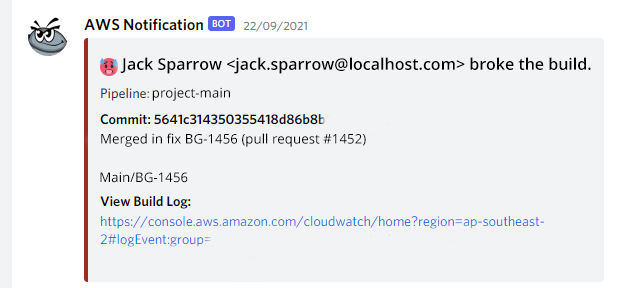
Meerkat works to deliver your AWS CodePipeline status and AWS CloudWatch Alarms to your Discord channel.
Where Meerkat shines is when it listens to AWS Code Pipeline Life Cycle Events. Meerkat tracks each action for pipeline execution. In the case of a pipeline failure Meerkat will run off and fetch helpful troubleshooting data before sending you an easily readable notification. To reduce noise pipeline action events are intentionally filtered so you will only receive one message per pipeline execution.
- All pipeline failures include the Commit Message, Author and a link to the commit.
- Build failures include a link to viewing the code build, and build log.
- Deploy failures (EC2) show the script and reason for the deployment failure.
- Deployment information is retrieved across AWS accounts.
- Beautify cloud watch alarms and shows state changes.
- Posts to Discord.
- Works with GitHub and Bitbucket.
- Your GitHub Username and Personal AccessToken or Bitbucket Username & Password
- Your repository id
- Your repository URL (The HTTP URL you would use with git clone)
- Discord Webhook Url
- A hosted .png file for the Discord avatar. 128px X 128px
- An AWS account (obviously)
- An AWS S3 Bucket.
- Upload the release zip file to your S3 Bucket and make a note of the bucket name and object key.
- Create a cloud formation stack using the cloud formation template provided in this repository: /cloudformation meerkat.yaml
The cloud formation will provision the resources and permission required by Meerkat.
If you already have an SNS Topic that is receiving Code Pipeline Events or Cloud Watch alarms simply subscribe meerkat to that topic. Otherwise, you can use the provisioned SNS Topic as a target for notifications.
For the bot to receive success and failure notifications.
The bot requires notification of the following events so that the bot can collate the information required to send notifications that are useful for troubleshooting build and deployment failures.
- Pipeline execution Failed
- Pipeline execution Succeeded
- Action execution Failed
- Action execution Succeeded.
Raises a notification if the Pipeline Execution Fails. However, this event does not contain sufficient detail to troubleshoot the pipeline failure.
As such, notifications based on this event rely on the availability of information collected by processing any associated "Action Events. Action events should be enabled to enrich notifications with troubleshooting data.
Raises a notification if the Pipeline Execution succeeds.
Allows collecting commit information from the Source Provider. (GitHub or Bitbucket)
Allows collecting detailed information causing the pipeline failure. Failed CodeDeploy actions show diagnostic information related to the first instance to which deployment failed. In the case of a CodeBuild failure, show a link to the build log.
This repository also contains an example cloud formation template that will provision an AWS Code pipeline that will send a notification to Discord using Meerkat.
The SNS Topic to which the Lambda is subscribed must receive all of the following Code Pipeline Events.
- failed (The bot determines pipeline failure only based on failed actions)
- succeeded (This is required to capture the git checkout to retrieve commit details that are not available from AWS.)
- success (Success messages are only sent on this event to avoid spamming users for a single pipeline success.)
- failed (Failed messages are only sent on this event to avoid spamming users for a single pipeline failure. The event is NOT used to determine if the pipeline failed.)
The Lambda execution role requires the following permissions in addition to the standard Lambda execution permissions:
- dynamodb:PutItem (To the table created for this lambda)
- dynamodb:GetItem (To the table created for this lambda)
- codebuild:BatchGetBuilds
- sts:AssumeRole (If using cross-account deployments, the role that is assumed to interact with code deploy. See the information for the DEPLOY_ARN environment variables.)
Set the chat service that is used to deliver notifications. The only current option is: "discord"
The name of the DynomDb table that is used to manage pipeline logs. Defaults to: "devops-pipeline-monitor".
The table must have a Partition key of type string named "executionId".
See the cloud formation template in the "cloudformation" folder for an example definition.
The role that is assumed when retrieving failure information from the code deploy service. This allows retrieving information across AWS accounts. The Lambda execution role must be able to assume the specified role. Only required if doing cross-account deployments.
The specified deploy role must have the following permissions:
- codedeploy:BatchGetDeploymentTargets
- codedeploy:ListDeploymentTargets
In cases where deployment environments are hosted in multiple AWS Accounts, the agent can be configured to assume roles in different AWS Accounts based on the pipeline name.
For example, You have three AWS Accounts.
- a) DevOpsIn - This is the AWS Account where the pipeline is defined and this lambda runs.
- b) Testing - This is an AWS account to which testing builds are deployed.
- c) Production - This is an AWS account to which production builds are deployed.
You can have a single lambda function handle notifications for all environments using the pipeline name.
The pipeline for testing could be called: "my-testing-pipeline", while the production pipeline could be named "the-real-deal:
To set the Arn for testing define and environment variables named "DEPLOY_ARN_testing". To set the Arn for production set another environment variable "DEPLOY_ARN_real-deal"
If "DEPLOY_ARN" is defined it will be used as a fallback in the case that no DEPLOY_ARN** variables can be matched to the pipeline name.
Finally, if the environment variable is set to an empty string or no DEPLOY_ARN variables are specified then the role assigned to the lambda function will be used to call the Code Deploy API.
Constructive feedback, feature requests and discussions are welcomed.
A public URL to an image that will be used as the Discord avatar. The image is shown next to the message thread. The image must conform to the dimensions required by Discord.
A 128px x 128px png file with alpha transparency is known to work.
Override the displayed username when posting to Discord.
The Discord webhook to which notifications are posted.
The password that is used to connect to the git provider. For GitHub, this is a Personal Access Token with permission to read commits.
The service hosting the repository. Valid values are "bitbucket" or "github". The default is: github
The username that is used to connect to the git provider.
The Slack Bot Token (starts with xoxb-) used for sending messages and user lookup features.
When configured, the bot will attempt to mention users by looking up their Slack user ID based on their git commit email address.
To obtain this token:
- Create a Slack App at https://api.slack.com/apps
- Add OAuth Scopes:
chat:write- For sending messagesusers:read- For user lookupusers:read.email- For email-based user lookup
- Install the app to your workspace
- Copy the Bot User OAuth Token
The Slack channel name or ID where notifications should be sent. The bot must be invited to this channel.
For local development and testing only. Absolute path to a local JSON file containing Slack routing configuration. When this environment variable is set, Meerkat will load routing rules from the specified file instead of AWS Systems Manager Parameter Store.
If the file cannot be read, Meerkat will automatically fall back to loading from AWS Parameter Store.
Example:
SLACK_ROUTES_CONFIG_FILE=/home/user/meerkat/config/slack-routes.jsonThe file should contain the same JSON structure as documented in the Slack Message Routing section below.
Meerkat supports advanced message routing for Slack, allowing you to send different types of notifications to different channels based on configurable rules. This is particularly useful for separating production alerts from development notifications, or routing different types of events to specialized channels.
Routing rules can be configured in two ways:
- AWS Systems Manager Parameter Store (recommended for production)
- Local JSON file (for development/testing)
Store your routing configuration as a JSON string in AWS Systems Manager Parameter Store with the parameter name /meerkat/slack/routes:
{
"slack": {
"routes": [
{
"expression": "type:PipelineNotification&name~.*prod.*",
"channel": "#prod-pipeline"
},
{
"expression": "type:PipelineNotification&name~.*test.*",
"channel": "#test-pipeline"
},
{
"expression": "type:AlarmNotification&alert.name~.*Critical.*",
"channel": "#critical-alerts"
},
{
"expression": "type:PipelineNotification",
"channel": "#general-pipeline"
},
{
"expression": "type:AlarmNotification",
"channel": "#alerts"
}
]
}
}For development, you can use a local JSON file instead of AWS Systems Manager Parameter Store by setting the SLACK_ROUTES_CONFIG_FILE environment variable to the absolute path of your configuration file.
Example configuration file (slack-routes.json):
{
"slack": {
"routes": [
{
"expression": "type:PipelineNotification&name~.*prod.*",
"channel": "#prod-pipeline"
},
{
"expression": "type:PipelineNotification",
"channel": "#general-pipeline"
}
]
}
}Set the environment variable:
export SLACK_ROUTES_CONFIG_FILE=/absolute/path/to/slack-routes.jsonIf the file cannot be read, Meerkat will automatically fall back to loading from AWS Parameter Store.
Routing expressions support powerful filtering capabilities with the following operators:
-
:(Exact Match) - Matches exact valuestype:PipelineNotification -
~(Regex Match) - Matches using regular expressionsname~.*prod.* -
!(NOT) - Negates the condition!type:AlarmNotification -
&(AND) - All conditions must be truetype:PipelineNotification&name~.*prod.* -
|(OR) - Any condition can be truetype:PipelineNotification|type:AlarmNotification
Use dot notation to access nested object properties:
alert.name:HighCPUUsage
alert.severity:HIGH
commit.author~.*john.*
{
"expression": "type:PipelineNotification&name~.*prod.*",
"channel": "#prod-deployments"
}Routes production pipeline notifications to #prod-deployments
{
"expression": "type:PipelineNotification&successfull:false",
"channel": "#pipeline-failures"
}Routes failed pipeline notifications to #pipeline-failures
{
"expression": "type:AlarmNotification&alert.name~.*Database.*",
"channel": "#database-alerts"
}Routes database-related alarms to #database-alerts
{
"expression": "type:AlarmNotification&alert.name~.*(Critical|High).*",
"channel": "#critical-alerts"
}Routes critical or high severity alarms to #critical-alerts
{
"expression": "type:PipelineNotification&(name~.*prod.*|name~.*staging.*)",
"channel": "#important-deployments"
}Routes production or staging pipeline notifications
{
"expression": "!type:AlarmNotification&!type:PipelineNotification",
"channel": "#other-notifications"
}Routes all notifications except alarms and pipeline events
type: "PipelineNotification"name: Pipeline namesuccessfull: boolean (true/false)commit.author: Commit author namecommit.authorEmail: Commit author emailcommit.summary: Commit messagefailureDetail.type: "CodeBuild" or "CodeDeploy" (when failed)
type: "AlarmNotification"alert.name: Alarm namealert.description: Alarm descriptionalert.reason: Alarm trigger reasonalert.type: "alarm"alert.date: Timestamp
type: "SimpleNotification"subject: Message subjectmessage: Message body
type: "ManualApprovalNotification"name: Approval nameapprovalAttributes.link: Approval linkapprovalAttributes.comment: Approval comment
Routes are evaluated in the order they appear in the configuration. The first matching rule determines the target channel. This means:
- Place more specific rules first
- Place general catch-all rules last
- Test your routing logic thoroughly
{
"slack": {
"routes": [
{
"expression": "type:PipelineNotification&name~.*prod.*&successfull:false",
"channel": "#prod-failures"
},
{
"expression": "type:PipelineNotification&name~.*prod.*",
"channel": "#prod-deployments"
},
{
"expression": "type:PipelineNotification&name~.*test.*",
"channel": "#test-deployments"
},
{
"expression": "type:AlarmNotification&alert.name~.*(Critical|Emergency).*",
"channel": "#critical-alerts"
},
{
"expression": "type:AlarmNotification&alert.name~.*Database.*",
"channel": "#database-team"
},
{
"expression": "type:ManualApprovalNotification",
"channel": "#approvals"
},
{
"expression": "type:PipelineNotification",
"channel": "#general-deployments"
},
{
"expression": "type:AlarmNotification",
"channel": "#general-alerts"
},
{
"expression": "!type:AlarmNotification",
"channel": "#general"
}
]
}
}- No messages received: Check that your expressions match the actual notification properties
- Wrong channel: Verify rule order - earlier rules take precedence
- Regex not working: Test your regular expressions separately and escape special characters
- Route not loading: Check AWS Systems Manager permissions and parameter name
- Fallback behavior: If no routes match, messages go to the default
SLACK_CHANNEL
Create a .env file in the project root and specify the environment variables.
The build script expects to be run from a bash terminal. The zip package must also be installed. (sudo apt install zip). If on windows use the Linux subsystem for Windows (WSL)
The name of the local AWS profile used to connect to AWS. When running in production this variable is not required as the SDK will use the role assigned to the Lambda.
For the details of setting up AWS profiles see: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cli/latest/userguide/cli-configure-profiles.html
Absolute path to a local JSON file containing Slack routing configuration. When set, Meerkat will load routing rules from this file instead of AWS Systems Manager Parameter Store. If the file cannot be read, it will automatically fall back to AWS Parameter Store.
Example:
SLACK_ROUTES_CONFIG_FILE=/home/user/meerkat/config/slack-routes.jsonA sample configuration file is provided at config/slack-routes-sample.json.
Set this to point to the Dynamo DB endpoint to which PipeLogs are saved. To work with the provided docker container on the local machine set this to: http://localhost:8000"
Set this value to true to run integration tests as a part of the unit testing suite. Integration test require a connection to Dynamo DB. Run the local docker container or use a profile that can connect to AWS.
$MEERKAT/_dev/start.sh
The environment variable should contain the absolute filesystem path to the "root" of this project.
There is a Bug/Feature in jest where running a single test will execute all tests if the file name of the single test is contained in the absolute file-path on the system.
For example, suppose the project root is in the file system at: /home/jack/meerkat. Running a test called "meerkat" or "user" will run ALL unit-tests since those words are contained in the absolute file path.
As a workaround, the "meerkat" unit test has been renamed to meerkat-service.test.ts.