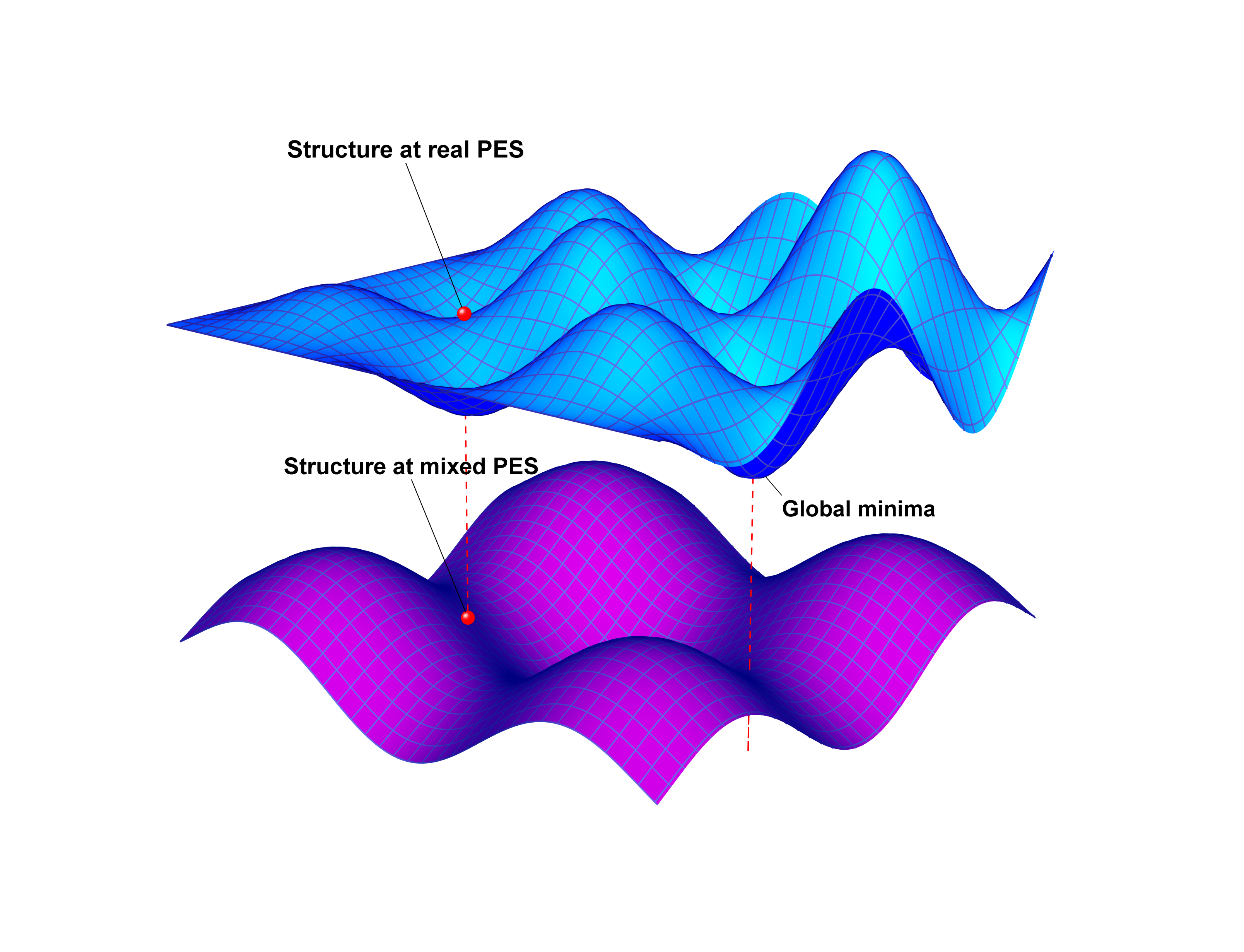
Reformpy is a high-performance Python package for structure optimization using atomic fingerprints. Version 2.0.0 includes critical bug fixes for entropy maximization:
- Reform_Calculator: Original fingerprint-based calculator for symmetry-driven optimization
- EntropyMaximizingCalculator: New wrapper that adds entropy maximization to ANY ASE calculator
- 🆕 EntropyMaximizingCalculator: Universal wrapper to add entropy to any calculator
- 🆕 Modular Architecture: Clean separation between fingerprint and entropy calculations
- 🆕 Optimized Entropy Functions: JIT-compiled with Numba for performance
- 🆕 Combine Any Calculators: Wrap DFT, ML potentials, or even Reform_Calculator itself
- Python >= 3.8.5
- C compiler (gcc/icc)
- LAPACK/BLAS libraries (MKL recommended)
# Create conda environment
conda create -n reformpy python=3.8 pip
conda activate reformpy
# Install dependencies
conda install -c conda-forge lapack
pip install numpy>=1.24.4 scipy>=1.10.1 numba>=0.58.1 ase>=3.22.1 mpi4py>=3.1.6
# Install libfp (fingerprint library)
git clone https://github.com/Rutgers-ZRG/libfp.git
cd libfp
pip install --no-cache-dir -e .
cd ..
# Install Reformpy
git clone https://github.com/Rutgers-ZRG/ReformPy.git
cd ReformPy
pip install --no-cache-dir -e .import libfp
from reformpy import Reform_Calculator, EntropyMaximizingCalculator
print("Installation successful!")from reformpy import Reform_Calculator
from ase.build import bulk
from ase.optimize import BFGS
# Create structure
atoms = bulk('Cu', 'fcc', a=3.6, cubic=True)
# Initialize Reform_Calculator (optimizes for symmetry)
calc = Reform_Calculator(
atoms=atoms,
ntyp=1, # Number of atom types
nx=300, # Max neighbors
cutoff=6.0, # Cutoff radius in Angstroms
znucl=[29], # Atomic numbers (Cu)
)
atoms.calc = calc
# Optimize structure toward high symmetry
opt = BFGS(atoms)
opt.run(fmax=0.01)
print(f"Energy: {atoms.get_potential_energy():.4f} eV")from reformpy import EntropyMaximizingCalculator, Reform_Calculator
# Option 1: Add entropy to Reform_Calculator
base_calc = Reform_Calculator(atoms=atoms, ntyp=1, nx=300, cutoff=6.0, znucl=[29])
calc = EntropyMaximizingCalculator(
calculator=base_calc,
k_factor=5.0, # Entropy weight
cutoff=6.0 # Fingerprint cutoff for entropy
)
# Option 2: Add entropy to any other calculator (e.g., DFT)
from ase.calculators.vasp import Vasp
vasp_calc = Vasp(...)
calc = EntropyMaximizingCalculator(calculator=vasp_calc, k_factor=2.0, cutoff=4.0)
atoms.calc = calc
# This will generate diverse atomic environments
opt = BFGS(atoms)
opt.run(fmax=0.01)
# Access entropy information
print(f"Total energy: {atoms.get_potential_energy():.4f} eV")
print(f"Base energy: {calc.get_base_energy(atoms):.4f} eV")
print(f"Entropy: {calc.get_entropy(atoms):.4f}")from reformpy import EntropyMaximizingCalculator
from ase.calculators.emt import EMT # Or any ASE calculator
# Add entropy maximization to any calculator
calc = EntropyMaximizingCalculator(
calculator=EMT(), # Base calculator
k_factor=1.0, # Entropy weight
cutoff=5.0 # Fingerprint cutoff
)
atoms.calc = calc
energy = atoms.get_potential_energy()The modular design of Reformpy v2.0.0 allows maximum flexibility:
┌─────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Any ASE Calculator (VASP, QE, │
│ EMT, GAP, NequIP, Reform_Calc...) │
└──────────────┬──────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────────────┐
│ EntropyMaximizingCalculator Wrapper│
│ • Adds entropy bonus S │
│ • Modifies forces by -k∇S │
│ • Preserves base calculator props │
└─────────────────────────────────────┘
This clean separation means:
- No modifications needed to existing calculators
- Can combine multiple optimization strategies
- Easy to enable/disable entropy on the fly
- Works with ANY ASE-compatible calculator
from mpi4py import MPI
calc = Reform_Calculator(
atoms=atoms,
comm=MPI.COMM_WORLD, # MPI communicator
parallel=True, # Enable parallel mode
**parameters
)from reformpy.mixing import MixedCalculator
from ase.calculators.emt import EMT
# Combine Reformpy with other calculators
calc = MixedCalculator(
calc_list=[
Reform_Calculator(mode='entropy', **params),
EMT()
],
weights=[0.7, 0.3] # Weight factors
)# Start with high entropy for exploration
calc.k_entropy = 10.0
opt.run(steps=50)
# Reduce for refinement
calc.k_entropy = 2.0
opt.run(steps=50)| Parameter | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
cutoff |
float | 4.0 | Cutoff radius in Angstroms |
ntyp |
int | 1 | Number of atom types |
nx |
int | 300 | Maximum number of neighbors |
znucl |
list | None | List of atomic numbers |
stress_mode |
str | 'finite' | Stress calculation: 'finite' or 'analytical' |
contract |
bool | False | Use contracted Gaussian-type orbitals |
lmax |
int | 0 | 0 for s orbitals only, else s and p orbitals |
| Parameter | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
calculator |
ASE Calculator | Required | Base calculator to wrap |
k_factor |
float | 1.0 | Entropy scaling factor |
cutoff |
float | 4.0 | Fingerprint cutoff radius |
natx |
int | None | Max neighbors (None = 4×natoms) |
from ase.constraints import StrainFilter
from ase.optimize import FIRE
# Apply strain filter for cell optimization
sf = StrainFilter(atoms)
atoms.calc = Reform_Calculator(mode='symmetry', **params)
opt = FIRE(sf, maxstep=0.1)
opt.run(fmax=0.001)from ase.md import VelocityVerlet
from ase import units
# MD with entropy maximization
base_calc = Reform_Calculator(**params)
calc = EntropyMaximizingCalculator(calculator=base_calc, k_factor=5.0, cutoff=4.0)
atoms.calc = calc
dyn = VelocityVerlet(atoms, timestep=1.0*units.fs)
# Collect diverse configurations
configurations = []
for i in range(100):
dyn.run(10)
if i % 10 == 0:
configurations.append(atoms.copy())# Compare Reform_Calculator (symmetry) vs with entropy
atoms_sym = atoms.copy()
calc_sym = Reform_Calculator(**params)
atoms_sym.calc = calc_sym
atoms_ent = atoms.copy()
base_calc = Reform_Calculator(**params)
calc_ent = EntropyMaximizingCalculator(calculator=base_calc, k_factor=5.0, cutoff=4.0)
atoms_ent.calc = calc_ent
# Optimize both
BFGS(atoms_sym).run(fmax=0.01)
BFGS(atoms_ent).run(fmax=0.01)
print(f"Symmetry optimization energy: {atoms_sym.get_potential_energy():.4f}")
print(f"Entropy optimization energy: {atoms_ent.get_potential_energy():.4f}")
print(f"Entropy value: {calc_ent.get_entropy(atoms_ent):.4f}")- JIT Compilation: Critical loops compiled with Numba
- MPI Support: Parallel execution across multiple nodes
- Smart Caching: Fingerprints cached between calculations
- Vectorized Operations: NumPy-optimized array operations
| System Size | Symmetry Mode | Entropy Mode | Speedup with MPI (8 cores) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 32 atoms | 0.05s | 0.06s | 4.2× |
| 128 atoms | 0.24s | 0.28s | 5.8× |
| 512 atoms | 1.85s | 2.10s | 6.9× |
Minimizes fingerprint distances between atoms for symmetry optimization:
E = Σᵢⱼ ||fpᵢ - fpⱼ||²
Adds entropy regularization to ANY base calculator:
S = (1/N) Σᵢ log(N × δqₘᵢₙ,ᵢ)
E_total = E_base - k × S
F_total = F_base - k × ∇S
Where:
- δqₘᵢₙ,ᵢ is the minimum fingerprint distance for atom i
- E_base and F_base come from the wrapped calculator (DFT, ML, Reform_Calculator, etc.)
- k is the entropy weight factor
MPI Error: Reinstall mpi4py with system MPI
pip uninstall mpi4py
pip install --no-cache-dir mpi4pyImport Error: Check DYLD_LIBRARY_PATH
export DYLD_LIBRARY_PATH="$CONDA_PREFIX/lib:$DYLD_LIBRARY_PATH"Numerical Instabilities: Adjust entropy threshold
calc = Reform_Calculator(entropy_threshold=1e-6, ...)We welcome contributions! Please see CONTRIBUTING.md for guidelines.
git clone https://github.com/Rutgers-ZRG/ReformPy.git
cd ReformPy
pip install -e .[dev]
pytest tests/If you use Reformpy in your research, please cite:
@article{taoAcceleratingStructuralOptimization2024,
title = {Accelerating Structural Optimization through Fingerprinting Space Integration on the Potential Energy Surface},
author = {Tao, Shuo and Shao, Xuecheng and Zhu, Li},
year = {2024},
journal = {J. Phys. Chem. Lett.},
volume = {15},
number = {11},
pages = {3185--3190},
doi = {10.1021/acs.jpclett.4c00275}
}
@article{zhuFingerprintBasedMetric2016,
title = {A Fingerprint Based Metric for Measuring Similarities of Crystalline Structures},
author = {Zhu, Li and Amsler, Maximilian and others},
year = {2016},
journal = {The Journal of Chemical Physics},
volume = {144},
number = {3},
pages = {034203},
doi = {10.1063/1.4940026}
}Reformpy is released under the Academic Software Licence ("ASL"). See LICENSE.md for details.
Important: ASL is an academic non-commercial license. For commercial use, please contact the rights holders.
Copyright © 2024 Rutgers-ZRG. All rights reserved.