Inputs can be taken in two ways in shell scripting 1. While executing (read command) 2. Before executing (special variables)
Special Variables: 0-9, *, @, # -> Inputs
$0 -> Script Name
$1 -> First argument
$2 -> Second Argument
..... $9
$10 -> Ideally it is not a right way, But still you can access it by bounding the variable while accessing
${10}
$*, $@ -> All arguments.
$# -> Number of arguments.
$$ -> PID of the script
? -> Exit Status.
Exit states ranges from 0-255
0 -> Successful
1-255 -> Failure / Partial Failure / Partial Successful
1-125 -> Command/ script exit states
126 -> Permission Denied
127 -> Command not found
128+n -> Kill Signals
Ex: 128+n=143 => n=143-128 => n=15
exit command can send custom exit status to shell
Syntax: exit 0-255
Ex: exit 2
exit 0
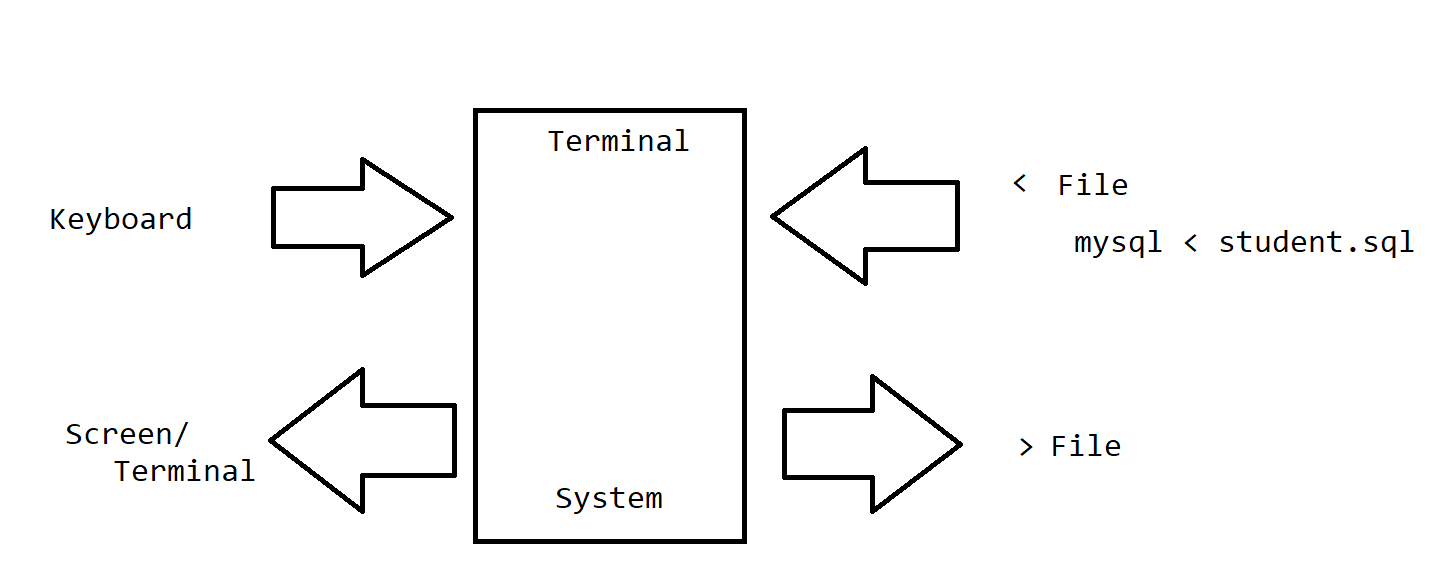
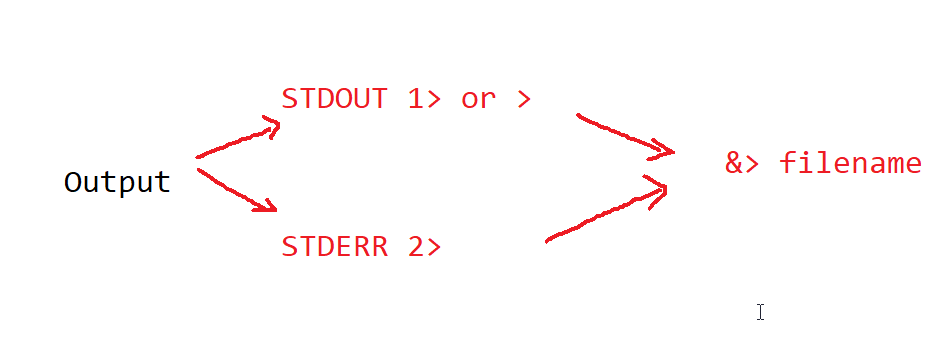
/dev/null is special property file which nullifies the output