-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 5
iOS




AR-Evacuation With Beacons is the name of the application and made for iOS devices. AR-Evacuation With Beacons detects the beacons inside of K-SW Square building which is in the Purdue University. The application estimates user's current location indoor and inform the optimized path to each user to flee safely from fire situation.
ARNavigationViewController mainly displays the AR Navigation system. The application is made of MVC pattern. So this viewcontroller does lots of works. Mainly this viewcontroller change angle of 3D AR arrow and spawn the 3d object in next route based on given angle and distance from VectorService and IndoorLocationManager. With these information, the app can help evacuee flee safely.
This code block is main function of the viewcontroller. When the vector is set, the ARKit make the arrow change the angle in every 60 frames. The important things in AR world is that the app is using the gravityAndheading world configuration. With this, we are able to use absolute orientation, which means we can make our own 2d coordinate systems.
@objc private func movenotification(_ noti: Notification) {
guard let userLocation = noti.object as? Position else {return}
mapContentScrollView.scroll(to: map2DViewController.annotationView.currentPoint)
// 1.when the path is there
guard !path.path.isEmpty else {return}
// 2. find the location
guard let index = path.path.firstIndex(of: userLocation) else {return}
// 3. if the location is not the destination
if index < path.path.count - 1 {
// find the vector bwt 2 points
let start = VectorService.transformCellToCGPoint(cellname: path.path[index])
let end = VectorService.transformCellToCGPoint(cellname:path.path[index+1])
let vector = VectorService.vectorBetween2Points(from: start, to: end)
// get angle
directionDegree = vector.angle
// get dist
let dist = vector.dist
// generate sphere to next cell
// 1 cell = 36cm
let newnode = generateSphereNode()
sceneView.scene.rootNode.addChildNode(newnode)
newnode.position = SCNVector3(x: arrow.position.x, y: arrow.position.y, z: arrow.position.z - (Float(dist) / 10 * 0.36) + 1.0)
} else {
bannerText = "Safely Exit"
let alert = UIAlertController(title: "YOU ARE SAFE😀", message: nil, preferredStyle: .alert)
self.present(alert, animated: true)
}
}Map2DViewController can user see the 2D map. Map2DViewController contains 3 views drawn by UIBeizerPath and 1 view that annotate user's location. The view of viewcontroller is ported in the scrollview inside ARNavigationViewController. Also, Map2DViewController can display the status of fire situation. Green cell is the optimized path. Red cell is the fire cell. Orange Cell is the fire nearby cell. Yellow cell is the conjestion cell.
IndoorLocationManager manage the beacon part and heading part from CoreLocation. The app use trained model to estimate the user's location with beacons' RSSI. Also, in order to adjust the user's location, we fusioned the result of the model and compass sensor.
private func adjustLocation(from previousLocation: Position, to currentLocation: Position, with heading: Double) -> Position {
if previousLocation == .unknown || currentLocation == .unknown {return previousLocation}
let adjacentCells = adjacentCells(nearby: previousLocation)
let currentDirection = headingToDirection(with: heading)
if adjacentCells.contains(currentLocation) {
return locationWhenAdjacentCellInCandidateCells(from: previousLocation,
to: currentLocation,
with: currentDirection)
}
return locationWhenAdjacentCellNotInCandidateCells(from: previousLocation,
to: currentLocation,
with: currentDirection)
}
private func locationWhenAdjacentCellNotInCandidateCells(from previousLocation: Position, to currentLocation: Position, with currentDirection: Direction) -> Position {
// if not adjacent cell, but heading of user and angle between previous location and the result are same, we judge the user moves fast.
let currentPosPoint = VectorService.transformCellToCGPoint(cellname: currentLocation)
let prevPosPoint = VectorService.transformCellToCGPoint(cellname: previousLocation)
let indicatedHeading = Double(VectorService.vectorBetween2Points(from: prevPosPoint, to: currentPosPoint).angle)
let direction = headingToDirection(with: indicatedHeading)
if direction == currentDirection {
return candidateCells(by: previousLocation, with: direction).first ?? previousLocation
}
return previousLocation
}
private func candidateCells(by previousLocation: Position, with direction: Direction) -> [Position] {
var candidateCells = previousLocation.adjacentCell[direction.rawValue]
removeUnknownCellFromCandidateCells(candidateCells: &candidateCells)
return candidateCells
}
private func locationWhenAdjacentCellInCandidateCells(from previousLocation: Position, to currentLocation: Position, with currentDirection: Direction) -> Position {
let candidateCells = candidateCells(by: previousLocation, with: currentDirection)
if candidateCells.contains(currentLocation) {
return currentLocation
}
return previousLocation
}
private func removeUnknownCellFromCandidateCells(candidateCells: inout [Position]) {
candidateCells.removeAll { $0 == .unknown }
}Kalman Filter is used to smooth the RSSI from beacons. Kalman Filter runs recursively to estimate the next state with current state. This code is the init of KalmanFilter
init(R: Float, Q: Float, stateVector: Float = 1, controlVector: Float = 0, measureVector: Float = 1) {
self.R = R
self.Q = Q
self.stateVector = stateVector
self.controlVector = controlVector
self.measureVector = measureVector
}R is system noise, Q is measurement noise, and there are 3 vector. stateVector is used to estimate the next statement with equation. measureVector is used to estimate the measure of RSSI. three vector are usually set by the machine that we use. We reinit the filter when beacon's RSSI exceed the threshold. The Threshold will be selected by top 5% and bottom 5% in normal distribution.
In VectorService, we calculate the angle to direction in 2d coordinate. Also, we use atan2 function to find out angle between 2 points.
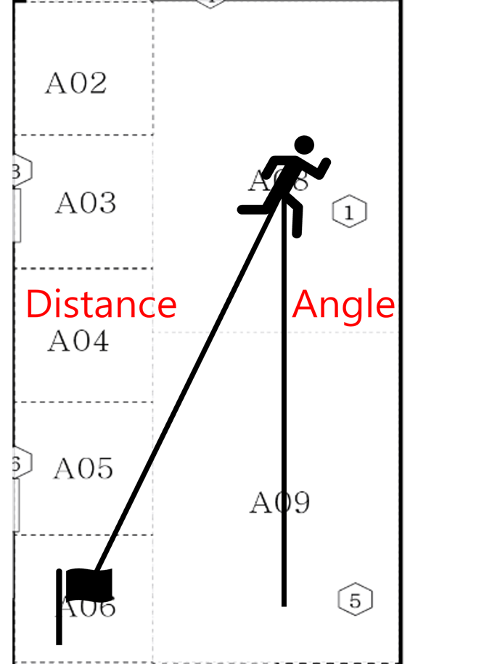
static func vectorBetween2Points(from: CGPoint, to: CGPoint) -> (angle: Float, dist: Double) {
var degree: Float = 0.0
let tan = atan2(from.x - to.x, from.y - to.y) * 180 / .pi
degree = 180 - Float(tan)
return (angle: degree, dist: sqrt(pow(from.x - to.x, 2) + pow(from.y - to.y, 2)))
}