Create the channel for qc to install fastp fastqc multiqc install
- Step:1
- Tool installation
# create env and install tools
$ conda create --yes -n qc fastp fastqc multiqc
# activate env
$ conda activate qc- Step: 2
conda create --yes -n qc fastp fastqc multiqc
----------------------------
vi run_qc.sh
#!/bin/bash
set -e
#--Activate the qc environment
source activate qc
#-- Check the reads quality
cd ~/analysis/015_seed_transcriptomics/01.quality_preprocessing/raw
fastqc -t 32 -o ~/analysis/015_seed_transcriptomics/01.quality_preprocessing/raw *.fastq.gz &> log.fastqc &#---Trimming
#!/bin/bash
set -e
for reads in *_1.fastq.gz
do
base=$(basename $reads _1.fastq.gz)
fastp --detect_adapter_for_pe \
--overrepresentation_analysis \
--correction --cut_right --thread 2 \
--html ../trim/${base}.fastp.html --json ../trim/${base}.fastp.json \
-i ${base}_1.fastq.gz -I ${base}_2.fastq.gz \
-o ../trim/${base}_R1.fastq.gz -O ../trim/${base}_R2.fastq.gz
done
#----Run
bash run_fastp.sh &>log.fastp &#---Let's run fastqc again on the trimmed data
cd ../trim/
fastqc -t 32 *
#--Let's run multiQC on both untrimmed and trimmed files
cd ..
multiqc raw trim
source deactivate qc
#--Bye
$ bash run_qc.sh &> log.qc &
Note:
--detect_adapter_for_pe: Specifies that we are dealing with paired-end data.
--overrepresentation_analysis: Analyse the sequence collection for sequences that appear too often.
--correction: Will try to correct bases based on an overlap analysis of read1 and read2.
--cut_right: Will use quality trimming and scan the read from start to end in a window. If the quality in the window is below what is required, the window plus all sequence towards the end is discarded and the read is kept if its still long enough.
--thread: Specify how many concurrent threads the process can use.
--html and --json: We specify the location of some stat files.
-i data/anc_R1.fastq.gz -I data/anc_R2.fastq.gz: Specifies the two input read files
-o trimmed/anc_R1.fastq.gz -O trimmed/anc_R2.fastq.gz: Specifies the two desired output read files
Use this command if you have InterProScan result (make sure you edit the annotation.prop file, change the value next to InterProScanImportParameters.inputFormat):
/usr/local/blast2go/blast2go_cli.run -properties annotation.prop -useobo go.obo -loadblast blastresults.xml -loadips50 ipsout.xml -mapping -annotation -annex -statistics all -saveb2g myresult -saveannot myresult -savereport myresult -tempfolder ./ >& annotatelogfile &
Very important file format problem
The output file from BLAST2GO myresult.annot is formatted for Windows PC. It will cause problems if you use it on Linux computer. Make sure to convert the file to LINUX line ends for this file. The command is:
dos2unix myresult.annot
#!/bin/bash
set -e
cd /NABIC/HOME/senthil83/analysis/009_Assembly_quality_metrics_s_alatum
ln -fs /NABIC/HOME/senthil83/analysis/004_denovo_assembly_s_alatum_rna/s_alatum_trinity_out/Trinity.fasta .
echo "Activate the busco environment"
source activate busco_env
echo "BUSCO analysis for S_alatum"
busco \
-i Trinity.fasta \
-o busco_S_alatum_embryophyta \
-l /NABIC/HOME/senthil83/analysis/009_Assembly_quality_metrics_s_alatum/eudicots_odb10.2020-09-10/eudicots_odb10 \
-m transcriptome
#deactivate busco environment
source deactivate busco_env
bash run.sh &> log &#exit
- References
Transcriptome Assembly Quality Assessment
A Tissue-Mapped Axolotl De Novo TranscriptomeEnables Identification of Limb Regeneration Factors
##Install DIAMOND BLASTX tool https://anaconda.org/bioconda/diamond
##create specific environment for diamond conda create --name diamond_env
source activate diamond_env
conda install -c bioconda diamond conda install -c bioconda/label/cf201901 diamond
https://github.com/bbuchfink/diamond
wget http://github.com/bbuchfink/diamond/releases/download/v2.0.8/diamond-linux64.tar.gz tar xzf diamond-linux64.tar.gz
./diamond makedb --in reference.fasta -d reference
./diamond blastp -d reference -q queries.fasta -o matches.tsv
./diamond blastx -d reference -q reads.fasta -o matches.tsv
update_blastdb --decompress --blastdb_version 5 swissprot ./diamond blastp -d swissprot -q queries.fasta -o matches.tsv
##Making database###
/usr/bin/time -o output.txt -v diamond makedb -p 32 --in uniprot_sprot.fasta -d uniprot_sprot &>log &
/usr/bin/time -o outputswissprot.txt -v diamond makedb -p 32 --in swissprot.fasta -d swissprot &>log.swissprt &
/usr/bin/time -o outputnr.txt -v diamond makedb -p 32 --in nr.fasta -d nr &>log.nrdb &##Run Blastx##
/usr/bin/time -o outputblastx.txt -v diamond blastx -p 32 -d uniprot_sprot -q alatum.transcripts.fasta -o alatum_matches.xml --outfmt 5 &> log.blastx.xml &
/usr/bin/time -o output_sprotblastx.txt -v diamond blastx -p 32 -d swissprot -q alatum.transcripts.fasta -o swissprot.alatum_matches.xml --outfmt 5 &> log.swisprot.blastx.xml &
/usr/bin/time -o output_nrblastx.txt -v diamond blastx -p 32 -sensitive -d nr -q alatum.transcripts.fasta -o nr.alatum_matches.xml --outfmt 5 &> log.nr.blastx.xml &
NUCELOTIDE QUERY REF Biostar_help Biopython
/data/www/augustus/augustus/bin/augustus --species=arabidopsis --strand=both --singlestrand=false --genemodel=partial --codingseq=on --sample=100 --keep_viterbi=true --alternatives-from-sampling=true --minexonintronprob=0.2 --minmeanexonintronprob=0.5 --maxtracks=2 /data/www/augustus/webservice/data/AUG-1481299735/input.fa --exonnames=on
$ seqtk subseq your.input.fasta the_header_of_interest_IDs.list > your_output.fasta
$ cat file.fa | awk '$0 ~ ">" {print c; c=0;printf substr($0,2,100) "\t"; } $0 !~ ">" {c+=length($0);} END { print c; }'
How to generate sequence length distribution from Fasta file
For PFAM annotations, I used hmmscan against the full database downloaded from the xfam page. To download the databank and create the hmmscan file:
wget ftp://ftp.ebi.ac.uk/pub/databases/Pfam/current_release/Pfam-A.hmm.gz #download
$ gunzip Pfam-A.hmm.gz #unzip the database
$ hmmpress Pfam-A.hmm #parse the database
And to run the scan against the query sequences:
$ hmmscan --tblout MySu_v1.PFAM.txt Pfam-A.hmm MySu01_v1.proteins.fasta
pfam_scan_env
#download
wget http://ftp.ebi.ac.uk/pub/databases/Pfam/current_release/Pfam-A.hmm.dat.gz for Pfam-B.hmm.dat wget http://ftp.ebi.ac.uk/pub/databases/Pfam/releases/Pfam33.1/active_site.dat.gz for active_site.dat
##after download
hmmpress Pfam-A.hmm hmmpress Pfam-B.hmm
pfam_scan.pl -fasta ourproteinsequence.fasta -cpu 32 -outfile outputfilename.txt - as -dir thewholepathofthedirectorofdb
pfam_scan.pl -fasta suwon.blastpep.fasta -cpu 32 -outfile suwon.hmmresults.txt - as -dir /NABIC/HOME/senthil10/datafiles/05.pfam_db
To install and run InterProScan
./interproscan.sh -appl CDD,COILS,Gene3D,HAMAP,MobiDBLite,PANTHER,Pfam,PIRSF,PRINTS,PROSITEPATTERNS,PROSITEPROFILES,SFLD,SMART,SUPERFAMILY,TIGRFAM -i /path/to/sequences.fasta
Gene Set Enrichment Analysis with ClusterProfiler
library(ggplot2)
dat <- data.frame(
FunctionClass = factor(c("A", "B", "C", "D", "E", "F", "G", "H", "I", "J", "K", "L", "M", "N", "O", "P", "Q", "R", "S", "T", "U", "V", "W", "Y", "Z"), levels=c("A", "B", "C", "D", "E", "F", "G", "H", "I", "J", "K", "L", "M", "N", "O", "P", "Q", "R", "S", "T", "U", "V", "W", "Y", "Z")),
legend = c("A: RNA processing and modification", "B: Chromatin structure and dynamics", "C: Energy production and conversion", "D: Cell cycle control, cell division, chromosome partitioning", "E: Amino acid transport and metabolism", "F: Nucleotide transport and metabolism", "G: Carbohydrate transport and metabolism", "H: Coenzyme transport and metabolism", "I: Lipid transport and metabolism", "J: Translation, ribosomal structure and biogenesis", "K: Transcription", "L: Replication, recombination and repair", "M: Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis", "N: Cell motility", "O: Posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones", "P: Inorganic ion transport and metabolism", "Q: Secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport and catabolism", "R: General function prediction only", "S: Function unknown", "T: Signal transduction mechanisms", "U: Intracellular trafficking, secretion, and vesicular transport", "V: Defense mechanisms", "W: Extracellular structures", "Y: Nuclear structure", "Z: Cytoskeleton"),
Frequency=c(1516,232,1011,257,934,341,1689,393,1019,1395,2777,862,354,1,2548,849,960,0,8789,3423,1226,258,25,15,476)
)
p <- ggplot(data=dat, aes(x=FunctionClass, y=Frequency, fill=legend))+
geom_bar(stat="identity", position=position_dodge(), colour="seashell")
p + guides (fill = guide_legend(ncol = 1))
p <- ggplot(data=dat, aes(x=FunctionClass, y=No.of.Transcripts, fill=legend))+
geom_bar(stat="identity", position=position_dodge(), colour="seashell")
p + guides (fill = guide_legend(ncol = 1))+
xlab("Factor Class")+
ggtitle("Cluster of Orthologous")
[Krait: an ultrafast tool for genome-wide survey of microsatellites and primer design] (https://academic.oup.com/bioinformatics/article/34/4/681/4557187)
Du, L., Zhang, C., Liu, Q., Zhang, X. & Yue, B. Krait: an ultrafast tool for genome-wide survey of microsatellites and primer design. Bioinformatics 34, 681–683 (2018).
A Literature Review of Gene Function Prediction by Modeling Gene Ontology
Tandem UGT71B5s Catalyze Lignan Glycosylation in Isatis indigotica With Substrates Promiscuity
EnTAP: Bringing Faster and Smarter Functional Annotation to Non-Model Eukaryotic Transcriptomes
Comparative transcriptome analysis of cultivated and wild seeds of Salvia hispanica (chia)
De novo Assembly of Leaf Transcriptome in the Medicinal Plant Andrographis paniculata
Data of de novo assembly and functional annotation of the leaf transcriptome of Impatiens balsamina
Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Key Seed-Development Genes in Common Buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum)
Gene expression profiles that shape high and low oil content sesames
[Genome sequencing of the important oilseed crop Sesamum indicumL (https://genomebiology.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/gb-2013-14-1-401#ref-CR37)
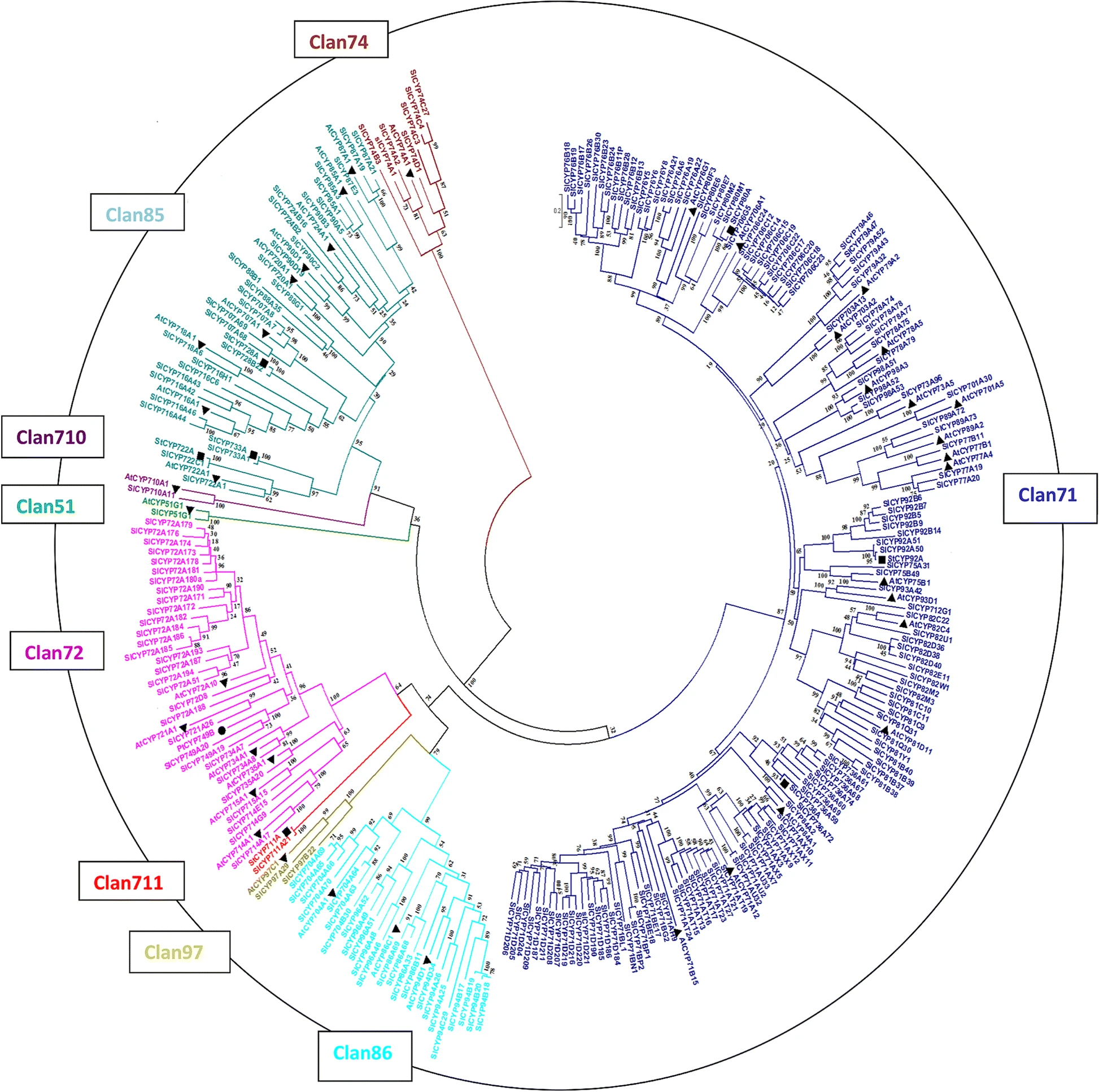
Phylogenomic analysis of cytochrome P450 multigene family and their differential expression analysis in Solanum lycopersicum L. suggested tissue specific promoters
Computational Identification and Systematic Classification of Novel Cytochrome P450 Genes in Salvia miltiorrhiza
(+)‐Sesamin‐oxidising CYP92B14 shapes specialised lignan metabolism in sesame
Oxidative rearrangement of (+)-sesamin by CYP92B14 co-generates twin dietary lignans in sesame
Lignans of Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.): A Comprehensive Review
The cytochrome P450 superfamily: Key players in plant development and defense
Identification of a binding protein for sesamin and characterization of its roles in plant growth