Integration testing is a type of software testing in which we test the application as a whole, rather than mocking the application to it's routes as we do in unit testing.
We will use the Python package selenium to simulate a user interacting with our application directly, and test the results are as expected.
We can use the LiveServerTestCase class to create a live instance of our application for our integration tests to use, so we don't need the application to be running for the tests to work.
from flask_testing import LiveServerTestCaseWe must create a subclass of this, and define the following methods:
create_app: run once, at the very start of testing - here, we overwrite the app's configsetUp: run before every test case - here, we setup the driver and create our test databasetearDown: run after every test case - here, we quit the driver and drop the test database
Example
from selenium import webdriver
from flask_testing import LiveServerTestCase
from application import app, db
class TestBase(LiveServerTestCase):
def create_app(self):
app.config['SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI'] = "sqlite:///test.db" # change to a test sqlite database
return app
def setUp(self):
chrome_options = webdriver.chrome.options.Options()
chrome_options.add_argument('--headless') # must be headless
self.driver = webdriver.Chrome(options=chrome_options)
db.create_all() # create schema before we try to get the page
self.driver.get(f'http://localhost:5000/')
def tearDown(self):
self.driver.quit()
db.drop_all()Note: in order to use Selenium, we must have a browser and driver installed. See the tutorial for installation steps.
Once we have created a TestBase class, which inherits from the LiveServerTestCase class, we can define some test cases.
Each test case must be defined within a class which inherits from TestBase.
It should now look something like this:
class TestBase(LiveServerTestCase):
def create_app(self):
...
return app
def setUp(self):
...
def tearDown(self):
...
class TestExample(TestBase):
def test_case_1(self):
...XPaths are essentially a way to find any element, such as an input field or button, on any HTML or XML document.
Selenium can use an XPath to find the element we want, and we can then manipulate this element in our testing.
Finding the XPath of an element in Chrome
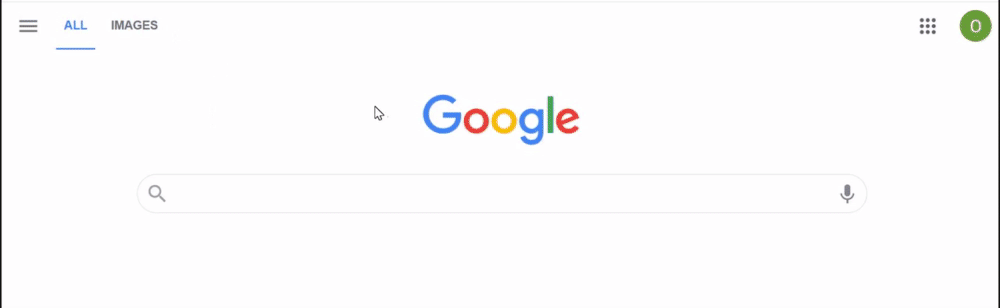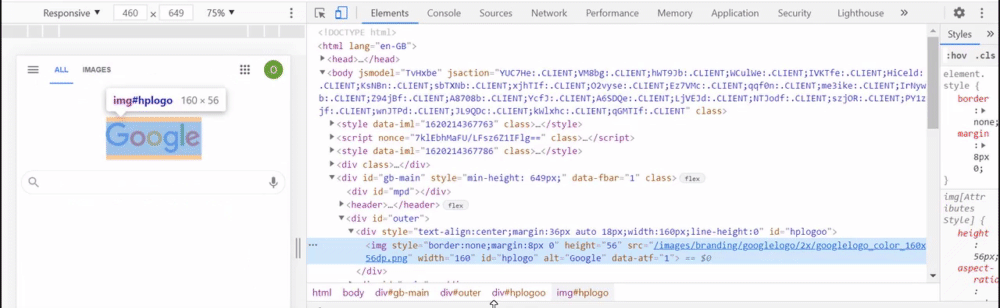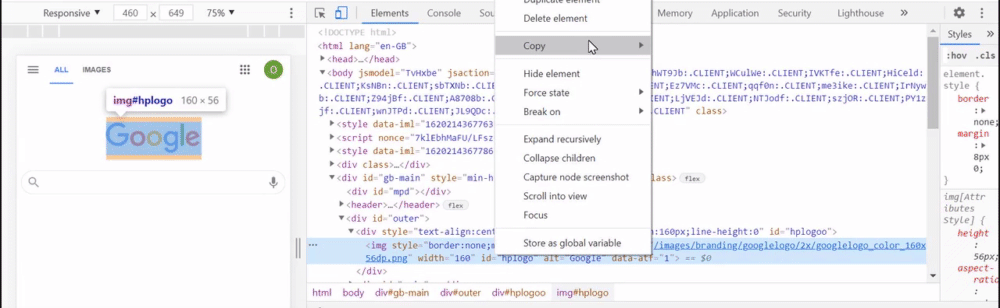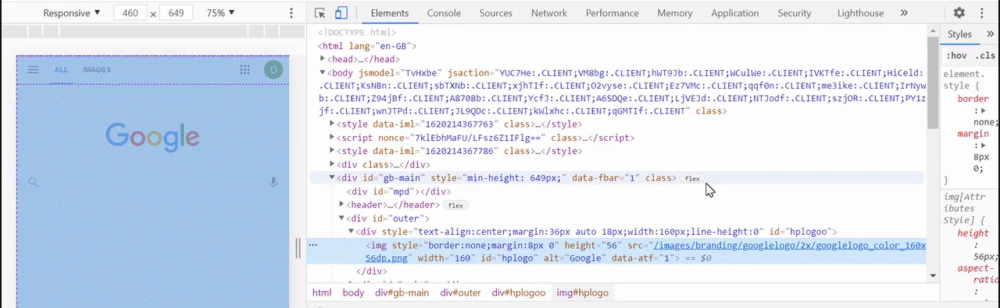
Once your application is running, navigate to the page the element belongs to and complete the following steps:
- Right click on the element, and click
Inspect. The HTML for the element should pop up. - Right click on the HTML for the element in the inspect tab, it should be highlighted.
- Choose
Copy, and thenCopy XPath.
We can use the selenium driver to find elements on a page, and do things with these elements.
We use the following syntax to find an element on the page:
element = self.driver.find_element_by_xpath('<XPath>')We can then use any of the following methods on this element:
element.click()
element.send_keys('<any string>') # simulates typing
element.clear()We can also inspect the text inside the element using
element.textExample
Let's assume our application has an input box on the /create route. When this box is submitted, the user is directed to /index.
from selenium import webdriver
from flask_testing import LiveServerTestCase
from application import app, db
class TestBase(LiveServerTestCase):
...
class TestCreate(TestBase):
def test_create(self):
self.driver.get(f'http://localhost:5000/create') # go to /create route
input_box = self.driver.find_element_by_xpath('//*[@id="name"]')
input_box.send_keys('Hello World')
self.driver.find_element_by_xpath('//*[@id="submit"]').click() # submit field
assert self.driver.current_url == 'http://localhost:5000/index'Note: LiveServerTestCase has built in methods for assertEqual, assertIn, etc. that we may choose to use instead of assert.
An Ubuntu 18.04 VM with Python installed and port 5000 open.
Note: This is unlikely to work on Ubuntu 20.04.
Run the following commands to install chromium-browser and chromedriver:
Installing the browser
sudo apt install chromium-browser -yInstalling the driver (must have the browser installed for this to work!)
sudo apt install wget unzip -y
version=$(curl -s https://chromedriver.storage.googleapis.com/LATEST_RELEASE_$(chromium-browser --version | grep -oP 'Chromium \K\d+'))
wget https://chromedriver.storage.googleapis.com/${version}/chromedriver_linux64.zip
sudo unzip chromedriver_linux64.zip -d /usr/bin
rm chromedriver_linux64.zipClone down this repository and change directory into it:
git clone https://github.com/QACTrainers/selenium-example.git
cd selenium_exampleInstall all pip dependencies in a virtual environment:
sudo apt install python3-pip python3-venv -y
python3 -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate
pip3 install -r requirements.txtLet's see what the application is doing.
Use
python3 create.py
python3 app.pyYou should be able to see that we can submit entries that will show in the History section of the index page.
Submitting an empty entry will give us an error, saying "The name field can't be empty!"
Let's get the XPath of where the error message should be.
On your app, submit an empty name using the 🗸. An error message should pop up as expected.
Follow the tutorial here to get the XPath of this error message.
Let's create a test case to check the validation of our form, so that we know the user can't submit an empty input.
In tests/test_int.py, line 62, configure test_empty_validation as follows:
def test_empty_validation(self):
self.submit_input('')
self.assertIn(url_for('index'), self.driver.current_url)
text = self.driver.find_element_by_xpath('<XPath>').text
self.assertIn("The name field can't be empty!", text)
entries = Games.query.all()
self.assertEqual(len(entries), 0) # database should be emptyMake sure to replace '<XPATH>' with the XPath we found in the previous step!
We are checking 3 things here:
- We are redirected back to the index page correctly,
- The error message is displayed properly,
- The database is still empty, so the empty entry was ignored as expected.
Run the tests using
python3 -m pytestWrite a test case for test_length_validation. If the submitted input has a length greater than 30, the error "This name is too long!" should be displayed, and the input should not be added to the database.
Use the test_empty_validation method for reference.