker container. To enable running on Docker containers,Docker Desktopis needed. - Docker Desktop
- In order to use
gitfeatures,gitneeds to be installed on the host system. - Git for Windows
- Clone the Repository:
-
- Navigate to where you would like to clone Instrument Server.
-
- In
Windows Explorer, right-click and clickGIt Bash Here. This will pop-up a terminal style CLI. If the option is not available, navigate to the desired directory viaGit Bashapp for Windows.
- In
-
- Run
git clone https://github.com/DataCQProject/InstrumentServer.git(HTTPS). We prefer you setup a SSH Private/Public keypair to use with GitHub
- Run
-
- A new directory will be created called
InstrumentServer.
- A new directory will be created called
-

- Instrument Server uses various Python packages, these packages need to be installed prior to running Instrument Server. This project uses the Python
pippackage-management system to facilitate this. These packages will be installed into an isolated Python environment (separate from host python) facilitated byvirtualenv. - A Windows "Batch" script was written to automate this: setupEnv.bat which is meant to run from a Windows CMD Terminal:
- Open Terminal / Command Prompt
- Navigate to the cloned
InstrumentServerdirectory... (You can also right-click in File Explorer and click "Open Terminal" (might not be present). - Run the batch script (press return twice):
Example:
C:\GitHub\Test\InstrumentServer>setupEnv.bat
"This script will install virtualenv & setup a Python Virtual Environment -> venv"
Press any key to continue . . .
"Installing Python virtualenv"
"Checking for pip updates..."
...
(venv) C:\GitHub\Test\InstrumentServer>
- Notice the
venvin front of the command prompt. That indicates that you are inside of thevenvpython virtual environment that was just created. Leave the terminal open while proceeding to the next step.
- We will use
pipto install all the packages we need. All the required packages and specific versions are specified in requirements.txt. - Another Windows "Batch" script was written to automate this: installPackages.bat
- (Inside of
venvvirtual environment, runinstallPackages.bat:
(venv) C:\GitHub\Test\InstrumentServer>installPackages.bat
- This might take a while... make some ☕ and or take a break 🙂
- Now with docker desktop installed, we are ready to deploy the
PostgreSQLdatabase. - In Windows Command Prompt (Terminal), navigate to where
InstrumentServerwas clone and go into the\DBdirectory. - There is a docker-compose.yaml file that defines the containerized
PostgreSQLas well as a local web application calledadminerwhich can be used to manage the DB (optional, but enabled by default). It also sets up a Docker Volume calleddb_pgdatawhich will be used for DB storage (persistence). - In the same directory as
docker-compose.yaml, run the following command to deploy the DB:
C:\GitHub\InstrumentServer\DB>docker-compose up -d
- You can see all running containers with
docker ps(optional):
C:\GitHub\InstrumentServer\DB>docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
14b42997fd70 postgres:15.2-alpine "docker-entrypoint.s…" 5 weeks ago Up 33 minutes 0.0.0.0:5432->5432/tcp instrument_server_db
cb4242c9e441 adminer "entrypoint.sh php -…" 5 weeks ago Up 33 minutes 0.0.0.0:8080->8080/tcp adminer_client
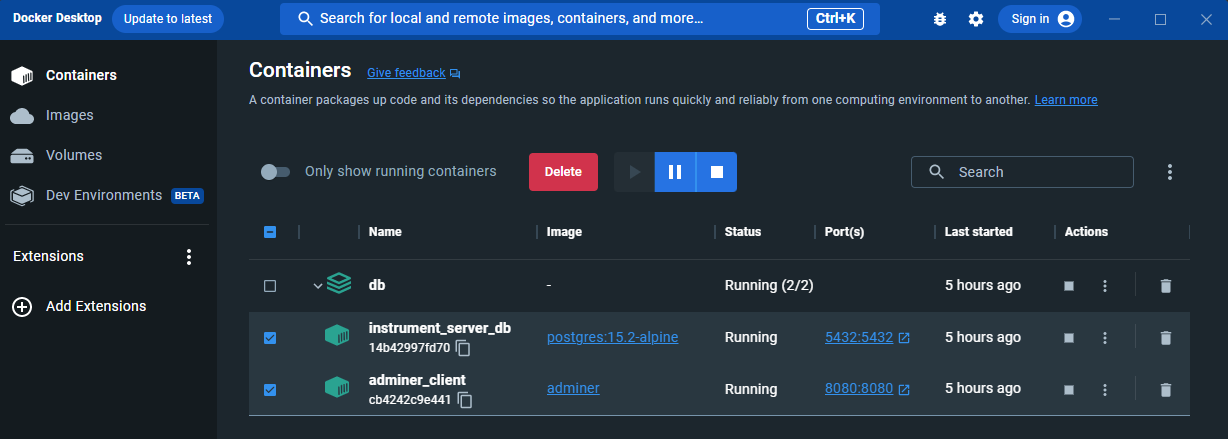
- You can also see all the Docker containers & volumes in Docker Desktop application:
- A script was written to easily deploy Instrument Server (note: The DB needs to be deployed/enabled prior to running).
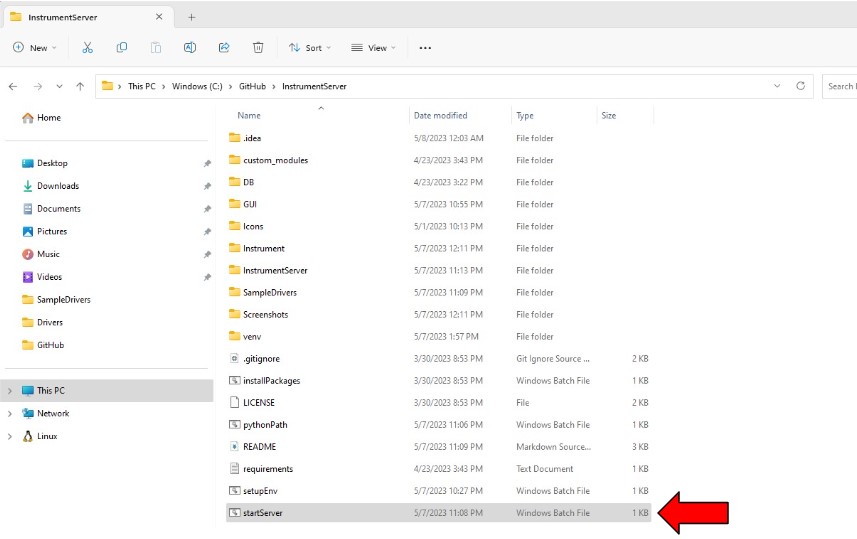
- In File Explorer, navigate to the area where
InstrumentServerrepository was cloned. - Double-click on startServer.bat. This will deploy instrument server in a couple of seconds.
- Home
- License
- Architecture
- User Guide
1. Install Guide
2. Instrument Server
3. Manual Instrument Control
4. Drivers and Managers
4a. Drivers
4b. InstrumentManager
4c. QuantityManager
5. Experiment Module
5a. Create Experiment
5b. Experiment Runner