Personal Contributions: Clustering Displaying Elbow Method and Displaying Centroids
DOTA2 is a team oriented multiplayer online battle arena (MOBA) game with 6.5 million monthly players published by Valve Corporation. In each match, two teams of five players select and control ‘heros’ which have unique attributes and play one of nine possible roles on a team.
Apriori association rule mining is used to identify essential hero roles that should be present on each team. Clustering is used to identify types of teams that players can form. Lastly, linear regression is used to identify factors that that increase the chance of winning a combat engagement called a team fight, which result in a the temporary death of 3 or more players.
The purpose of this project is to discover detailed insights to inexperienced beginner players to the implicit strategies of the game. Another objective of this project is for the developers of Dota 2, the increase in these metrics can increase the number of regular players they have,improve the user experience, and drive up other essential metrics such as revenue.
K Means should result in three different team types (3 clusters should be most optimal) such that one type is offensive, one type is defensive, and the last type is a balanced team. A balanced team is a team that has a good mix of defensive heroes and offensive heroes.
The binary matrix is then applied to the KMeans function offered by Sklearn. A potential discovery has been made that using the K-Means offered by Sklearn is not ideal for clustering due to the function using euclidean distances as the distance metric for clustering. Euclidean distance does not work well with binary data.
However, after confirmation with Professor Lukasz Golab, using K-Means offered by Sklearn (that implements Euclidean distance as the distance metric) is an acceptable approach for the binary matrix input due to KMeans clustering data at 111 dimensions. The 111 dimensions is from the binary matrix consisting of 111 columns (111 instead of 112 because of a missing value at column 24).
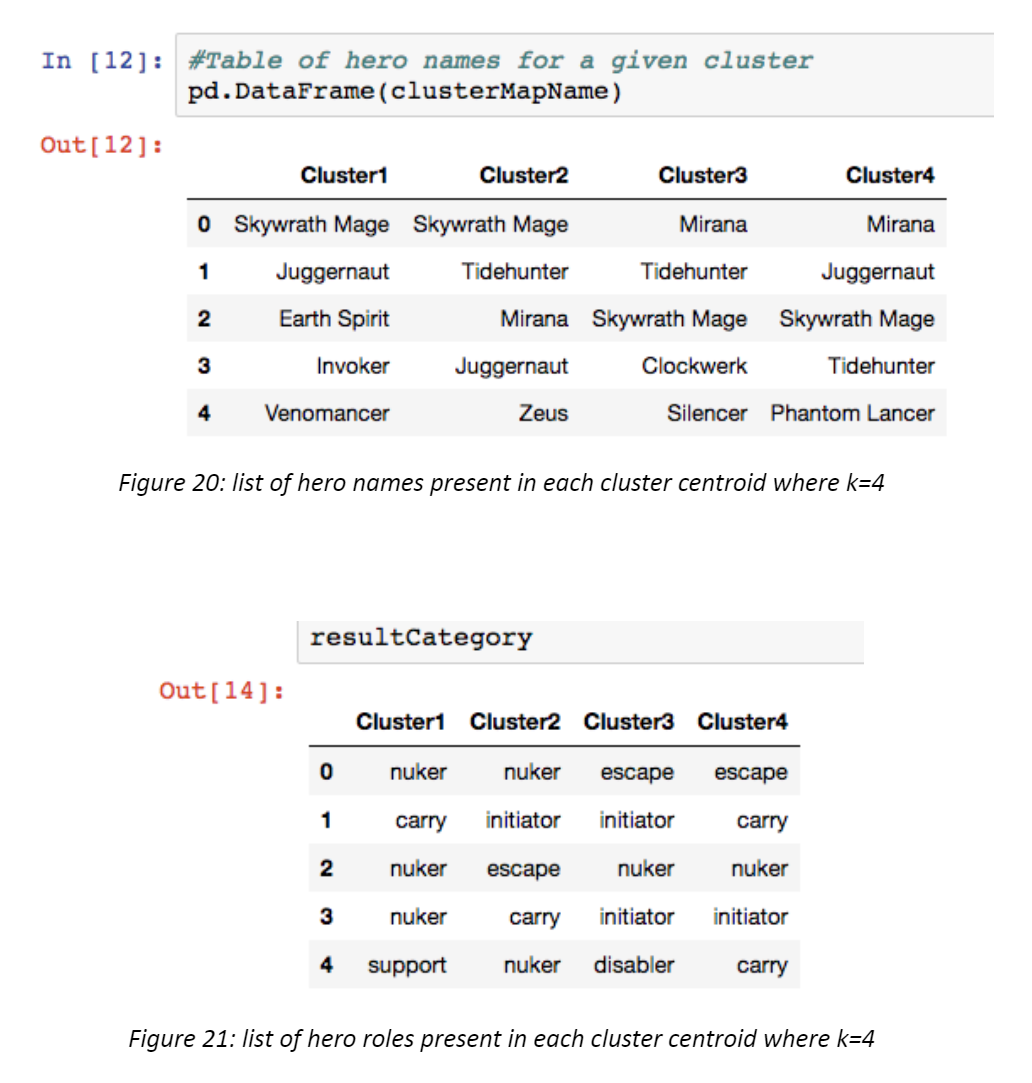
Running the K-Means function with the number of clusters set as 4 resulted in an array of 4 subarrays. Each sub array has 111 elements because there are 111 hero IDs. Hence, each index within the subarray represents a hero. Since there are 111 heros, there are 111 dimensions in each of the 4 clusters. Each value within the subarray is the centroid of the cluster for a specific dimension. By taking top 5 highest values and their corresponding array index (hero ID), the results are the five heros that are most frequently chosen with respect to the other 111 heroes for a given team.
Based on clustering using K Means, the results did not exactly match the hypothesis that there are 3 clusters representing three types of team compositions: offensive, balanced team (mix of offensive and defensive heroes), and defensive team.
Using the elbow method, 4 clusters were determined to be most optimal. The first and second clusters were oriented towards offensive play styles, with the first cluster being more powerful in the early game, and the second cluster gaining power in the late game. The third cluster represented a balanced team composition whereas the 4th clustered represented a team composition suitable for a defensive playstyle.