This repository is a simple, unofficial implementation of "FakeTagger: Robust Safeguards against DeepFake Dissemination via Provenance Tracking" (https://arxiv.org/abs/2009.09869).
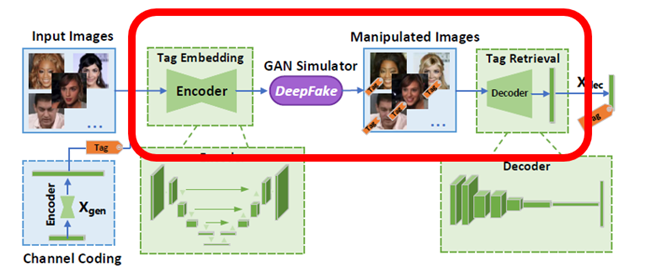
FakeTagger is composed of 5 modules.
- Message Generator creates a message with 0, and 1 and adds redundant data on the message.
- Image Encoder inserts the redundant message generated by the Message Generator into the original image, thereby generating an embedded image that is indistinguishable from the original input image.
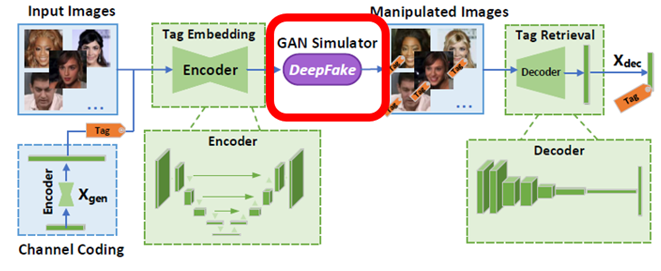
- GAN Simulator applies a deepfake algorithm to the embedded image, generating a manipulated embedded image.
- Image decoder extracts redundant messages from the embedded image or the manipulated embedded image.
- Message Decoder extracts the original message from the redundant message.
In this repository, only Image Encoder, GAN Simulator, Image Decoder are implemented.
-
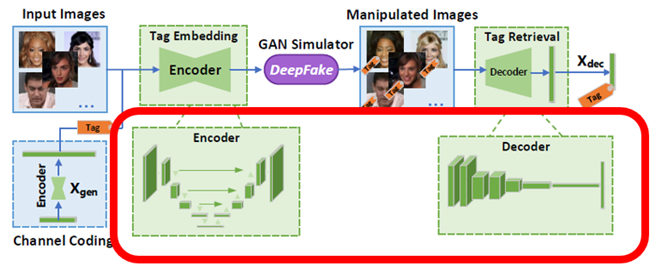
Image encoder combines a message and an image into an embedded image. We utilize U-Net same as the original paper. The message is concatenated with the output of the U-Net encoder and then passed to the U-Net decoder.
-
U-Net source code : https://colab.research.google.com/github/usuyama/pytorch-unet/blob/master/pytorch_unet_resnet18_colab.ipynb
-
Image decoder extracts a message from an input image. This is composed of 7 convolution layers following an FC layer and a sigmoid layer, generating a vector of which the length is the same as the message.
- GAN Simulator manipulates an embedded image with a deepfake algorithm. We utilize faceswap algorithm which changes the faces of two people with one encoder and two decoders.
- Faceswap source : https://github.com/Oldpan/Faceswap-Deepfake-Pytorch
python train.py --batch_size 128 --name name
python train.py --batch_size 128 --name name
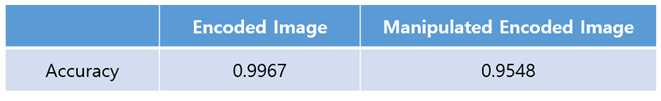
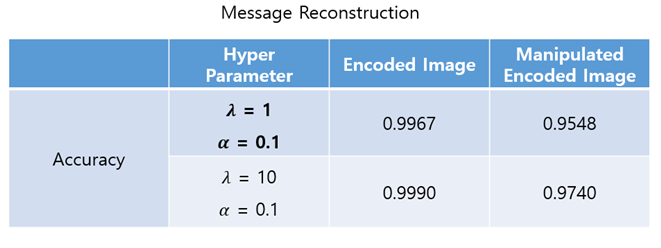
This table shows how exactly the image decoder extracts messages from embedded images and manipulated embedded images. In most cases, the image decoder obtains the messages from input images. Only the accuracy of the manipulated embedded images decreases by 4% points from the embedded images.
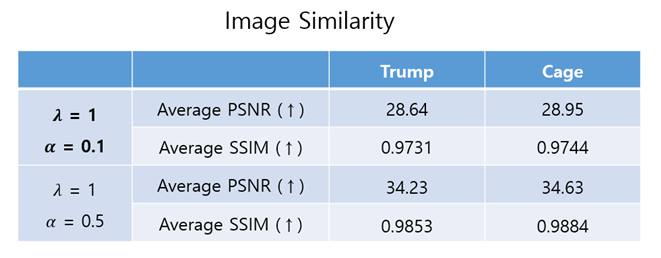
This table shows how simmilar the embedded images and the original images are each other in terms of PSNR (Peak Signal-to-noise ratio) and SSIM (Structural Similarity Index Measure).
The image encoder generates easily-distinguishable images when 𝜆 is too large. The above figure and table show the input images/output images of each module and the message reconstruction accuracy when 𝜆 = 10, 𝛼 = 0.1. You can see that the message reconstruction accuracy increases while the similarity of images decreases when 𝜆 increases.
If 𝛼 is too large, the image decoder can't extract the messages from input images. The above figure and table show the input images/output images of each module and the message reconstruction accuracy when 𝜆 = 1, 𝛼 = 0.5. You can see that the image similarity increases while the message reconstruction accuracy decreases when 𝛼 increases.