Overview
| Installation
| Examples
| Remarks
| FAQs
| Benchmarks
| Compiling
Faster Stata for big data. This packages uses C plugins and hashes to provide a massive speed improvements to common Stata commands, including: collapse, reshape, winsor, pctile, xtile, contract, egen, isid, levelsof, duplicates, and unique/distinct.
This package provides a fast implementation of various Stata commands
using hashes and C plugins. The syntax and purpose is largely analogous
to their Stata counterparts; for example, you can replace collapse
with gcollapse, reshape with greshape, and so on. For a
comprehensive list of differences (including some extra features!)
see the remarks below; for details and examples see the
official project page.
Quickstart
ssc install gtools
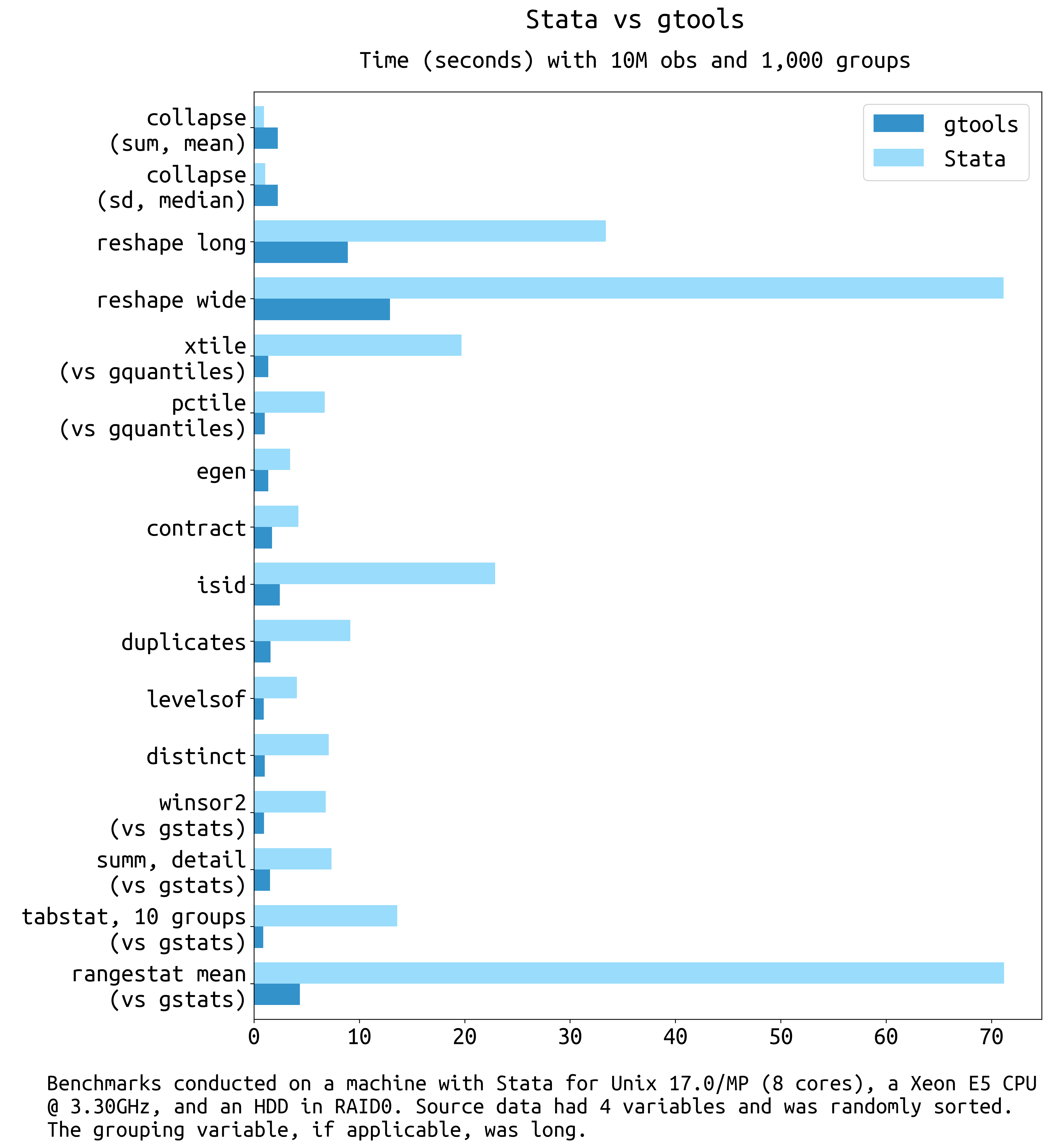
gtools, upgradeSome quick benchmarks:
Gtools commands with a Stata equivalent
| Function | Replaces | Speedup (IC / MP) | Unsupported | Extras |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| gcollapse | collapse | 9 to 300 / 4 to 120 (+) | Quantiles, merge, nunique, label output | |
| greshape | reshape | 4 to 20 / 4 to 15 | advanced syntax | fast, spread/gather (tidyr equiv) |
| gegen | egen | 9 to 26 / 4 to 9 (+,.) | labels | Weights, quantiles, nunique |
| gcontract | contract | 5 to 7 / 2.5 to 4 | ||
| gisid | isid | 8 to 30 / 4 to 14 | using, sort |
if, in |
| glevelsof | levelsof | 3 to 13 / 2 to 7 | Multiple variables, arbitrary levels | |
| gduplicates | duplicates | 8 to 16 / 3 to 10 | ||
| gquantiles | xtile | 10 to 30 / 13 to 25 (-) | by(), various (see usage) |
|
| pctile | 13 to 38 / 3 to 5 (-) | Ibid. | ||
| _pctile | 25 to 40 / 3 to 5 | Ibid. |
(+) The upper end of the speed improvements are for quantiles (e.g. median, iqr, p90) and few groups. Weights have not been benchmarked.
(.) Only gegen group was benchmarked rigorously.
(-) Benchmarks computed 10 quantiles. When computing a large
number of quantiles (e.g. thousands) pctile and xtile are prohibitively
slow due to the way they are written; in that case gquantiles is hundreds
or thousands of times faster, but this is an edge case.
Extra commands
| Function | Similar (SSC/SJ) | Speedup (IC / MP) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| fasterxtile | fastxtile | 20 to 30 / 2.5 to 3.5 | Can use by() |
| egenmisc (SSC) (-) | 8 to 25 / 2.5 to 6 | ||
| astile (SSC) (-) | 8 to 12 / 3.5 to 6 | ||
| gstats winsor | winsor2 | 10 to 40 / 10 to 20 | Can use weights |
| gunique | unique | 4 to 26 / 4 to 12 | |
| gdistinct | distinct | 4 to 26 / 4 to 12 | Also saves results in matrix |
| gtop (gtoplevelsof) | groups, select() | (+) | See table notes (+) |
(-) fastxtile from egenmisc and astile were benchmarked against
gquantiles, xtile (fasterxtile) using by().
(+) While similar to the user command 'groups' with the 'select'
option, gtoplevelsof does not really have an equivalent. It is several
dozen times faster than 'groups, select', but that command was not written
with the goal of gleaning the most common levels of a varlist. Rather, it
has a plethora of features and that one is somewhat incidental. As such, the
benchmark is not equivalent and gtoplevelsof does not attempt to implement
the features of 'groups'
Extra features
Several commands offer additional features on top of the massive speedup. See the remarks section below for an overview; for details and examples, see each command's help page:
In addition, several commands take gsort-style input, that is
[+|-]varname [[+|-]varname ...]This does not affect the results in most cases, just the sort order. Commands that take this type of input include:
- gcollapse
- gcontract
- gegen
- glevelsof
- gtop (gtoplevelsof)
Ftools
The commands here are also faster than the commands provided by
ftools; further, gtools commands take a mix of string and numeric
variables, which is a limitation of ftools. (Note I could not get
several parts of ftools working on the Linux server where I have
access to Stata/MP; hence the IC benchmarks.)
| Gtools | Ftools | Speedup (IC) |
|---|---|---|
| gcollapse | fcollapse | 2-9 (+) |
| gegen | fegen | 2.5-4 (.) |
| gisid | fisid | 4-14 |
| glevelsof | flevelsof | 1.5-13 |
| hashsort | fsort | 2.5-4 |
(+) A older set of benchmarks showed larger speed gains in part due to
mulit-threading, which has been removed as of 0.8.0, and in part because the
old benchmarks were more favorable to gcollapse; in the old benchmarks, the
speed gain is still 3-23, even without multi-threading. See the old collapse
benchmarks
(.) Only egen group was benchmarked rigorously.
Limitations
-
strLvariables only partially supported on Stata 14 and above;gcollapseandgcontractdo not supportstrLvariabes. -
Due to a Stata bug, gtools cannot support more than
2^31-1(2.1 billion) observations. See this issue -
Due to limitations in the Stata Plugin Interface, gtools can only handle as many variables as the largest
matsizein the user's Stata version. For MP this is more than 10,000 variables but in IC this is only 800. See this issue. -
Gtools uses compiled C code to achieve it's massive increases in speed. This has two side-effects users might notice: First, it is sometimes not possible to break the program's execution. While this is already true for at least some parts of most Stata commands, there are fewer opportunities to break Gtools commands relative to their Stata counterparts.
Second, the Stata GUI might appear frozen when running Gtools commands. If the system then runs out of RAM (memory), it could look like Stata has crashed (it may show a "(Not Responding)" message on Windows or it may darken on *nix systems). However, the program has not crashed; it is merely trying to swap memory. To check this is the case, the user can monitor disk activity or monitor their system's pagefile or swap space directly.
-
The OSX version of gtools was implemented with invaluable help from @fbelotti in issue 11.
-
Gtools was largely inspired by Sergio Correia's (@sergiocorreia) excellent ftools package. Further, several improvements and bug fixes have come from to @sergiocorreia's helpful comments.
I only have access to Stata 13.1, so I impose that to be the minimum.
You can install gtools from Stata via SSC:
ssc install gtools
gtools, upgradeBy default this syncs to the master branch, which is stable. To install the latest version directly, type:
local github "https://raw.githubusercontent.com"
net install gtools, from(`github'/mcaceresb/stata-gtools/master/build/)The syntax is generally analogous to the standard commands (see the corresponding help files for full syntax and options):
sysuse auto, clear
* gquantiles [newvarname =] exp [if] [in] [weight], {_pctile|xtile|pctile} [options]
gquantiles 2 * price, _pctile nq(10)
gquantiles p10 = 2 * price, pctile nq(10)
gquantiles x10 = 2 * price, xtile nq(10) by(rep78)
fasterxtile xx = log(price) [w = weight], cutpoints(p10) by(foreign)
* gstats winsor varlist [if] [in] [weight], [by(varlist) cuts(# #) options]
gstats winsor price gear_ratio mpg, cuts(5 95) s(_w1)
gstats winsor price gear_ratio mpg, cuts(5 95) by(foreign) s(_w2)
drop *_w?
* hashsort varlist, [options]
hashsort -make
hashsort foreign -rep78, benchmark verbose mlast
* gegen target = stat(source) [if] [in] [weight], by(varlist) [options]
gegen tag = tag(foreign)
gegen group = tag(-price make)
gegen p2_5 = pctile(price) [w = weight], by(foreign) p(2.5)
* gisid varlist [if] [in], [options]
gisid make, missok
gisid price in 1 / 2
* gduplicates varlist [if] [in], [options gtools(gtools_options)]
gduplicates report foreign
gduplicates report rep78 if foreign, gtools(bench(3))
* glevelsof varlist [if] [in], [options]
glevelsof rep78, local(levels) sep(" | ")
glevelsof foreign mpg if price < 4000, loc(lvl) sep(" | ") colsep(", ")
glevelsof foreign mpg in 10 / 70, gen(uniq_) nolocal
* gtop varlist [if] [in] [weight], [options]
* gtoplevelsof varlist [if] [in] [weight], [options]
gtoplevelsof foreign rep78
gtop foreign rep78 [w = weight], ntop(5) missrow groupmiss pctfmt(%6.4g) colmax(3)
* gcollapse (stat) out = src [(stat) out = src ...] [if] [if] [weight], by(varlist) [options]
gen h1 = headroom
gen h2 = headroom
local lbl labelformat(#stat:pretty# #sourcelabel#)
gcollapse (mean) mean = price (median) p50 = gear_ratio, by(make) merge v `lbl'
disp "`:var label mean', `:var label p50'"
gcollapse (iqr) irq? = h? (nunique) turn (p97.5) mpg, by(foreign rep78) bench(2) wild
* gcontract varlist [if] [if] [fweight], [options]
gcontract foreign [fw = turn], freq(f) percent(p)
* greshape wide varlist, i(i) j(j) [options]
* greshape long prefixlist, i(i) [j(j) string options]
*
* greshape spread varlist, j(j) [options]
* greshape gather varlist, j(j) value(value) [options]
gen j = _n
greshape wide f p, i(foreign) j(j)
greshape long f p, i(foreign) j(j)
greshape spread f p, j(j)
greshape gather f? p?, j(j) value(fp)See the FAQs or the respective documentation for a list of supported
gcollapse and gegen functions.
Functions available with gegen and gcollapse
gcollapse supports every collapse function, including their
weighted versions. In addition, weights can be selectively applied via
rawstat(), and nunique counts the number of unique values.
gegen technically does not support all of egen, but whenever a
function that is not supported is requested, gegen hashes the data and
calls egen grouping by the hash, which is often faster (gegen only
supports weights for internal functions, since egen does not normally
allow weights).
Hence both should be able to replicate all of the functionality of their Stata counterparts. The following are implemented internally in C:
| Function | gcollapse | gegen |
|---|---|---|
| tag | X | |
| group | X | |
| total | X | |
| nunique | X | X |
| sum | X | X |
| nansum | X | X |
| rawsum | X | |
| rawnansum | X | |
| mean | X | X |
| sd | X | X |
| max | X | X |
| min | X | X |
| count | X | X |
| nmissing | X | X |
| median | X | X |
| iqr | X | X |
| percent | X | X |
| first | X | X (+) |
| last | X | X (+) |
| firstnm | X | X (+) |
| lastnm | X | X (+) |
| semean | X | X |
| sebinomial | X | X |
| sepoisson | X | X |
| percentiles | X | X |
| skewness | X | X |
| kurtosis | X | X |
(+) first, last, firstmn, and lastnm are different from their counterparts in the egenmore package and, instead, they are analogous to the gcollapse counterparts.
The percentile syntax mimics that of collapse and egen, with the addition
that quantiles are also supported. That is,
gcollapse (p#) target = var [target = var ...] , by(varlist)
gegen target = pctile(var), by(varlist) p(#)where # is a "percentile" with arbitrary decimal places (e.g. 2.5 or 97.5).
Last, when gegen calls a function that is not implemented internally by
gtools, it will hash the by variables and call egen with by set to an
id based on the hash. That is, if fcn is not one of the functions above,
gegen outvar = fcn(varlist) [if] [in], by(byvars)would be the same as
hashsort byvars, group(id) sortgroup
egen outvar = fcn(varlist) [if] [in], by(id)but preserving the original sort order. In case an egen option might
conflict with a gtools option, the user can pass gtools_capture(fcn_options)
to gegen.
Differences and Extras
Differences from collapse
- String variables are not allowed for
first,last,min,max, etc. (see issue 25) nuniqueis supported.nmissingis supported.rawstatallows selectively applying weights.- Option
wildallows bulk-rename. E.g.gcollapse mean_x* = x*, wild gcollapse, mergemerges the collapsed data set back into memory. This is much faster than collapsing a dataset, saving, and merging after. However, Stata'smerge ..., updatefunctionality is not implemented, only replace. (If the targets exist the function will throw an error withoutreplace).gcollapse, labelformatallows specifying the output label using placeholders.gcollapse (nansum)andgcollapse (rawnansum)outputs a missing value for sums if all inputs are missing (instead of 0).gcollapse, sumcheckkeeps integer types withsumif the sum will not overflow.
Differences from greshape
- Allows an arbitrary number of variables in
i()andj() - Several option allow turning off error checks for faster execution,
including:
fast(similar tofastingcollapse),unsorted(do not sort the output),nodupcheck(allow duplicates ini),nomisscheck(allow missing values and/or leading blanks inj), ornochecks(all of the above). - Subcommands
gatherandspreadimplement the equivalent commands from R'stidyrpackage. - At the moment,
j(name [values])is not supported. All values ofjare used. - "reshape mode" is not supported. Reshape variables are not saved as
part of the current dataset's characteristics, meaning the user cannot
type
reshape wideandreshape longwithout further arguments to reverse thereshape. This syntax is very cumbersome and difficult to support;greshapere-wrote much of the code base and had to dispense with this functionality. - For that same reason, "advanced" syntax is not supported, including the subcommands: clear, error, query, i, j, xij, and xi.
@syntax is not (yet) supported but is planned for a future release.
Differences from xtile, pctile, and _pctile
- Adds support for
by()(including weights) - Does not ignore
altdefwithxtile(see this Statalist thread) - Category frequencies can also be requested via
binfreq[()]. xtile,pctile, and_pctilecan be combined viaxtile(newvar)andpctile(newvar)- There is no limit to
nquantiles()forxtile - Quantiles can be requested via
percentiles()(orquantiles()),cutquantiles(), orquantmatrix()forxtileas well aspctile. - Cutoffs can be requested via
cutquantiles(),cutoffs(), orcutmatrix()forxtileas well aspctile. - The user has control over the behavior of
cutpoints()andcutquantiles(). They obeyifinwith optioncutifin, they can be group-specific with optioncutby, and they can be de-duplicated viadedup. - Fixes numerical precision issues with
pctile, altdef(e.g. see this Statalist thread, which is a very minor thing so Stata and fellow users maintain it's not an issue, but I think it is because Stata/MP gives what I think is the correct answer whereas IC and SE do not). - Fixes a possible issue with the weights implementation in
_pctile; see this thread.
Differences from egen
grouplabel options are not supported- weights are supported for internally implemented functions.
nuniqueis supported.gegenupgrades the type of the target variable if it is not specified by the user. This means that if the sources aredoublethen the output will be double. All sums are double.groupcreates alongor adouble. And so on.egenwill default to the system type, which could cause a loss of precision on some functions.- For internally supported functions, you can specify a varlist as the source, not just a single variable. Observations will be pooled by row in that case.
- While
gegenis much faster fortag,group, and summary stats, most egen function are not implemented internally, meaning for arbitrarygegencalls this is a wrapper for hashsort and egen.
Differences from levelsof
- It can take a
varlistand not just avarname; in that case it prints all unique combinations of the varlist. The user can specify column and row separators. - It can deduplicate an arbitrary number of levels and store the results in a
new variable list or replace the old variable list via
gen(prefix)andgen(replace), respectively. If the user runs up against the maximum macro variable length, add optionnolocal.
Differences from isid
- No support for
using. The C plugin API does not allow to load a Stata dataset from disk. - Option
sortis not available. - It can also check IDs with
ifandinconditions.
Differences from gsort
hashsortbehaves as ifmfirstwas passed. To recover the default behavior ofgsortpass optionmlast.
Differences from duplicates
gduplicatesdoes not sortexamplesorlistby default. This massively enhances performance but it might be harder to read. Pass optionsort(sorted) to mimicduplicatesbehavior and sort the list.
There are two key insights to the massive speedups of Gtools:
-
Hashing the data and sorting a hash is a lot faster than sorting the data to then process it by group. Sorting a hash can be achieved in linear O(N) time, whereas the best general-purpose sorts take O(N log(N)) time. Sorting the groups would then be achievable in O(J log(J)) time (with J groups). Hence the speed improvements are largest when N / J is largest.
-
Compiled C code is much faster than Stata commands. While it is true that many of Stata's underpinnings are compiled code, several operations are written in
adofiles without much thought given to optimization. If you're working with tens of thousands of observations you might barely notice (and the difference between 5 seconds and 0.5 seconds might not be particularly important). However, with tens of millions or hundreds of millions of rows, the difference between half a day and an hour can matter quite a lot.
Stata Sorting
It should be noted that Stata's sorting mechanism is not inefficient as a
general-purpose sort. It is just inefficient for processing data by group. We
have implemented a hash-based sorting command, hashsort. While at times this
is faster than Stata's sort, it can also often be slower:
| Function | Replaces | Speedup (IC / MP) | Unsupported | Extras |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hashsort | sort | 2.5 to 4 / .8 to 1.3 | Group (hash) sorting | |
| gsort | 2 to 18 / 1 to 6 | mfirst (see mlast) |
Sorts are stable |
The overhead involves copying the by variables, hashing, sorting the hash,
sorting the groups, copying a sort index back to Stata, and having Stata do
the final swaps. The plugin runs fast, but the copy overhead plus the Stata
swaps often make the function be slower than Stata's native sort.
The reason that the other functions are faster is because they don't deal with
all that overhead. By contrast, Stata's gsort is not efficient. To sort
data, you need to make pair-wise comparisons. For real numbers, this is just
a > b. However, a generic comparison function can be written as compare(a, b) > 0.
This is true if a is greater than b and false otherwise. To invert
the sort order, one need only use compare(b, a) > 0, which is what gtools
does internally.
However, Stata creates a variable that is the inverse of the sort variable.
This is equivalent, but the overhead makes it slower than hashsort.
- Update benchmarks for all commands. Still on 0.8 benchmarks.
- Implement
gstats summarizeandgstats tabstat
These are options/features/improvements I would like to add, but I don't have an ETA for them:
- Implement
gmerge- Integration with ReadStat?
- Add support for binary
strLvariables. - Minimize memory use.
- Add memory(greedy|lean) to give user fine-grained control over internals.
- Create a Stata C hashing API with thin wrappers around core functions.
- This will be a C library that other users can import.
- Some functionality will be available from Stata via gtooos, api()
- Add option to
gtopto display top X results in alpha order - Improve debugging info.
- Improve code comments when you write the API!
- Have some type of coding standard for the base (coding style)
Hi! I'm Mauricio Caceres; I made gtools
after some of my Stata jobs were taking literally days to run because of repeat
calls to egen, collapse, and similar on data with over 100M rows. Feedback
and comments are welcome! I hope you find this package as useful as I do.
Along those lines, here are some other Stata projects I like:
-
ftools: The main inspiration for gtools. Not as fast, but it has a rich feature set; its mata API in particular is excellent. -
reghdfe: The fastest way to run a regression with multiple fixed effects (as far as I know). -
stata_kernel: A Stata kernel for Jupyter; extremely useful for interacting with Stata. -
stata-cowsay: Productivity-boosting cowsay functionality in Stata.
Gtools is MIT-licensed.
./lib/spookyhash and ./src/plugin/common/quicksort.c belong to their respective
authors and are BSD-licensed. Also see gtools, licenses.