I built a relatively simple implementation of a Dynamic k-NN using TensorFlow with GPU support.
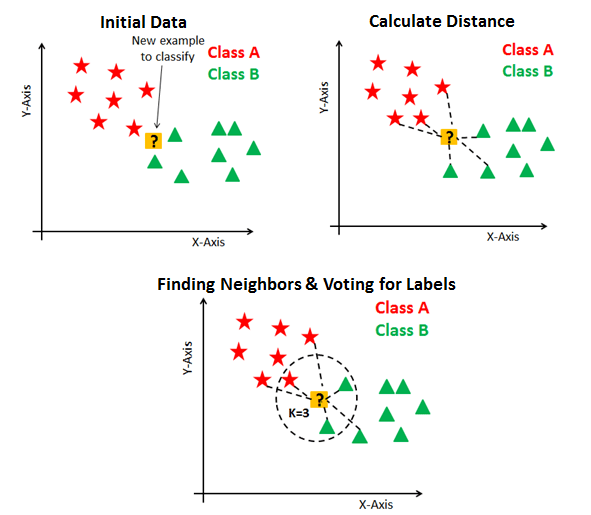 from datacamp
from datacamp
In k-NN classification, the output is a class membership. An object is classified by a majority vote of its neighbors, >with the object being assigned to the class most common among its k nearest neighbors (k is a positive integer, >typically small). If k = 1, then the object is simply assigned to the class of that single nearest neighbor.
from wikipedia
A dynamic k-NN allows for some parameters (such as the k parameter) to be defined on a per instance basis, instead of being fixed in the model. This can be useful in cases where the k is influenceed by some independent variable or whenever you need to add new training instances without requiring a fit step to your model.
Note: running TensorFlow on GPU is formally supported for only NVIDIA cards (CUDA backend).
For more detailed information abuot the benchmark check out the notebook with the experimental information.
These were done on a laptop with a GTX 870m, the results could've been even better with a faster GPU.
| TF GPU speedup over TF CPU: |
|---|
| 1.4x |
On large datasets, the GPU gains are more noticeable, however, even on a laptop, with a low powered GPU, the GPU performance gain can be around 40%.
| TF GPU speedup over Scikit CPU (dynamic k): |
|---|
| 50x |
As seen above, the results are quite favorable towards the k-NN implementation using TensorFlow with GPU support.
In the scenario where the k is static or when no new training instances are introduced this implementation of k-NN using TensorFlow with GPU support can be around 20% slower than the Scikit implementation (assuming you are using their efficient implementation with Ball Tree). However, this is also the worst scenario for this model and with a better GPU this difference might decrease.
In any case, it's impressive that we can obtain such results for such a simple implementation!
- TensorFlow >= 1.11
Run example with command:
python example.py
-
Adaptive k-Nearest-Neighbor Classification Using a Dynamic Number of Nearest Neighbors
-
Dynamic K-Nearest-Neighbor with Distance and attribute weighted for classification
Code is licensed under the Apache License 2.0