Welcome to simple greyscale Image processer. Using this image processer, you can simply apply fully blur(or/and))sharpened blur(or/and)find edges to your greyscaled image using MATLAB.
- The "GreyScale_Image_Processor.zip" folder has six files of which the matlab_file_io_pavan has the main code for the program to run.
- An example for greyscale image is provide with the name "GreyScaleImage.pgm" for the user.
- The images that were generated after the running the code is also included with names: blurred5andsharpen.pgm,blurred5times.pgm,edgedetection.pgm.
- On the Editor or Live Editor tab, in the Run section, click Run.
- Upload the greyscaled image for processing (If not available: Please choose the "GreyScaleImage.pgm" image form the folder)
- Choose the level of blur(or/and))sharpened blur(or/and)find edges to the image from 0 to 5. where,0 represents the no modification and 5 represents the highest modification.
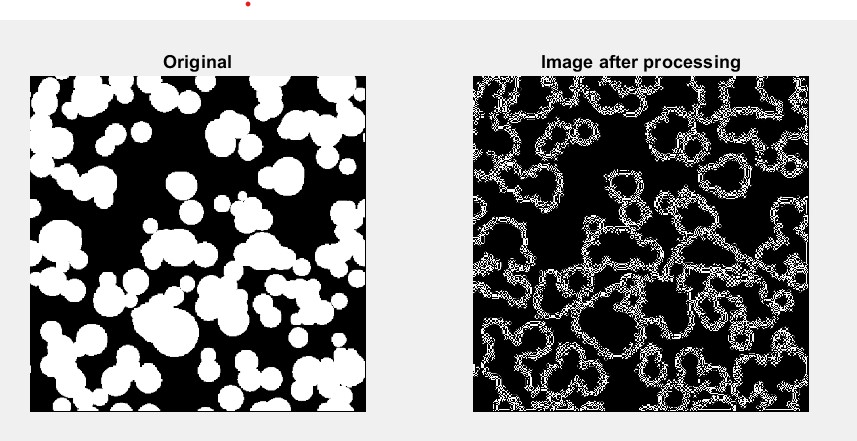
- Image processsing tool generates the processed image in comparision with the origional image.
- Inorder to save in the current folder the processed image please click "y" indicating yes
The Userinferace model dialog box collects the image with pixel values. The matlab UI facilitated this with well-customed prompt command called "uigetfile()" to save in the current folder with matlab folder of ".m"file. The greyscaled image is read as matrix of pixel intensities ranging from 0 to 255 occupied throughout the size of the image by the "imread()". The level of modification is considered by input() commands and stors in the variables such as nr_blur,nr_sharpen and nr_edgethickness.
Inorder to process the pixels of the image, a widely popular mathematical technique known as convolution is employed.In this technique, we consider a kernel based on the technique to be performed. For Gaussian blur we consider (1/16)*[1 2 1;2 4 2;1 2 1] and for edge detection we consider [0 -1 0;-1 4 -1;0 -1 0] as kernels.Similarly for sharpening the image [0 -1 0;-1 5 -1;0 -1 0] is preferred as kernel. A small matrix of size 3 by 3 is convoluted with the kernel and replaces the resulatant pixel,which deponds on the surrounding pixels, at in the middle of the matrix. The same operation iterated through out the image.So each pixel of image is calculated by considering intensities of other pixels in matrix.
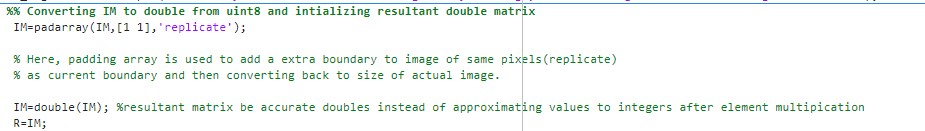
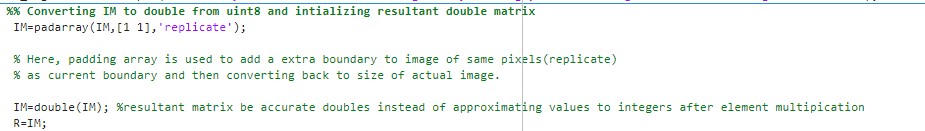
Although both double precision numbers in range of 0 to 1 and unsignedintegers in range of 0 to 255 can be used to describe images, the image datatype is converted to double because it is provides more accurate values in the describing each pixel intensities
After converting back into unsigned integer from double precision, the generated is compared using subplot() function. The processed image is then compared with with the user's original image.
Fig1: The above comparision represents comparison of the user image with the generated image after sharpening and edge detection.
- Requires MATLAB
- Matlab Image Processing Tool Box available for Mac, Windows and LINUX
- Parallel Computing Toolbox is required for image processing on GPU. A list of supported functions is available on the page.
- Deep Learning Toolbox is required for deep learning functionality. Parallel Computing Toolbox is required for GPU support.
- Project is done under the guidence of Dr. Uwe Pruefert