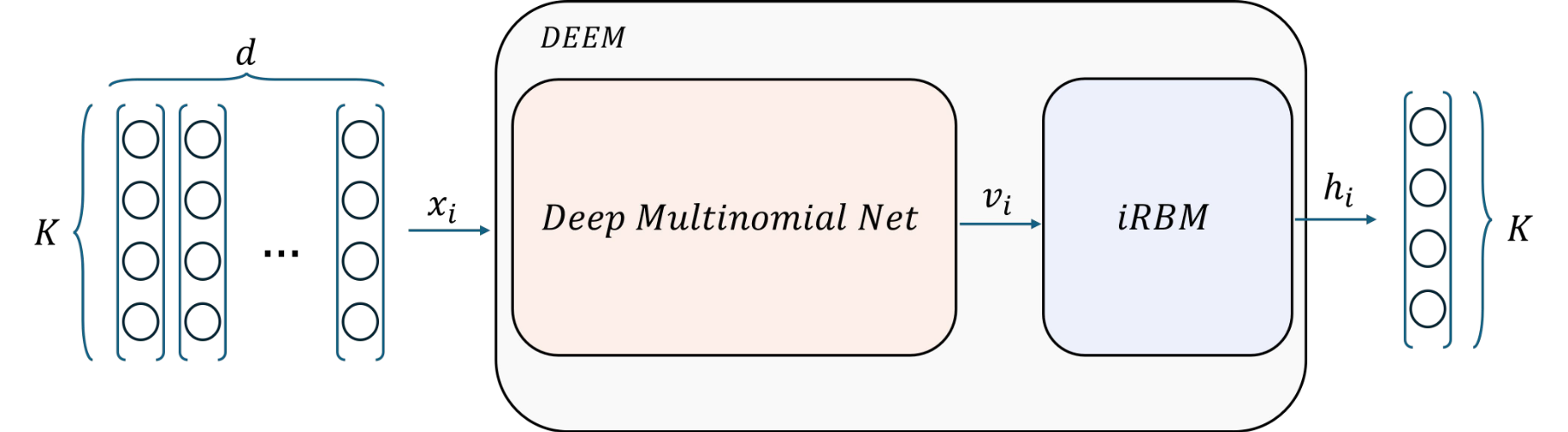
DEEM is a Python library for unsupervised ensemble learning using deep energy-based models. It uniquely discovers latent true labels from diverse, noisy unsupervised sources by disentangling correlations and minimizing the energy of a joint inverse Restricted Boltzmann Machine (iRBM) distribution, without requiring any ground truth.
Unsupervised ensemble learning emerged to address the challenge of combining multiple learners' predictions without access to ground truth labels or additional data. This paradigm is crucial in scenarios where evaluating individual classifier performance or understanding their strengths is challenging due to limited information. We propose a novel deep energy-based method for constructing an accurate meta-learner using only the predictions of individual learners, potentially capable of capturing complex dependence structures between them. Our approach requires no labeled data, learner features, or problem-specific information, and has theoretical guarantees for when learners are conditionally independent. We demonstrate superior performance across diverse ensemble scenarios, including challenging mixture of experts settings. Our experiments span standard ensemble datasets and curated datasets designed to test how the model fuses expertise from multiple sources. These results highlight the potential of unsupervised ensemble learning to harness collective intelligence, especially in data-scarce or privacy-sensitive environments.
- 🚀 Simple 3-line API - Fit and predict in just a few lines of code
- 🔬 Unsupervised Learning - No labels required for training (though they can be used for evaluation)
- 🧮 Energy-Based Models - Uses RBMs to learn the joint distribution of classifier predictions
- 🎯 Transparent Hungarian Alignment - Automatic label permutation handling via
align_toparameter - ⚡ GPU Acceleration - Full PyTorch backend with CUDA support
- 🔧 Scikit-learn Compatible - Standard
.fit(),.predict(),.score()interface - 📊 Automatic Hyperparameters - Optional meta-learning for hyperparameter selection
- 🎚️ Weighted Initialization - Better classifiers get more influence (default ON)
- 📈 Soft Label Support - Works with probability distributions (3D tensors)
pip install deemgit clone https://github.com/shaham-lab/deem.git
cd rbm_python
pip install -e .import numpy as np
from deem import DEEM
# Ensemble predictions from 15 classifiers on 100 samples with 3 classes
predictions = np.random.randint(0, 3, (100, 15))
# Train and predict in 3 lines!
model = DEEM()
model.fit(predictions)
consensus = model.predict(predictions)# If you have true labels, evaluate with automatic label alignment
model = DEEM(n_classes=3, epochs=50)
model.fit(train_predictions)
# Predict with transparent Hungarian alignment via align_to parameter
# Alignment is against MAJORITY VOTE, not true labels (unsupervised!)
consensus = model.predict(test_predictions, align_to=train_predictions)
# Or use score() which handles alignment automatically
accuracy = model.score(test_predictions, test_labels)
print(f"Consensus accuracy: {accuracy:.2%}")# Soft predictions: (n_samples, n_classes, n_classifiers)
# Each classifier outputs a probability distribution over classes
soft_predictions = np.random.rand(100, 3, 15)
soft_predictions = soft_predictions / soft_predictions.sum(axis=1, keepdims=True)
model = DEEM(n_classes=3)
model.fit(soft_predictions) # Automatically detects 3D and enables oh_mode
consensus = model.predict(soft_predictions)model = DEEM(
n_classes=5,
hidden_dim=1, # Number of hidden units (keep at 1 for best results)
learning_rate=0.01,
epochs=100,
batch_size=64,
cd_k=10, # Contrastive divergence steps
deterministic=True, # Use probabilities (more stable)
use_weighted=True, # Scale weights by classifier accuracy (default)
device='cuda' # Use GPU
)
model.fit(predictions)Aggregate noisy labels from multiple human annotators:
# annotator_labels: (n_samples, n_annotators) with values 0 to k-1
model = DEEM(n_classes=k)
model.fit(annotator_labels)
consensus_labels = model.predict(annotator_labels)Combine predictions from multiple trained classifiers:
# Get predictions from multiple models
predictions = np.column_stack([
model1.predict(X),
model2.predict(X),
model3.predict(X),
# ... more models
])
# Learn optimal aggregation
ensemble = DEEM()
ensemble.fit(predictions)
final_predictions = ensemble.predict(predictions)DEEM automatically handles cases where some classifiers don't provide predictions (use -1 for missing):
predictions = np.array([
[0, 1, -1, 2, 1], # Classifier 3 missing
[1, 1, 1, -1, 1], # Classifier 4 missing
# ...
])
model = DEEM(n_classes=3)
model.fit(predictions) # Missing values handled automaticallyBy default, DEEM scales RBM weights by each classifier's agreement with majority vote. This gives better classifiers more influence:
# Weighted initialization is ON by default (recommended)
model = DEEM(n_classes=3) # use_weighted=True by default
model.fit(predictions)
# Disable for ablation studies only
model = DEEM(n_classes=3, use_weighted=False)
model.fit(predictions) # All classifiers treated equallyDEEM uses Restricted Boltzmann Machines (RBMs) - energy-based models that learn the joint probability distribution over classifier predictions and hidden representations. The key insight is that multiple weak classifiers contain complementary information that can be combined through unsupervised learning.
- Energy Function: Models compatibility between visible (predictions) and hidden (consensus) states
- Contrastive Divergence: Trains the RBM using GWG (Gibbs with Gradients) sampling
- Hungarian Algorithm: Solves the label permutation problem during evaluation
- Weighted Initialization: Scales weights by classifier quality (agreement with majority vote)
- Buffer Initialization: Automatic sampler buffer initialization for better MCMC mixing
Classifier Predictions → [Preprocessing] → RBM → Hidden Representation → Consensus Label
(visible layer) (optional) (hidden layer)
When you call model.fit(predictions):
- Data Preparation: Filters samples with all missing values, infers n_classes
- Buffer Initialization: First batch initializes MCMC sampler buffer (transparent)
- Weighted Initialization: RBM weights scaled by classifier accuracy vs majority vote
- Training: Contrastive divergence learns the energy function
- Result: Model ready to predict consensus labels
When you call model.predict(data, align_to=reference):
- Forward Pass: Compute hidden layer probabilities
- Argmax: Get predicted class for each sample
- Hungarian Alignment: Match predicted labels to majority vote of reference
- Return: Aligned consensus predictions
Main class for ensemble aggregation.
Core Parameters:
n_classes(int, optional): Number of classes. Auto-detected if not specified.hidden_dim(int, default=1): Number of hidden units. Keep at 1 for best results.cd_k(int, default=10): Contrastive divergence steps.deterministic(bool, default=True): Use probabilities instead of sampling.learning_rate(float, default=0.001): Learning rate for SGD.momentum(float, default=0.9): SGD momentum.epochs(int, default=100): Training epochs.batch_size(int, default=128): Batch size.device(str, default='auto'): Device ('cpu', 'cuda', or 'auto').random_state(int, optional): Random seed.
Phase 3 Parameters (New):
use_weighted(bool, default=True): Scale weights by classifier accuracy vs majority vote.- Recommended: Keep True for production use.
- Set to False only for ablation studies.
auto_hyperparameters(bool, default=False): Auto-select hyperparameters based on data.model_dir(str, optional): Path to hyperparameter predictor models.
Preprocessing Parameters (Advanced):
use_preprocessing(bool, default=False): Add Multinomial preprocessing layers.preprocessing_layers(int, default=1): Number of preprocessing layers.preprocessing_activation(str, default='sparsemax'): Activation function.preprocessing_init(str, default='identity'): Weight initialization method.
Sampler Parameters (Advanced):
sampler_steps(int, default=5): MCMC sampling steps.sampler_oh_mode(bool, default=False): One-hot mode (auto-enabled for soft labels).
Methods:
fit(predictions, labels=None, **kwargs): Train the model (unsupervised)predict(predictions, return_probs=False, align_to=None): Get consensus predictionsalign_to: Reference data for Hungarian alignment (uses majority vote)
score(predictions, true_labels): Compute accuracy with automatic alignmentget_class_mapping(): Get the cached Hungarian class mappingreset_class_mapping(): Clear the cached mappingsave(path): Save model to diskload(path): Load model from diskget_params(): Get parameters (sklearn compatibility)set_params(**params): Set parameters (sklearn compatibility)
Attributes (after fit):
model_: The trained RBM modelclass_map_: Hungarian mapping (after alignment)n_classes_: Number of classesn_classifiers_: Number of classifiershistory_: Training historyis_fitted_: Whether model is trained
The align_to parameter provides transparent control over label alignment:
# Align predictions to majority vote of training data
train_consensus = model.predict(train_preds, align_to=train_preds)
# Same alignment is cached and reused
test_consensus = model.predict(test_preds) # Uses cached class_map_
# Force recomputation
model.reset_class_mapping()
new_consensus = model.predict(test_preds, align_to=test_preds)
# Get the mapping for inspection
mapping = model.get_class_mapping()
print(f"Predicted class 0 → Aligned class {mapping[0]}")Important: Alignment is always against MAJORITY VOTE, not true labels. This preserves the unsupervised nature of the model.
NEW: Hyperparameter prediction now works out-of-the-box! No need to specify model_dir.
# Simple - uses bundled trained models automatically
model = DEEM(
n_classes=10,
auto_hyperparameters=True # That's it!
)
model.fit(predictions, verbose=True) # Shows auto-selected hyperparameters
# Still optionally override specific hyperparameters
model = DEEM(
auto_hyperparameters=True,
epochs=100, # Override auto-selected epochs
batch_size=512 # Override auto-selected batch size
)
# Use custom trained models (for experiments)
model = DEEM(
auto_hyperparameters=True,
model_dir='path/to/custom/models' # Optional
)What gets predicted automatically:
batch_size: Training batch sizeepochs: Number of training epochslearning_rate: Optimizer learning rateinit_method: Weight initialization (mv_rand, mv_lo, rand)num_layers: Number of preprocessing layersactivation_func: Preprocessing activation functionmomentum: Optimizer momentumscheduler: Learning rate scheduler
The predictor uses dataset meta-features (n_samples, n_classifiers, token_density, etc.) to select optimal hyperparameters.
DEEM automatically detects and handles soft labels (3D tensors):
# soft_predictions: (n_samples, n_classes, n_classifiers)
# Each entry is a probability distribution over classes
soft_predictions = classifier_probabilities # Shape: (100, 3, 15)
model = DEEM(n_classes=3)
model.fit(soft_predictions) # Auto-detects 3D, enables oh_mode
consensus = model.predict(soft_predictions)What happens automatically:
- Detects 3D tensor → enables one-hot sampler mode
- Infers n_classes from tensor shape (dim 1)
- Normalizes probabilities if needed
# Save trained model
model.save('my_ensemble.pt')
# Load later
model = DEEM()
model.load('my_ensemble.pt')
predictions = model.predict(new_data)For complex datasets, add learnable preprocessing layers:
model = DEEM(
n_classes=3,
use_preprocessing=True,
preprocessing_layers=1,
preprocessing_activation='entmax',
preprocessing_init='identity'
)
model.fit(predictions)# Default behavior: classifiers weighted by accuracy vs majority vote
model = DEEM(n_classes=3, use_weighted=True) # Default
# For ablation studies: disable weighting
model = DEEM(n_classes=3, use_weighted=False)
model.fit(predictions) # All classifiers treated equally| Parameter | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
n_classes |
int, optional | None | Number of classes. Auto-inferred from data if not provided. |
hidden_dim |
int | 1 | Number of hidden units. Keep at 1 for best results. |
learning_rate |
float | 0.001 | Learning rate for optimizer. |
epochs |
int | 50 | Number of training epochs. |
batch_size |
int | 128 | Training batch size. Larger = faster, smaller = better mixing. |
momentum |
float | 0.0 | SGD momentum. Range: [0, 1]. |
device |
str | 'auto' | Device: 'auto', 'cpu', or 'cuda'. Auto selects GPU if available. |
| Parameter | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
cd_k |
int | 10 | Contrastive divergence steps. Higher = better but slower. |
deterministic |
bool | True | Use probabilities (True) vs sampling (False). Keep True for stability. |
init_method |
str | 'mv_rand' | Weight init: 'mv_rand' (majority vote + random), 'mv_lo', or 'rand'. |
use_weighted |
bool | True | Scale weights by classifier accuracy vs majority vote. Recommended: True. |
| Parameter | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
sampler_steps |
int | 10 | MCMC sampler steps. More steps = better samples but slower. |
sampler_oh_mode |
bool | False | One-hot mode for sampler. Auto-enabled for soft labels (3D tensors). |
| Parameter | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
use_preprocessing |
bool | False | Enable learnable preprocessing layers before RBM. |
preprocessing_layers |
int | 0 | Number of Multinomial layers. Ignored if preprocessing_layer_widths specified. |
preprocessing_layer_widths |
list[int], optional | None | Custom layer widths, e.g., [20, 15, 10]. Overrides preprocessing_layers. |
preprocessing_activation |
str | 'sparsemax' | Activation: 'sparsemax', 'entmax', 'softmax', 'relu', 'gelu', etc. |
preprocessing_init |
str | 'identity' | Preprocessing init: 'identity', 'rand', 'mv'. |
preprocessing_one_hot |
bool | False | Use one-hot encoding in preprocessing. |
preprocessing_use_softmax |
bool | False | Apply softmax in preprocessing layers. |
preprocessing_jitter |
float | 0.0 | Jitter coefficient for preprocessing. |
| Parameter | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
auto_hyperparameters |
bool | False | Enable automatic hyperparameter selection. Works out-of-the-box! |
model_dir |
str/Path, optional | None | Custom model directory. None = use bundled models. |
| Parameter | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
random_state |
int, optional | None | Random seed for reproducibility. |
kwargs |
dict | {} | Additional kwargs passed to RBM model (e.g., custom init_method). |
DEEM supports both hard labels (integers) and soft labels (probability distributions).
# Shape: (n_samples, n_classifiers)
# Each entry is an integer class label: 0, 1, 2, ..., k-1
hard_predictions = np.array([
[0, 1, 0, 2, 0], # Sample 1: classifiers predict 0, 1, 0, 2, 0
[1, 1, 2, 1, 1], # Sample 2: classifiers predict 1, 1, 2, 1, 1
[2, 2, 2, 1, 2], # Sample 3: classifiers predict 2, 2, 2, 1, 2
])
model = DEEM(n_classes=3)
model.fit(hard_predictions)# Shape: (n_samples, n_classes, n_classifiers)
# Each entry is a probability distribution over classes
soft_predictions = np.array([
# Sample 1 - 5 classifiers, each gives 3-class distribution
[[0.7, 0.2, 0.1], # Classifier 1: 70% class 0, 20% class 1, 10% class 2
[0.1, 0.8, 0.1], # Classifier 2: 10% class 0, 80% class 1, 10% class 2
[0.6, 0.3, 0.1], # Classifier 3: ...
[0.2, 0.3, 0.5], # Classifier 4: ...
[0.8, 0.1, 0.1]], # Classifier 5: ...
# Sample 2
[[0.1, 0.7, 0.2],
[0.2, 0.6, 0.2],
[0.3, 0.4, 0.3],
[0.1, 0.8, 0.1],
[0.2, 0.7, 0.1]],
])
# Shape: (2, 3, 5) = (n_samples=2, n_classes=3, n_classifiers=5)
# DEEM automatically detects 3D tensors as soft labels!
model = DEEM() # n_classes inferred from shape: 3
model.fit(soft_predictions) # Auto-enables oh_mode=True
consensus = model.predict(soft_predictions) # Returns hard labels: [0, 1, ...]What happens automatically with soft labels:
- ✅ 3D tensor detection: Checks if
predictions.shape[0] == 3 - ✅ Auto-infer n_classes: Extracts from
predictions.shape[1] - ✅ Enable oh_mode: Sets
sampler_oh_mode=Trueautomatically - ✅ Proper preprocessing: Converts distributions to one-hot during sampling
Converting between formats:
# Soft → Hard (argmax)
hard_preds = soft_preds.argmax(axis=1) # (N, K, D) → (N, D)
# Hard → Soft (one-hot)
from torch.nn.functional import one_hot
soft_preds = one_hot(torch.tensor(hard_preds), num_classes=3).numpy()
soft_preds = soft_preds.transpose(0, 2, 1) # (N, D, K) → (N, K, D)Preprocessing layers learn to transform classifier outputs before the RBM, useful for:
- Handling heterogeneous classifiers (different architectures)
- Learning calibration/alignment of classifier outputs
- Dimensionality transformation
# Add 2 preprocessing layers, each maintains same width (n_classifiers)
model = DEEM(
n_classes=3,
use_preprocessing=True,
preprocessing_layers=2, # Number of layers
preprocessing_activation='entmax', # Activation function
preprocessing_init='identity', # Initialize to identity transform
)
# Architecture: input(15) → Multinomial(15) → Multinomial(15) → RBM(15)# Transform classifier dimension: 15 → 20 → 15 → 10
model = DEEM(
n_classes=3,
use_preprocessing=True,
preprocessing_layer_widths=[20, 15, 10], # Explicit widths
preprocessing_activation='sparsemax',
)
# Architecture: input(15) → Multinomial(20) → Multinomial(15) → Multinomial(10) → RBM(10)| Activation | Description | When to Use |
|---|---|---|
sparsemax |
Sparse softmax (default) | General purpose, encourages sparsity |
entmax |
Entmax-1.5 | Adaptive sparsity, good for ensembles |
softmax |
Standard softmax | Dense distributions |
relu |
ReLU | Non-negative outputs |
gelu |
GELU | Smooth non-linearity |
| Init Method | Description | When to Use |
|---|---|---|
identity |
Identity transform (default) | Preserve input initially |
rand |
Random weights | Learn from scratch |
mv |
Majority vote statistics | Start near MV baseline |
# Research code YAML config:
# model:
# multinomial_net:
# num_layers: 1
# activation_func_name: 'entmax'
# init_method: 'identity'
# one_hot: False
# Python API equivalent:
model = DEEM(
n_classes=3,
use_preprocessing=True,
preprocessing_layers=1,
preprocessing_activation='entmax',
preprocessing_init='identity',
preprocessing_one_hot=False,
)Problem: Model initialized with random weights instead of majority vote.
Solution: Check init_method:
model = DEEM(init_method='mv_rand') # Should start near MV accuracyIf using auto_hyperparameters=True, this is handled automatically.
Problem: Buffer/weighted init messages print twice with identical timestamps.
Solution: This is a Jupyter display quirk with %autoreload 2, not actual duplicate calls. The functionality works correctly. To avoid, disable autoreload or ignore the duplicate.
Problem: model_dir not found warning when using auto_hyperparameters=True.
Solution (v0.2.0+): Models are now bundled! Just upgrade:
pip install --upgrade deemFor older versions, download models separately or specify model_dir.
Problem: 3D tensor not auto-detected as soft labels.
Check:
- Shape must be
(n_samples, n_classes, n_classifiers)- note the order! - Data type must be float (not int)
- Values should sum to ~1.0 along axis 1 (probability distributions)
# Verify shape and normalization
print(f"Shape: {soft_preds.shape}") # Should be (N, K, D)
print(f"Sum along axis 1: {soft_preds.sum(axis=1)}") # Should be ~1.0Problem: CUDA out of memory error.
Solutions:
- Reduce
batch_size:model = DEEM(batch_size=64) - Use CPU:
model = DEEM(device='cpu') - Use smaller dataset subset for experimentation
Problem: Accuracy looks random (~33% for 3 classes).
Solution: Use align_to parameter or score() method:
# Wrong - no alignment
accuracy = (predictions == labels).mean() # ❌ Random accuracy
# Correct - with alignment
accuracy = model.score(predictions, labels) # ✅ Proper accuracy
# Or:
consensus = model.predict(predictions, align_to=train_predictions)
accuracy = (consensus == labels).mean()Remember: Alignment is against MAJORITY VOTE, not true labels (unsupervised).
Solutions:
- Use GPU:
model = DEEM(device='cuda') - Increase
batch_size:model = DEEM(batch_size=512) - Reduce
cd_k:model = DEEM(cd_k=5)(default 10) - Reduce
sampler_steps:model = DEEM(sampler_steps=5)(default 10) - Use fewer
epochs:model = DEEM(epochs=20)(default 50)
Check:
use_weighted=True(default, gives better classifiers more influence)init_method='mv_rand'(starts near MV)- Sufficient
epochs(try 50-100) - Dataset quality (are classifiers diverse and reasonably accurate?)
Note: DEEM is designed to match or slightly exceed majority vote. Large improvements (>5-10%) are rare and depend on dataset characteristics.
Core Dependencies (installed automatically):
- Python >= 3.8
- PyTorch >= 1.9
- NumPy >= 1.19
- SciPy >= 1.7
- entmax >= 1.0
- scikit-learn >= 0.24 (for automatic hyperparameters)
- pandas >= 1.3 (for automatic hyperparameters)
- joblib >= 1.0 (for automatic hyperparameters)
Development (optional):
pip install deem[dev] # Includes pytest, ruffMaymona Albadri - @Rem4rkable
If you use DEEM in your research, please cite:
@software{deem2026,
title={DEEM: Deep Ensemble Energy Models for Classifier Aggregation},
author={Albadri, Maymona},
year={2026},
url={https://github.com/shaham-lab/deem}
}This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details.
Contributions are welcome! Please feel free to submit a Pull Request.
- Based on research in energy-based models and crowd learning
- Built with PyTorch and inspired by scikit-learn's API design
- GitHub: https://github.com/shaham-lab/deem
- Documentation: [Coming soon]
- Issues: https://github.com/shaham-lab/deem/issues
Made with 💜 for the machine learning community