Hibernate Introduction and basic opertaion
Hibernate concept and API usages
Hibernate configuration, 1to many and many to many
Hibernate query
- Java EE three Layers
-
Web - struts2 框架
-
Service - Spring 框架
-
Dao - Hibernate 框架
A comparison between JDBC and Hibernate:
- MVC 思想: 是一种公用的思想
-
M: 模型
-
V:视图
-
C:控制器
- What is Hibernate?
框架: 写一个程序,使用框架之后,能帮我们实现一部分功能。使用框架好处,少写一部分代码。
Hibernate(冬眠) 框架:应用在javaEE三层中的dao层的框架。
在dao层里面做对数据库crud操作,使用hibernate实现crud操作,hibernate底层代码就是jdbc,hibernate对jdbc进行了封装。
好处,1.不需要写复杂jdbc的代码了。2. 不需要写sql语句。3. Hibernate开源轻量级框架。4. Hibernate版本5.x。
- What is ORM?
在web中,javabean可以封装数据,在框架阶段,叫做实体类。
Object-Relational-Mapping:对象关系映射, 让实体类和数据表进行一一对应关系,让实体类属性和表里面字段对应。不需要直接操作数据库表,而操作表对应实体类就行。
Find the detailed comparison from the picture under /note.
- Create Hibernate Environment
-
import jar files: folder (JPA + Requires) + log4j.jar + mysql-connector-java.jar + slf4j-api.jar + slf4j-log4j12.jar
-
Create Entity Class (JavaBean)
public class User {
/* one unique value */
private int uid;
private String username;
private String password;
private String address;
public int getUid() {
return uid;
}
public void setUid(int uid) {
this.uid = uid;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
}-
Create database table (Hibernate has tool to create the table automatically without manually doing that).
-
配置实体类和数据库表一一对应关系(映射关系)
-
Create xml configuration file,实体类所在的包里进行创建,实体类名称.hbm.xml
-
Include hibernate xml dtd.
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">- Configure mapping information.
<hibernate-mapping>
<!--
1. Class Map to Table
name: Full path to Entity class
table: Table name in DB
-->
<class name="com.liyiandxuegang.entity.User" table="t_user">
<!-- 2. Map Entity id to Table id -->
<!--
id has two properties:
name: Entity id name
column: Table column name
-->
<id name="uid" column="uid">
<!--
Increase strategy id by?
native: primary key, auto_increment
-->
<generator class="native"></generator>
</id>
<!-- 3. Map other fields in Entity to Table -->
<property name="username" column="username" />
<property name="password" column="password" />
<property name="address" column="address" />
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>- Create hibernate core configuration file: name and location is fixed. (under src)
- xml header
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">- hibernate操作过程中,自动加载的文件只有核心配置文件,其他配置文件不会加载。
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<!-- Part 1: DB Information -->
<property name="hibernate.connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:8889/test</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.username">root</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.password">root123</property>
<!-- Part 2: Hibernate Information (Optional) -->
<property name="hibernate.show_sql">true</property>
<property name="hibernate.format_sql">true</property>
<!--
Hibernate Create table, after we configure the settings
update: If no table, create table.
-->
<property name="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto">update</property>
<!--
db Dialect
-->
<property name="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property>
<!-- Part 3: Including mapping xml -->
<mapping resource="com/liyiandxuegang/entity/User.hbm.xml" />
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>- Test: Load core setting xml file -> Create SessionFactory -> Create session object -> Open Transaction -> Logic -> Commit -> Close Resources
@Test
public void test() {
// 1. Load core xml file, since name and loaction is fixed, so no params needed.
Configuration cfg = new Configuration();
cfg.configure();
// 2. Create SessionFactory, according to mapping relation, create table in DB.
SessionFactory sessionFactory = cfg.buildSessionFactory();
// 3. Create session object, like connections in JDBC
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
// 4. Create transaction
Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
// 5. CRUD
// Insert
User user = new User();
user.setUsername("Frank Wang");
user.setPassword("123456");
user.setAddress("Canada");
// Call session save
session.save(user);
// 6. Commit transactions
transaction.commit();
// 7. Close resources
session.close();
sessionFactory.close();
}-
No requires for filename and location
-
Class tag: name property: Entity full path
-
Name property values in id tag and property tags should be same as Entity properties.
-
All subtags should be under
-
Part 1 required, Part 2 optional, Part 3 required.
-
File name and location should be fixed.
Configuration cfg = new Configuration();
cfg.configure();[Load configuration file] Program will go to src folder, and find "hibernate.cfg.xml" file. Then, load configuration file into Object.
// What will this do?
// 1. Connect to db, and create the table, if it is not disabled.
// 2. It needs lots of resources.
// 3. One project, have one sessionFactory object.
cfg.buildSessionFactory(); How to create only one sessionFactory Object
// Create util class, and use static code block.
public class HibernateUtils {
private static final Configuration cfg;
private static final SessionFactory sessionFactory;
// Static, only run once.
static {
cfg = new Configuration();
cfg.configure();
sessionFactory = cfg.buildSessionFactory();
}
// return session factory
public static SessionFactory getSessionFactory() {
return sessionFactory;
}
}-
session类似于jdbc中的connection
-
调用session里面的方法实现crud的操作。 save, update, delete, get
-
session对象是单线程对象, session对象不能公用,只能自己使用。
-
Transaction Object: beginTransaction(),
-
Methods: commit(), rollback();
-
Concept:
原子性,一致性,隔离性,持久性;
-
Step 1. Open preferences, and search "xml catalog"
-
Step 2. Click Add, fill the following information.
-
Location: Find dtd or schema file from local system.
-
Key Type: URI;
-
Key: Copy the url http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd;
-
Restart Eclipse.
-
属性私有化
-
方法set和get要使用public修饰
-
实体类有一个属性必须有唯一值。
-
实体类属性,建议不适应基本数据类型,而使用基本数据对应的包装类
-
八个数据基本类型:int-> Integer; char -> Character; double -> Double
-
why? For example: int score;
-
If student got 0, int score = 0; but if the student missed the exam, int score = 0 can not represent the student didn't show up.
-
But if Integer score = 0, means student got 0; If no show, then Integer score = null;
-
<generator class="native"></generator>根据底层数据库对自动生成表示符的能力来选择identity,sequence,hilo三种生成器的一种。
Hibernate采用128为的UUID算法来生成标识符。该算法能够在网络环境中生成唯一的字符串标识符,其UUID被编码为一个长度为32位的十六进制字符串。 这种策略不流行,因为字符串类型的主键比整数类型的主键占用更多的数据库空间。适用于代理主键。
private String uuid;and in xml settings, we need to change id generator by uuid
<generator class="uuid"></generator>- Call method save of session
session.save(user);- Query by Id: call method of get in session
@Test
public void test1() {
// Call sessionFactory
SessionFactory sessionFactory = HibernateUtils.getSessionFactory();
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
//Open transactions
Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
// Query by id
User user = session.get(User.class, 1);
System.out.println(user);
// Commit
transaction.commit();
// Close
session.close();
sessionFactory.close();
}- Update: First query and then update
User user = session.get(User.class, 1);
user.setPassowrd("123");
session.update(user); // session.save(user); - Delete:
- Query get the Entity instance, and delete (recommend method)
User user = session.get(User.class, 1);
session.delete(user);- Create Entity instance, and delete (Not recommended)
User user = new User();
user.setUid(1);
session.delete(user);- 瞬时态: 对象中没有id值,对象和session没有关联。主要用来save操作。
User user = new User();
user.setUsername("Frank");
user.setPassword("*sdfsfasww");
user.setAddress("Earch");
session.save(user);- 持久态:对象中有id值。并且和session有关联。
User user = session.get(User.class, 1);- 托管态: 对象有id值,但是对象跟session无关系。 (使用的不多)
User user= new User();
user.setUid(3);
session.save(user);Add new record
User user = new User();
user.setUsername("jack");
user.setPassword("529");
user.setAddress("Korean");
session.saveOrUpdate(user);Update record
User user = new User();
user.setUid(6);
user.setUsername("Rose");
user.setPassword("12312");
user.setAddress("Harbour Landing");
session.saveOrUpdate(user);update record
User user = session.get(User.class, 7);
user.setUsername("LiLei");
session.saveOrUpdate(user);数据存到数据库,而数据库本身是一个文件系统,Java中要使用流的方式来操作效率不是很高。
-
我们可以把数据存到内存中,不需要流方式读取,直接读取内存中数据。
-
把数据放到内存中,提高读取效率
-
Hibernate框架中提供了很多优化方式,hibernate的缓存就是一个优化方式。
-
缓存特点:
-
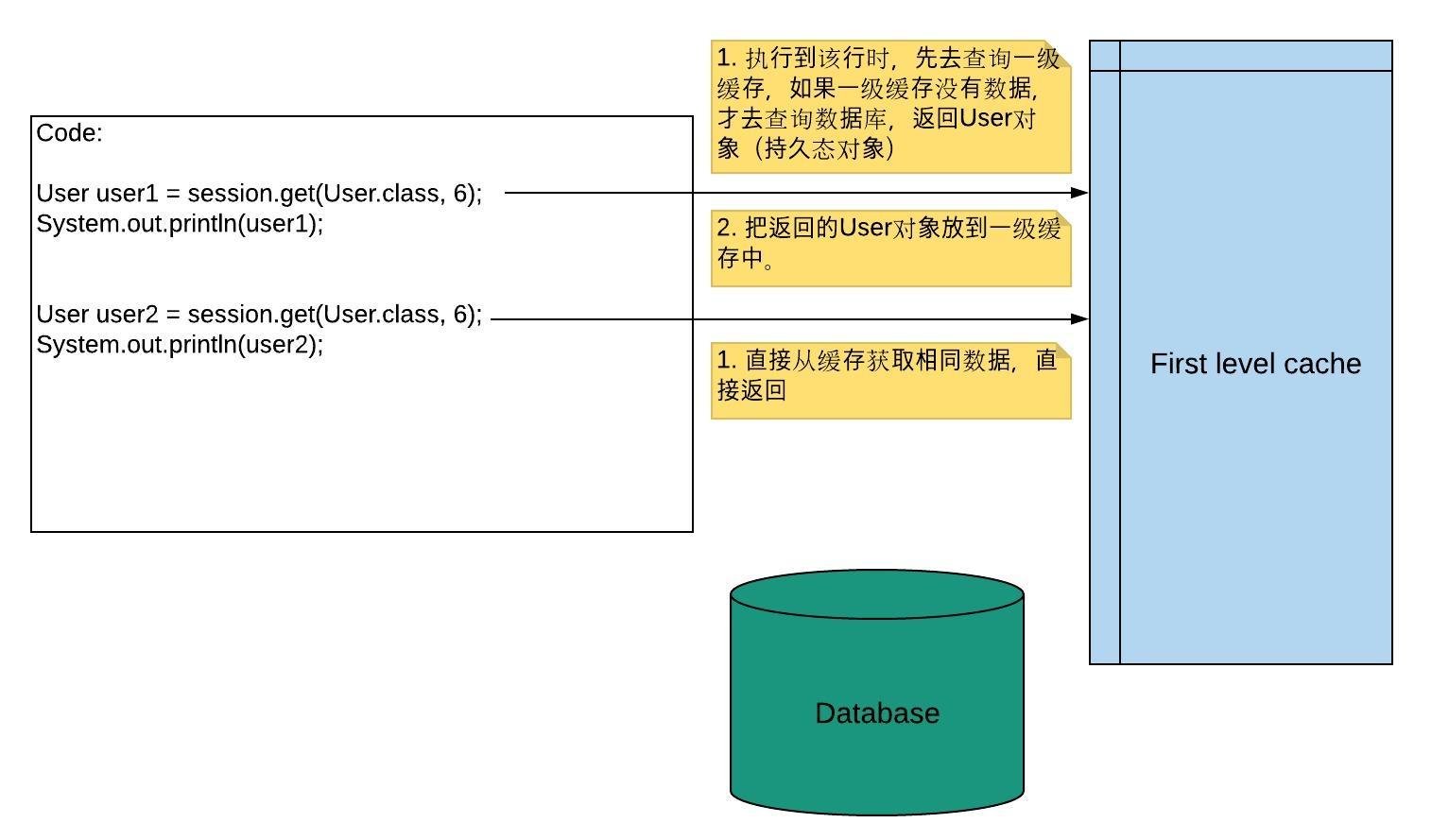
Hibernate first-level cache: 默认是开启状态;使用范围是session范围;存储的数据必须为持久态数据;
-
Hibernate second-level cache: 二级缓存已经被redis替代。需要配置来打开,使用范围是sessionFactory范围。
User user1 = session.get(User.class, 6);
System.out.println(user1);
User user2 = session.get(User.class, 6);
System.out.println(user2);The second time, hibernate won't query db, and the console prints the message below:
Hibernate:
select
user0_.uid as uid1_0_0_,
user0_.username as username2_0_0_,
user0_.password as password3_0_0_,
user0_.address as address4_0_0_
from
t_user user0_
where
user0_.uid=?
User [uid=6, username=Liyi, password=123456, address=Canada]
User [uid=6, username=Liyi, password=123456, address=Canada]sIt only do the query once.
See below how does it work?
- 持久态实体,会自动更新数据库
User user = session.get(User.class, 1);
user.setUsername("FrankandLiyi"); // data will be updated automatically. We don't need to call function session.update(user), the data in db has been updated.
How it works?
- 脏读; 2. 不可重复读; 3. 虚读
hibernate.connect.isolation = 4
1 - Read uncommited isolation
2 - Read committed isolation
4 - Repeatable read isolation
8 - Serializable isolcaiton
<property name="hibernate.connection.isolcation">4</property>- code
SessionFactory sessionFactory = null;
Session session = null;
Transaction transaction = null;
try {
// open transaction
// commit transaction
sessionFactory = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory();
session = sessionFactory.openSession();
transaction = session.beginTransaction();
// you code is here
transaction.commit();
} catch() {
// rollback transcation
transaction.rollback();
} finally {
// close transaction
session.close();
sessionFactory.close();
}-
session is similar to JDBC connection.
-
Bind to local thred.
- Add to core configuration file:
<!-- 配置与本地线程绑定的session -->
<property name="hibernate.current_session_context_class">thread</property>- Get local session method
// retur local thread
public static Session getSessionObj() {
return sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
}- No need to close the session if it is defined by this way.
No need to write SQL statement, but you need hql statement. Hibernate query language.
HQL VS SQL?
-
sql works directly on table and talbe fields
-
hql works on Entity class and Entity properties
- How to use? hql
-
Create Query object
-
Class query method and return the result.
- code
Query query = session.createQuery("from User");
// get all user list
List<User> userList = query.list();
for(User user : userList) {
System.out.println(user);
}Code shows below:
Criteria criteria = session.createCriteria(User.class);
List<User> userList = criteria.list();- Sometimes, we have to call sql statement.
SQLQuery sqlQuery = session.createSQLQuery("SELECT * FROM t_user");
sqlQuery.addEntity(User.class);
List<User> userList = sqlQuery.list();- One to one
- One husband & one wife
- Many to Many
- One to Many
-
example: Categorizations & Prods;
-
Customer & Contact
以客户和联系人为例:
-
创建实体类
-
让两个实体类之间互相表示
-
客户实体类里面表示多个联系人;
-
在联系人里面表示所属客户;
- 配置映射关系
-
把映射基本配置完成
-
在映射文件中,配置一对多关系
- 在客户映射文件中,表示所有联系人
<!--
表示所有联系人, 使用set标签
使用set标签表示所有联系人
set标签里面有name属性:
属性值写在客户实体类里面表示联系人的set集合名称
-->
<set name="setLinkMans">
<!--
hibernate中,双向维护外健,在一和多的地方都需要配置外健。
key中column值就是外键名称。
-->
<key column="clid" />
<one-to-many class="com.liyiandxuegang.newentity.LinkMan"/>
</set>- 在联系人映射文件中,表示所属客户
<!--
表示联系人所属的关系
name: 因为在联系人实体类使用customer对象表示,写customer名称
class: customer全路径
column: 外键名称
-->
<many-to-one name="customer" class="com.liyiandxuegang.newentity.Customer" column="clid" />- Include to core hibernate settings
<mapping resource="com/liyiandxuegang/newentity/Customer.hbm.xml"/>
<mapping resource="com/liyiandxuegang/newentity/LinkMan.hbm.xml"/> Test it, and you will find there are two tables created in db.
- 级联保存:
添加一个客户,为这个客户添加多个联系人
实现:添加一个客户,为这个客户添加一个联系人
Solution 1:
// Add one customer and one link man
// 1. Create customer and linkman
Customer customer = new Customer();
customer.setCustName("SGI");
customer.setCustLevel("vip");
customer.setCustMobile("306-581-8888");
customer.setCustPhone("911");
customer.setCustSource("Internet");
LinkMan linkMan = new LinkMan();
linkMan.setLkm_name("Frank");
linkMan.setLkm_gender("Male");
linkMan.setLkm_phone("8384");
// 2. Create the connection between customer and linkman
// 2.1 Customer and linkman
customer.getSetLinkMans().add(linkMan);
// 2.2 Linkman and customer
linkMan.setCustomer(customer);
// 3. Save to db
session.save(customer);
session.save(linkMan);Solution 2
一般是根据客户添加联系人:
第一步: 在客户映射文件中进行配置
<!--Add cascade attribute to set tag-->
<set name="setLinkMans" cascade="save-update">第二步: 创建客户和联系人对象,只需要把联系人放到客户里面就可以了。
第三步:只需要保存客户就行了。
@Test
public void testAdd2() {
SessionFactory sessionFactory = null;
Session session = null;
Transaction transaction = null;
try {
sessionFactory = HibernateUtils.getSessionFactory();
session = sessionFactory.openSession();
transaction = session.beginTransaction();
// Add one customer and one link man
// 1. Create customer and linkman
Customer customer = new Customer();
customer.setCustName("SGI CANADA");
customer.setCustLevel("Normal");
customer.setCustMobile("306-581-8080");
customer.setCustPhone("911");
customer.setCustSource("Book");
LinkMan linkMan = new LinkMan();
linkMan.setLkm_name("Lee");
linkMan.setLkm_gender("FeMale");
linkMan.setLkm_phone("88888888");
// 2. Create the connection between customer and linkman
customer.getSetLinkMans().add(linkMan);
// 3. Save to db
session.save(customer);
transaction.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
transaction.rollback();
} finally {
session.close();
sessionFactory.close();
}
}- 级连删除
删除一个客户,把相对应的联系人也删除
需求:删除一个客户,并且把客户里面所有的联系人删除
第一步:在客户映射文件set标签中,进行配置
<set name="setLinkMans" cascade="save-update, delete"> 第二步:删除
// delete the customer
Customer customer = session.get(Customer.class, 3);
session.delete(customer);
/*
删除步骤:
1. 查询客户
2. 根据外键值,查询联系人
3. 设置联系人的外键值为null
4. 删除联系人
5. 删除客户
Hibernate:
select
customer0_.cid as cid1_0_0_,
customer0_.custName as custName2_0_0_,
customer0_.custLevel as custLeve3_0_0_,
customer0_.custSource as custSour4_0_0_,
customer0_.custPhone as custPhon5_0_0_,
customer0_.custMobile as custMobi6_0_0_
from
t_customer customer0_
where
customer0_.cid=?
Hibernate:
select
setlinkman0_.clid as clid5_1_0_,
setlinkman0_.lkm_id as lkm_id1_1_0_,
setlinkman0_.lkm_id as lkm_id1_1_1_,
setlinkman0_.lkm_name as lkm_name2_1_1_,
setlinkman0_.lkm_gender as lkm_gend3_1_1_,
setlinkman0_.lkm_phone as lkm_phon4_1_1_,
setlinkman0_.clid as clid5_1_1_
from
t_linkman setlinkman0_
where
setlinkman0_.clid=?
Hibernate:
update
t_linkman
set
clid=null
where
clid=?
Hibernate:
delete
from
t_linkman
where
lkm_id=?
Hibernate:
delete
from
t_customer
where
cid=?
*/- 一对多修改操作
@Test
public void testupdate() {
SessionFactory sessionFactory = null;
Session session = null;
Transaction transaction = null;
try {
sessionFactory = HibernateUtils.getSessionFactory();
session = sessionFactory.openSession();
transaction = session.beginTransaction();
// get linkman,
Customer customer = session.get(Customer.class, 1);
LinkMan linkMan = session.get(LinkMan.class, 2);
// Set persistence value
customer.getSetLinkMans().add(linkMan);
linkMan.setCustomer(customer);
transaction.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
transaction.rollback();
} finally {
session.close();
sessionFactory.close();
}
}因为hibernate双向维护外健,在客户和联系人里面都需要维护外键,修改客户时,修改一次外键,而修改联系人时,外键被修改了又一次。这样会造成资源浪费
解决:让客户这方放弃外健的维护。
<set name="setLinkMans" cascade="save-update, delete" inverse="true">
<!--
Only one time update.
Hibernate:
select
customer0_.cid as cid1_0_0_,
customer0_.custName as custName2_0_0_,
customer0_.custLevel as custLeve3_0_0_,
customer0_.custSource as custSour4_0_0_,
customer0_.custPhone as custPhon5_0_0_,
customer0_.custMobile as custMobi6_0_0_
from
t_customer customer0_
where
customer0_.cid=?
Hibernate:
select
linkman0_.lkm_id as lkm_id1_1_0_,
linkman0_.lkm_name as lkm_name2_1_0_,
linkman0_.lkm_gender as lkm_gend3_1_0_,
linkman0_.lkm_phone as lkm_phon4_1_0_,
linkman0_.clid as clid5_1_0_
from
t_linkman linkman0_
where
linkman0_.lkm_id=?
Hibernate:
select
setlinkman0_.clid as clid5_1_0_,
setlinkman0_.lkm_id as lkm_id1_1_0_,
setlinkman0_.lkm_id as lkm_id1_1_1_,
setlinkman0_.lkm_name as lkm_name2_1_1_,
setlinkman0_.lkm_gender as lkm_gend3_1_1_,
setlinkman0_.lkm_phone as lkm_phon4_1_1_,
setlinkman0_.clid as clid5_1_1_
from
t_linkman setlinkman0_
where
setlinkman0_.clid=?
Hibernate:
update
t_linkman
set
lkm_name=?,
lkm_gender=?,
lkm_phone=?,
clid=?
where
lkm_id=?
-->
- 多对多的配置
实例:用户和角色演示
第一步: 创建实体类,用户和角色
第二步:让两个实体类相互表示
- 一个用户里面有多个角色,使用set集合, User.hbm.xml
<hibernate-mapping>
<class name="com.liyiandxuegang.manytomany.User" table="t_user">
<id name="user_id" column="user_id">
<generator class="native"></generator>
</id>
<property name="user_name" column="user_name" />
<property name="user_password" column="user_password" />
<!--
在用户里面表示所有角色,使用set标签
name属性:角色set集合的名称
table属性:第三张表
-->
<set name="setRoles" table="t_userrole">
<!--
配置当前映射文件在第三张表中外键的名称
-->
<key column="userid" />
<!-- column表示角色在第三张表中外键的名称 -->
<many-to-many class="com.liyiandxuegang.manytomany.Role" column="roleid" />
</set>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>- 一个角色有多个用户,使用set集合, Role.hbm.xml
<hibernate-mapping>
<class name="com.liyiandxuegang.manytomany.Role" table="t_role">
<id name="role_id" column="role_id">
<generator class="native"></generator>
</id>
<property name="role_name" column="role_name" />
<property name="role_memo" column="role_memo" />
<set name="setUsers" table="t_userrole">
<key column="roleid" />
<many-to-many class="com.liyiandxuegang.manytomany.User" column="userid"/>
</set>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>第三步:配置映射关系
第四步:在核心配置文件中,引入映射文件
<mapping resource="com/liyiandxuegang/manytomany/User.hbm.xml"/>
<mapping resource="com/liyiandxuegang/manytomany/Role.hbm.xml"/>测试: how to create table t_userrole
/*
CREATE TABLE `t_userrole` (
`userid` int(11) NOT NULL,
`roleid` int(11) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`roleid`,`userid`),
KEY `FK726f9j5a1sy5ul99knaue6fvm` (`userid`),
CONSTRAINT `FK726f9j5a1sy5ul99knaue6fvm` FOREIGN KEY (`userid`) REFERENCES `t_user` (`user_id`),
CONSTRAINT `FK9a4q7igohl5jgv9b2afoh9sf3` FOREIGN KEY (`roleid`) REFERENCES `t_role` (`role_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
*/- 多对多的保存
-
在用户配置文件中set标签进行配置,casade值save update
-
创建用户和角色对象,把角色放到用户中,进行保存
public class HibernateManytoMany {
@Test
public void test() {
SessionFactory sessionFactory = null;
Session session = null;
Transaction transaction = null;
try {
sessionFactory = HibernateUtils.getSessionFactory();
session = sessionFactory.openSession();
transaction = session.beginTransaction();
// Add two users and add two roles to each user
User user1 = new User();
user1.setUser_name("Liyi&Tian");
user1.setUser_password("123456");
User user2 = new User();
user2.setUser_name("Frank");
user2.setUser_password("1111111");
Role role1 = new Role();
role1.setRole_name("Manager");
role1.setRole_memo("Manager makes more money.");
Role role2 = new Role();
role2.setRole_name("Director");
role2.setRole_memo("Director is the boss in the department.");
Role role3 = new Role();
role3.setRole_name("VP");
role3.setRole_memo("VP is big boss.");
// 2 Create connections
// user1 -- r1/r2
user1.getSetRoles().add(role1);
user1.getSetRoles().add(role2);
// user2 -- r2/r3
user2.getSetRoles().add(role2);
user2.getSetRoles().add(role3);
// 3. Save user
session.save(user1);
session.save(user2);
transaction.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
transaction.rollback();
} finally {
session.close();
sessionFactory.close();
}
}
}- 多对多删除
类似于一对多的操作,在set标签进行配置,添加cascade值delete,然后在程序中进行删除。(一般不用这么删除)
- 维护第三张表
用户和角色是多对多关系,维护关系通过第三张表维护。
- 赋给某个用户某个角色
// Add one role to one user
User user = session.get(User.class, 1);
Role role = session.get(Role.class, 3);
user.getSetRoles().add(role);- 删除某个用户某个角色
// Add one role to one user
User user = session.get(User.class, 2);
Role role = session.get(Role.class, 3);
// remove the role
user.getSetRoles().remove(role);- 根据id查询某个客户,再查询这个客户里面所有的数据
- 根据id查询某一条记录,返回对象
public class HibernateQuery {
@Test
public void test() {
SessionFactory sessionFactory = null;
Session session = null;
Transaction transaction = null;
try {
sessionFactory = HibernateUtils.getSessionFactory();
session = sessionFactory.openSession();
transaction = session.beginTransaction();
Customer customer = session.get(Customer.class, 1);
Set<LinkMan> linkMans = customer.getSetLinkMans();
System.out.println(linkMans.size());
transaction.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
} finally {
session.close();
sessionFactory.close();
}
}
}Hibernate Query Language: one sql statement from Hibernate.
HQL vs. SQL: 普通sql操作数据库表和字段,hql操作实体类和属性。
- Query对象,写hql语句实现查询
// query all customers: from Entity class name
Query query = session.createQuery("from Customer");
// get result
List<Customer> resultCustomers = query.list();
for(Customer customer : resultCustomers) {
System.out.println(customer.getCid() + ", " + customer.getCustName());
}- Conditional query: from Entity name where property name =? and ...
// query all customers: from Entity class name
Query query = session.createQuery("from Customer where cid=? and custName=?");
// set condition value: int: position; args: value
query.setParameter(0, 2);
query.setParameter(1, "SGI CANADA");- Query with order
SELECT * FROM t_customer ORDER BY cid DESC;
Query query = session.createQuery("from Customer order by cid desc");
List<Customer> customers = query.list();
/*
Hibernate:
select
customer0_.cid as cid1_0_,
customer0_.custName as custName2_0_,
customer0_.custLevel as custLeve3_0_,
customer0_.custSource as custSour4_0_,
customer0_.custPhone as custPhon5_0_,
customer0_.custMobile as custMobi6_0_
from
t_customer customer0_
order by
customer0_.cid desc
*/- Query with pagination
Query has two functions: setFirstResult(0) and setMaxResults(3);
Query query = session.createQuery("from Customer");
query.setFirstResult(0); // start
query.setMaxResults(1); // end- Query with Project (get part of the value, not all the value of the fields)
Query query = session.createQuery("select custName from Customer");
List<Object> customers = query.list();
for(Object customer : customers) {
System.out.println("Customer: " + customer);
}- Query with aggregation functions (count, sum, avg, max, min)
Query query = session.createQuery("select count(*) from Customer");
Object obj = query.uniqueResult(); // if only one result, you can use uniqueResult()
System.out.println("Total customer: " + obj.intValue());不需要写sQL或者HQL语句,使用方法实现;
- Query all result
Criteria criteria = session.createCriteria(Customer.class);
List<Customer> customers = criteria.list();- Query with conditions
Criteria criteria = session.createCriteria(Customer.class);
// add restrictions
criteria.add(Restrictions.eq("cid", 1));
criteria.add(Restrictions.eq("custName", "SGI"));
/*
SQL
Hibernate:
select
this_.cid as cid1_0_0_,
this_.custName as custName2_0_0_,
this_.custLevel as custLeve3_0_0_,
this_.custSource as custSour4_0_0_,
this_.custPhone as custPhon5_0_0_,
this_.custMobile as custMobi6_0_0_
from
t_customer this_
where
this_.cid=?
and this_.custName=?
*/like condition:
Criteria criteria = session.createCriteria(Customer.class);
criteria.add(Restrictions.like("custName", "%CANA%"));- QBC with Order
Criteria criteria = session.createCriteria(Customer.class);
criteria.addOrder(Order.desc("cid"));- QBC with pagination
Start position = (current page - 1) * perpageamt;
Criteria criteria = session.createCriteria(Customer.class);
criteria.setFirstResult(1);
criteria.setMaxResults(1);- QBC with Stats
Criteria criteria = session.createCriteria(Customer.class);
criteria.setProjection(Projections.rowCount());
Object count = criteria.uniqueResult();
System.out.println(((Long)count).intValue());(1) Projections class has batch of functions. (2) Conn't conver obj to int directly.
- QBC query offline
Offline query: 应用场景:
servlet调用service,service调用dao: dao里面对数据库操作,而使用hibernate框架时,调用session里面的方法,实现功能。
如果在逻辑层拼接条件时,可以使用这种方式来实现
// Create detachedCriteria class
DetachedCriteria detachedCriteria = DetachedCriteria.forClass(Customer.class);
// executable session
Criteria criteria = detachedCriteria.getExecutableCriteria(session);
List<Customer> list = criteria.list();
for(Customer customer : list) {
System.out.println("Customer: " + customer.getCid() + ", " + customer.getCustName());
}