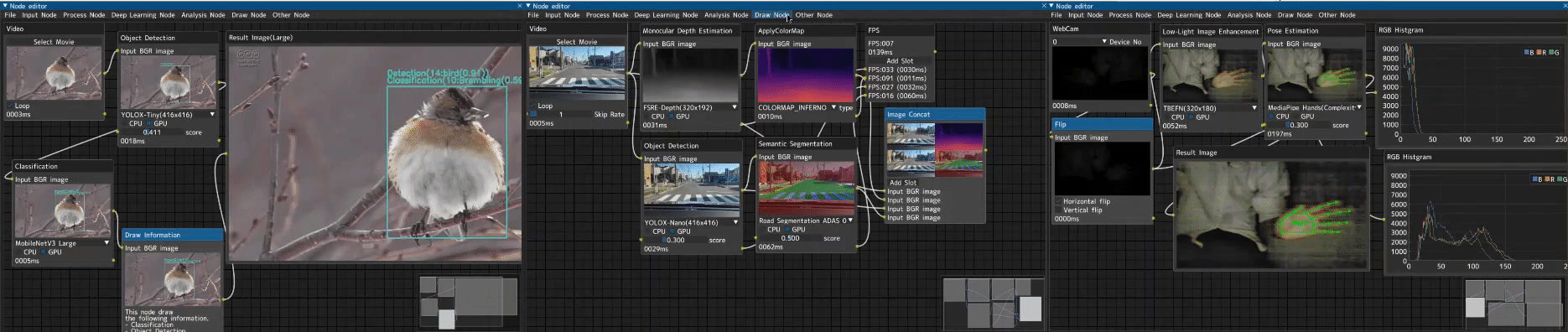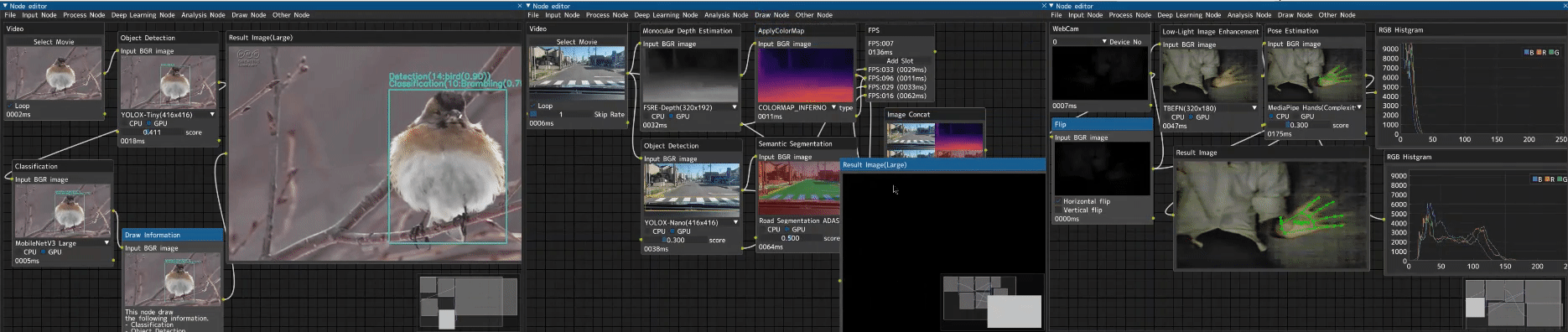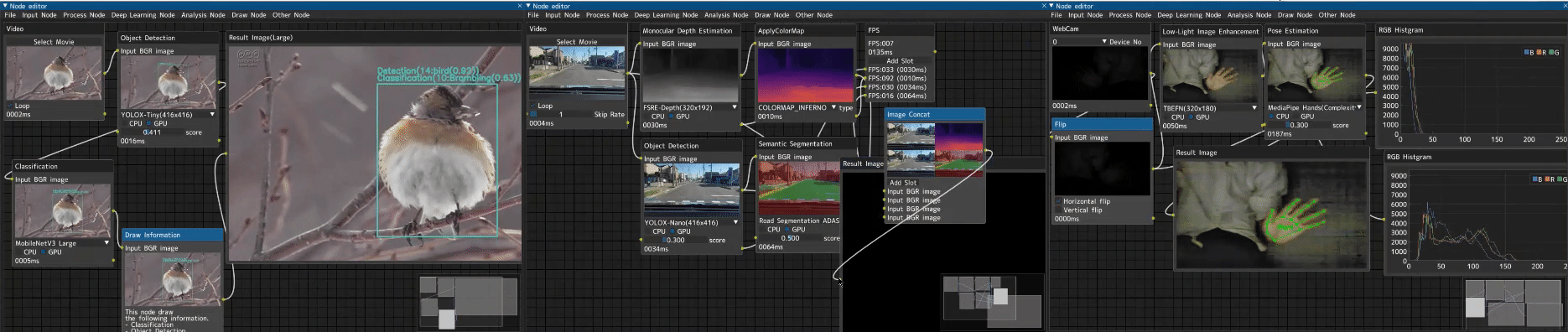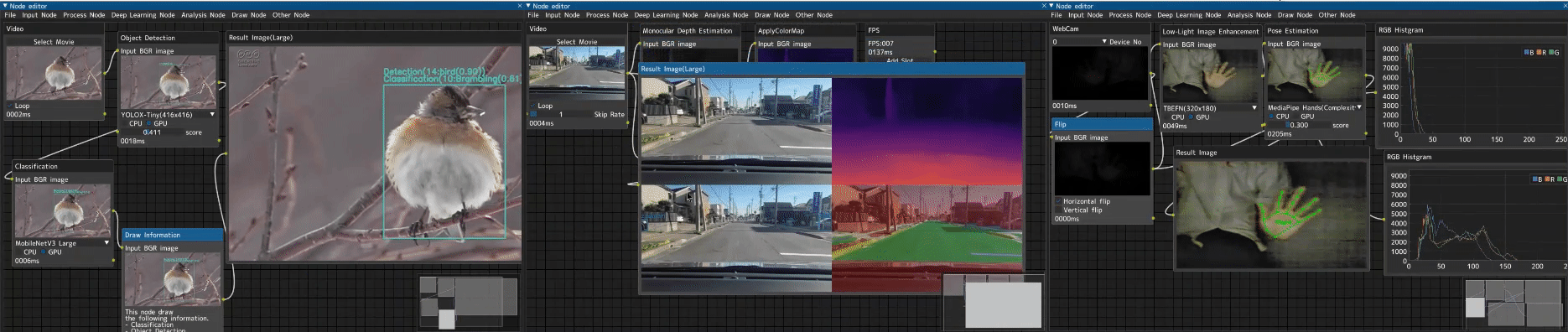
A professional node-based image processing application for computer vision development, verification, and comparison.
CV Studio is an advanced node-based image processing application that allows you to visually create computer vision pipelines through an intuitive drag-and-drop interface. Perfect for:
- Prototyping - Quickly test and compare different CV algorithms
- Education - Learn computer vision concepts interactively
- Development - Build and validate processing pipelines before production
- Research - Experiment with ML models and traditional CV techniques
- 🎨 Visual Node Editor - Intuitive drag-and-drop interface powered by DearPyGUI
- 🔄 Real-time Processing - See results instantly as you build your pipeline
- 🧩 100+ Built-in Nodes - Input, processing, ML/DL, analysis, and visualization nodes
- 🤖 ML/DL Integration - Support for ONNX models, MediaPipe, and custom models
- 📹 Multiple Input Sources - Webcam, video files, images, RTSP streams, screen capture
- 💾 Save & Load - Export and import your processing graphs as JSON
- 🏗️ Modern Architecture - Professional codebase with proper error handling, logging, and testing
- 🔌 Extensible - Easy to add custom nodes and processing algorithms
Python 3.7 or later
opencv-python 4.5.5.64 or later
onnxruntime 1.16.0 or later
dearpygui 1.11.0 or later
mediapipe 0.8.10 or later ※ Required for MediaPipe nodes
protobuf 3.20.0 or later ※ Required for MediaPipe nodes
filterpy 1.4.5 or later ※ Required for MOT (Multi-Object Tracking) nodes
📘 Windows Users: For detailed Windows-specific installation instructions with troubleshooting, see:
- 🇬🇧 INSTALLATION_WINDOWS.md (English)
- 🇫🇷 INSTALLATION_WINDOWS_FR.md (Français)
-
Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/hackolite/CV_Studio.git cd CV_Studio -
Install dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txt
-
Run the application
python main.py
# Create virtual environment
python -m venv venv
# Activate virtual environment
# On Windows:
venv\Scripts\activate
# On Linux/Mac:
source venv/bin/activate
# Install dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txt
# Run the application
python main.py# Install build tools first
# Windows: https://visualstudio.microsoft.com/visual-cpp-build-tools/
# Ubuntu: sudo apt-get install build-essential libssl-dev libffi-dev python3-dev
# Install required packages
pip install Cython numpy wheel
# Install from GitHub
pip install git+https://github.com/hackolite/CV_Studio.git
# Run the application
ipn-editorSee Image-Processing-Node-Editor/docker/nvidia-gpu for Docker setup instructions.
For Windows users who want a standalone .exe file that doesn't require Python installation:
No Python or build tools installation required! Simply trigger a build on GitHub:
- Go to the Actions tab in this repository
- Click on "Build Windows Executable" in the left sidebar
- Click "Run workflow" → Select branch → Click green "Run workflow" button
- Wait 10-15 minutes for the build to complete
- Download the
CV_Studio-Windows-Executable.zipfrom the Artifacts section - Extract and run
CV_Studio.exe- Done! 🎉
📖 Detailed instructions: See COMMENT_OBTENIR_EXE.md (Français) or HOW_TO_GET_EXE.md (English)
The easiest way to build locally! Just download and run a script that does everything automatically:
Using Batch Script (Simple - Double-click to run):
- Download
build_windows.bat - Double-click the file
- Wait 5-15 minutes
- Find your executable in
dist/CV_Studio/CV_Studio.exe
Using PowerShell (Modern):
# Download the script (or clone the repo to get it)
powershell -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -File build_windows.ps1The script automatically:
- ✅ Clones the repository (if needed)
- ✅ Installs all Python dependencies
- ✅ Builds the .exe with PyInstaller
- ✅ Shows you where to find the result
📖 Full guide: See BUILD_WINDOWS_SCRIPT.md for detailed instructions and troubleshooting
Before building the executable, ensure you have:
- Python 3.7+ installed (tested with Python 3.12)
- Git for cloning the repository
- Windows OS (for building Windows executables)
Étape 1 : Cloner le dépôt / Step 1: Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/hackolite/CV_Studio.git
cd CV_StudioÉtape 2 : Installer les dépendances principales / Step 2: Install main dependencies
# Install main dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txtÉtape 3 : Installer les dépendances de build / Step 3: Install build dependencies
# Install PyInstaller and build tools
pip install -r requirements-build.txt
# Or manually: pip install pyinstallerÉtape 4 : Construire l'exécutable / Step 4: Build the executable
# Standard build with clean
python build_exe.py --clean
# Alternative: Build without console window (GUI only)
python build_exe.py --clean --windowed
# Alternative: With custom icon
python build_exe.py --clean --icon your_icon.icoThe build process will:
- ✅ Verify all dependencies are installed
- ✅ Clean previous build artifacts (if --clean flag used)
- ✅ Package all Python dependencies
- ✅ Include all nodes (Input, Process, DL, Audio, etc.)
- ✅ Bundle all ONNX models for object detection
- ✅ Create the standalone executable
Build time: Approximately 5-15 minutes depending on your system.
Étape 5 : Localiser l'exécutable / Step 5: Locate your executable
Your .exe file is ready at:
dist/CV_Studio/CV_Studio.exe
The dist/CV_Studio/ folder contains:
CV_Studio.exe- Main executablenode/- All node implementations and ONNX modelsnode_editor/- Editor core and settingssrc/- Source utilities_internal/- Python runtime and dependencies
Étape 6 : Tester l'exécutable / Step 6: Test the executable
# Navigate to the dist folder
cd dist/CV_Studio
# Run the executable
CV_Studio.exe
# Or run with debug output
CV_Studio.exe --use_debug_printÉtape 7 : Vérifier les fonctionnalités / Step 7: Verify functionality
Test that everything works:
- Open the application
- Add an Image node (Input → Image)
- Add an Object Detection node (VisionModel → Object Detection)
- Select a YOLOX model
- Add a Result Image node
- Connect the nodes and verify object detection works
Étape 8 : Distribution / Step 8: Distribution
To share your executable:
# Create a ZIP archive
cd dist
# On Windows PowerShell:
Compress-Archive -Path CV_Studio -DestinationPath CV_Studio_v1.0.zip
# Or use 7-Zip (if installed):
7z a CV_Studio_v1.0.zip CV_StudioThe ZIP file can be distributed to users who just need to:
- Extract the ZIP file
- Run
CV_Studio.exe - No Python installation required!
- ✅ All nodes (Input, Process, DL, Audio, etc.)
- ✅ All ONNX models for object detection (YOLOX, YOLO, FreeYOLO, etc.)
- ✅ Complete Python runtime (no separate Python installation needed)
- ✅ All required libraries (OpenCV, DearPyGUI, ONNX Runtime, etc.)
- ✅ Configuration files and fonts
Size: Approximately 800 MB - 1.5 GB
# Clean build (recommended)
python build_exe.py --clean
# GUI mode without console window
python build_exe.py --windowed
# Debug mode with detailed logging
python build_exe.py --debug
# Custom icon (if you have an icon file)
python build_exe.py --icon your_icon.ico
# Combine options
python build_exe.py --clean --windowed --icon your_icon.icoProblem: PyInstaller not found
pip install pyinstallerProblem: Missing dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txt
pip install -r requirements-build.txtProblem: Exe doesn't start
- Install Visual C++ Redistributable
- Run from command line to see error messages:
CV_Studio.exe --use_debug_print - Check antivirus isn't blocking the executable
Problem: ONNX models not found
- Verify the
dist/CV_Studio/node/DLNode/directory structure is intact - Rebuild with
python build_exe.py --clean
For comprehensive guides, see:
- Quick Reference - Quick start guide
- Full Guide (English) - Complete documentation with all options
- Guide complet (Français) - Documentation complète en français
Start the application with:
python main.py--setting <path>- Specify custom configuration file (default:node_editor/setting/setting.json)--unuse_async_draw- Disable asynchronous drawing for debugging--use_debug_print- Enable debug output
Example:
python main.py --setting custom_config.json --use_debug_printSelect a node from the menu and click to add it to the canvas.
Drag from an output terminal to an input terminal to create connections. Only compatible terminal types can be connected.
Select the node and press the Delete key.
Save your processing pipeline as a JSON file via the Export menu option.
Load a previously saved processing pipeline from a JSON file.
Here are some practical examples to help you get started with common computer vision tasks:
For complete, runnable code examples including DearPyGui usage patterns, see the examples/ directory:
- dearpygui_node_editor_colored_combo_example.py - Demonstrates node editor with themed combo boxes, domain-based coloring, and dynamic UI updates
See examples/README.md for detailed documentation on each example.
Task: Apply blur and edge detection to an image
- Add an Image node (Input → Image)
- Add a Blur node (VisionProcess → Blur)
- Add a Canny node (VisionProcess → Canny)
- Add a Result Image node (Visual → Result Image)
- Connect: Image → Blur → Canny → Result Image
- Click "Select Image" in the Image node to load your image
- Adjust blur and Canny parameters using the sliders
Result: You'll see real-time edge detection applied to your blurred image.
Task: Detect objects in real-time from your webcam
- Add a WebCam node (Input → WebCam)
- Add an Object Detection node (VisionModel → Object Detection)
- Add a Draw Information node (Overlay → Draw Information)
- Add a Result Image node (Visual → Result Image)
- Connect: WebCam → Object Detection → Draw Information → Result Image
- Select your camera device in the WebCam node
- Choose a detection model in the Object Detection node
Result: Real-time object detection with bounding boxes drawn on your webcam feed.
Task: Process a video file with multiple filters
- Add a Video node (Input → Video)
- Add multiple processing nodes (e.g., Brightness, Contrast, Grayscale)
- Add an Image Concat node (Overlay → Image Concat) to compare results
- Add a Result Image node (Visual → Result Image)
- Connect the Video node to each processing node
- Connect all processing outputs to the Image Concat node
- Connect Image Concat to Result Image
Result: Side-by-side comparison of different processing effects on your video.
Task: Detect faces and apply effects
- Add an Image or WebCam node
- Add a Face Detection node (VisionModel → Face Detection)
- Add a Draw Information node (Overlay → Draw Information)
- Add a Crop node (VisionProcess → Crop) - optional, to extract faces
- Connect nodes in sequence
- Use the Draw Information node to visualize detected faces
Result: Automatic face detection with bounding boxes and optional face extraction.
- Organize Your Workspace: Arrange nodes logically from left (inputs) to right (outputs) for better readability
- Use Image Concat: Compare different processing approaches side-by-side using the Image Concat node
- Check Terminal Colors: Nodes can only connect if terminal types match (indicated by color)
- Start Simple: Begin with a basic pipeline and add complexity incrementally
- Save Frequently: Use Export to save your work regularly
- Reduce Resolution: Use the Resize node early in your pipeline to speed up processing
- Toggle Nodes: Use the ON/OFF Switch node to temporarily disable expensive operations
- Limit Video FPS: Adjust skip rate in Video nodes to process fewer frames
- GPU Acceleration: Enable GPU in Deep Learning nodes when available (requires ONNX Runtime GPU)
- Use Debug Print: Launch with
--use_debug_printto see detailed node execution logs - Disable Async Draw: Use
--unuse_async_drawif you experience UI issues - Check Connections: Verify all node connections are properly established (no red indicators)
- Monitor Performance: Use the FPS node to track processing speed
- Test Incrementally: Add one node at a time and verify it works before adding more
-
Input Nodes:
- Use Image for static images and prototyping
- Use WebCam for real-time testing
- Use Video for batch processing and testing on recorded content
- Use RTSP for network camera streams
-
Processing Nodes:
- Start with basic nodes (Brightness, Contrast, Blur) before complex ones
- Chain multiple processing nodes to create sophisticated effects
- Use Grayscale before Threshold for better results
-
ML/DL Nodes:
- Check GPU availability before enabling GPU inference
- Different models have different performance characteristics - experiment!
- Combine detection nodes with tracking for smoother results
-
Visualization:
- Use Result Image for final output
- Use Result Image (Large) when you need more detail
- Use PutText to add custom labels and timing information
- Use RGB Histogram for color analysis
| Action | Shortcut/Method |
|---|---|
| Add Node | Click menu item, then click on canvas |
| Delete Node | Select node, press Delete key |
| Pan Canvas | Middle mouse button drag or Ctrl + Left mouse drag |
| Connect Nodes | Drag from output terminal to input terminal |
| Disconnect Nodes | Right-click on connection line, select delete |
| Select Multiple | Ctrl + Click on nodes |
| Minimap | Click minimap in bottom-right to navigate large graphs |
Problem: Application crashes on startup
- Solution: Check if required dependencies are installed:
pip install -r requirements.txt - Solution: Ensure you have a compatible Python version (3.7+)
- Solution: Try disabling async drawing:
python main.py --unuse_async_draw
Problem: Webcam not detected
- Solution: Close other applications using the webcam
- Solution: Check camera permissions in your OS settings
- Solution: Try different device numbers in the WebCam node dropdown
Problem: Cannot connect two nodes
- Solution: Verify terminal types match (same color)
- Solution: Check that output terminal connects to input terminal (not output to output)
- Solution: Some nodes require specific input types - check node documentation
Problem: Deep Learning node shows "Model not found" error
- Solution: Download the required model files (see node-specific README files)
- Solution: Check the model path in the node configuration
- Solution: Verify you have the correct ONNX runtime installed
Problem: Low FPS / Slow processing
- Solution: Add a Resize node to reduce image resolution
- Solution: Enable GPU acceleration in DL nodes if available
- Solution: Reduce video skip rate or use lower resolution input
- Solution: Close unnecessary nodes and connections
Problem: Export/Import doesn't work
- Solution: Ensure you're saving to a writable location
- Solution: Check that the JSON file is valid and not corrupted
- Solution: Import files should be loaded before adding new nodes
Problem: Node parameters don't update
- Solution: Try reconnecting the node connections
- Solution: Restart the application
- Solution: Check if the node is receiving valid input data
Create custom configuration files to save your preferred settings:
# Create a custom config
cp node_editor/setting/setting.json my_config.json
# Edit my_config.json to set your preferences
# - webcam_width/height: Camera resolution
# - process_width/height: Processing resolution
# - editor_width/height: Window size
# - use_gpu: Enable GPU acceleration
# - use_pref_counter: Enable performance monitoring
# Run with custom config
python main.py --setting my_config.jsonCV Studio supports multiple cameras simultaneously:
- The application automatically detects available cameras on startup
- Each WebCam node can select a different camera device
- Use multiple WebCam nodes to process multiple camera feeds in parallel
- Combine feeds using Image Concat for multi-camera display
Extend CV Studio with your own nodes:
# Create a new node file in node/ProcessNode/
from node.ProcessNode.node_abc import ProcessNodeABC
class MyCustomNode(ProcessNodeABC):
node_label = 'My Custom Filter'
node_tag = 'MyCustomFilter'
def update(self, node_id, connection_list, node_image_dict, node_result_dict):
# Your processing logic here
input_image = self._get_input_image(node_image_dict, connection_list)
# Process input_image...
output_image = input_image # Replace with your processing
return {"image": output_image, "json": None}See the Development section for more details on creating custom nodes.
Process multiple files efficiently:
- Create your processing pipeline using an Image node
- Test with a single image
- Export the graph configuration
- Modify the exported JSON to point to different images
- Import and process each configuration
For video batch processing:
- Use the Video node with your pipeline
- Add a Video Writer node to save output
- Configure output settings in
setting.json - Process multiple videos by changing the input file
CV Studio supports integration with external systems:
- API Integration: Use API input nodes to receive data from REST endpoints
- WebSocket Streaming: Real-time data streaming for live applications
- RTSP Streams: Connect to IP cameras and network video sources
- Serial Communication: Interface with Arduino and other embedded devices (enable in settings)
See tests/dummy_servers/README.md for examples of external server integration.
CV Studio features a modern, professional architecture designed for scalability and maintainability.
New in this version: CV Studio now implements a timestamped queue system for node data communication that ensures:
- ✅ FIFO Data Retrieval - Oldest data is retrieved first from node queues
- ✅ Automatic Timestamping - All data automatically timestamped when created
- ✅ Thread-Safe Operations - Safe concurrent access across all nodes
- ✅ Backward Compatibility - Existing nodes work without modifications
- ✅ Queue Management - Automatic size limits prevent memory overflow
Each node that sends data to other nodes does so through its own timestamped queue. When nodes retrieve data, they get the oldest data from the FIFO queue, ensuring chronological processing order. See TIMESTAMPED_QUEUE_SYSTEM.md for detailed documentation.
Benefits:
- Proper temporal ordering of video frames and audio data
- Prevention of data race conditions
- Better synchronization between nodes
- Monitoring and debugging capabilities
CV_Studio/
├── src/ # New professional architecture
│ ├── core/ # Core business logic
│ │ ├── nodes/ # Node abstractions (BaseNode, NodeFactory, EnhancedNode)
│ │ ├── config/ # Settings management
│ │ └── pipeline/ # Processing pipeline (future)
│ ├── nodes/ # Node implementations with adapters
│ │ ├── input/ # Input node adapters
│ │ ├── process/ # Processing node adapters
│ │ ├── ml/ # ML/DL node adapters
│ │ └── examples/ # Example implementations
│ ├── utils/ # Reusable utilities
│ │ ├── exceptions.py # Custom exception hierarchy
│ │ ├── logging.py # Centralized logging
│ │ └── resource_manager.py # Resource lifecycle management
│ └── gui/ # GUI components (future)
│
├── node/ # Original node implementations (fully compatible)
│ ├── InputNode/ # Input sources (webcam, video, images)
│ ├── ProcessNode/ # Image processing nodes
│ ├── DLNode/ # Deep learning nodes
│ ├── ActionNode/ # Action/control nodes
│ ├── OverlayNode/ # Drawing and overlay nodes
│ ├── timestamped_queue.py # Timestamped FIFO queue system (NEW)
│ ├── queue_adapter.py # Backward-compatible queue adapter (NEW)
│ └── ... # Other node categories
│
├── node_editor/ # Node editor core and UI
├── tests/ # Test suite (52+ tests, including queue system)
├── main.py # Application entry point
└── requirements.txt # Python dependencies
The src/ directory introduces professional development practices:
from src.utils.exceptions import NodeExecutionError, NodeConfigurationError
# Clear, structured error handling
raise NodeExecutionError(node_id, "Processing failed", original_exception)from src.utils.logging import get_logger
logger = get_logger(__name__)
logger.info("Processing node...")
logger.error("Node failed", exc_info=True)from src.utils.resource_manager import get_resource_manager
manager = get_resource_manager()
manager.register('video_capture', video_cap, cleanup_func=lambda v: v.release())from src.core.config import Settings
settings = Settings('config.json')
width = settings.get('webcam_width', 640)
settings.set('use_gpu', True)from src.core.nodes import EnhancedNode
class MyNode(EnhancedNode):
node_label = 'My Custom Node'
node_tag = 'MyNode'
# Built-in logging, error handling, resource management
def update(self, node_id, connection_list, node_image_dict, node_result_dict):
result = self.safe_execute(self.process_image, node_image_dict)
return {"image": result, "json": None}100% backward compatible - All existing code in the node/ and node_editor/ directories continues to work unchanged. The new architecture in src/ provides optional enhancements for future development.
- src/README.md - Technical architecture documentation
- Timestamped Queue System - FIFO queue documentation 🆕
CV Studio includes comprehensive test coverage with 150+ test files and pytest configuration.
# Run all tests
python -m pytest tests/ -v
# Run specific test suite
python -m pytest tests/test_utils/ -v
python -m pytest tests/test_core/ -v
# Run queue system tests
python -m pytest tests/test_timestamped_queue.py tests/test_queue_adapter.py tests/test_queue_integration.py -v
# Run with coverage report
python -m pytest tests/ --cov=src --cov=node --cov-report=htmlCore Architecture Tests:
- ✅ Base node class (14 tests) 🆕
- ✅ Enhanced node class (22 tests) 🆕
- ✅ DPG node ABC (16 tests) 🆕
- ✅ Node factory (7 tests)
- ✅ Settings management (10 tests)
Utilities Tests:
- ✅ Exception hierarchy (7 tests)
- ✅ Logging utilities (6 tests)
- ✅ Resource management (8 tests)
- ✅ GPU utilities (7 tests)
Queue System Tests:
- ✅ Timestamped queue system (35 tests)
- Core queue functionality (17 tests)
- Backward compatibility adapter (12 tests)
- Integration with node system (6 tests)
Node Integration Tests:
- ✅ 150+ integration tests for various node implementations
- ✅ Video processing nodes
- ✅ Audio processing nodes
- ✅ Object detection and tracking nodes
- ✅ And many more...
Input Node
| Image |

|
Node that reads still images (bmp, jpg, png, gif) and outputs images Open the file dialog with the "Select Image" button |
| Video |

|
A node that reads a video (mp4, avi) and outputs an image for each frame Open the file dialog with the "Select Movie" button Check "Loop" to play the video in a loop "Skip rate" sets the interval for skipping the output image. |
| Video(Set Frame Position) |

|
A node that reads a video (mp4, avi) and outputs an image at the specified frame position Open the file dialog with "Select Movie" button |
| WebCam |

|
A node that reads a webcam and outputs an image for each frame Specify the camera number in the Device No drop-down list |
| RTSP |

|
A node that reads the RTSP input of a network camera and outputs an image for each frame |
| Microphone | (Audio Input Node) |
A node that captures real-time audio from a microphone and outputs audio data Select audio device from the dropdown list Configure sample rate (8kHz to 48kHz) and chunk duration (0.1s to 5.0s) Click "Start" to begin recording, "Stop" to pause Outputs audio data compatible with Spectrogram and other audio processing nodes See README_Microphone.md for details |
| Int Value |

|
Node that outputs an integer value |
| Float Value |

|
Node that outputs the float value |
Process Node
Deep Learning Node
You can specify the model in the drop-down list and change the device at the time of inference with the CPU / GPU checkbox.
- If the model does not support GPU inference, checking GPU will still result in CPU inference
Refer to each directory of "node/deep_learning_node/XXXXXXXX" for the license of the model used by the node.
Analysis Node
Draw Node
Other Node
| ON/OFF Switch |

|
Node to switch whether to output the input image or not |
| Video Writer |

|
Node to export the input image as a video Output destination, output size, FPS are specified in "setting.json" |
Preview Release Node
Nodes whose specifications may change significantly in the future
| MOT |

|
Node that inputs an Object Detection node and executes MOT(Multi Object Tracking) Supports 6 tracking algorithms: motpy, ByteTrack, Norfair, IOU Tracker, SORT, and CenterTrack See TrackerNode/mot/README.md for details on each algorithm |
| Exec Python Code |

|
Node that executes Python code The variable for the input image is "input_image" The variable for the output image is "output_image" |
| Screen Capture |

|
Node that captures and outputs the desktop full screen |
It is a node published in other repositories.
To use it with Image-Processing-Node-Editor, follow the installation instructions for each repository.
Input Node
| YouTube |

|
Node that reads YouTube and outputs images Please specify the URL of the YouTube video in the URL field and press the "Start" button It will take some time before playback starts Specify the YouTube loading interval with "Interval(ms)" |
You can extend CV Studio by creating custom nodes. Use the new architecture for enhanced development experience:
from src.core.nodes import EnhancedNode
from src.utils.logging import get_logger
import cv2
logger = get_logger(__name__)
class MyCustomNode(EnhancedNode):
"""Example custom node with enhanced features"""
node_label = 'My Custom Node'
node_tag = 'CustomNode'
_ver = '1.0.0'
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
logger.info(f"Initialized {self.node_tag}")
def add_node(self, parent, node_id, pos, opencv_setting_dict=None):
"""Add node to GUI"""
# Implement your GUI setup here
pass
def update(self, node_id, connection_list, node_image_dict, node_result_dict):
"""Process the node"""
try:
# Your processing logic here
input_image = self._get_input_image(node_image_dict, connection_list)
output_image = cv2.cvtColor(input_image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
return {"image": output_image, "json": None}
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Node processing failed: {e}", exc_info=True)
return {"image": None, "json": None}See src/nodes/examples/example_enhanced_node.py for a complete example.
We welcome contributions! Here's how you can help:
- Fork the repository
- Create a feature branch (
git checkout -b feature/amazing-feature) - Make your changes using the new architecture in
src/ - Add tests for new functionality
- Ensure tests pass (
python -m pytest tests/) - Commit your changes (
git commit -m 'Add amazing feature') - Push to the branch (
git push origin feature/amazing-feature) - Open a Pull Request
- Use the new architecture in
src/for new code - Add tests for new functionality
- Update documentation as needed
- Maintain backward compatibility
- Follow existing code style and conventions
- Fix RGB Histogram node graph always appearing in foreground
- Fix connection line remaining when deleting connected nodes
- Improve import feature to work after nodes are added
- Pipeline processing system (graph-based execution)
- GUI component refactoring
- Plugin system for dynamic node loading
- Type safety with comprehensive type hints
- Auto-generated API documentation
- Performance monitoring and optimization
- Export to production-ready code
Original Author:
Fork from Kazuhito Takahashi (@KzhtTkhs)
Repository Builder :
hackolite
We appreciate all contributions from the community!
This project is licensed under the Apache License 2.0 - see the LICENSE file for details.
- The source code of CV Studio itself is under Apache-2.0 license
- Each algorithm/node implementation is subject to its own license
- Please check the LICENSE file in each node directory for specific algorithm licenses
- Third-party dependencies have their own licenses
Sample images are sourced from:
- Original Image-Processing-Node-Editor project
- DearPyGUI for the GUI framework
- OpenCV for computer vision functionality
- ONNX Runtime for ML model inference
- MediaPipe for ML solutions
- All contributors and users of this project
- Issues: GitHub Issues
- Discussions: GitHub Discussions
- Documentation: See the docs in this repository
Made with ❤️ for the Computer Vision Community
⭐ Star this repo if you find it useful!