I implement a VAE, where the encoder is an LSTM network and the decoder is a convolutional network. I used MNIST dataset. MNIST is an image dataset, however you can treat each image as a sequence of rows. For instance, MNIST dataset has 28 × 28 images, which can be treated as a 28 dimensional multivariate sequence of length 28.
- install version of tensorflow==1.14.0 (strict requirement)
- execute "python main.py" to train model and generate 100 images from decoder after training. takes 3 min to train the model and generate images.
- new_images.png is generated at the end of execution.
- new_model.ckpt.meta is generated at the end of execution.
- Implementing a single layer LSTM as the encoder of the VAE
- See encoder() in Network class of model.py. Dense layers are used to calculate mu and sigma of latent space after LSTM layer. encoder() maps an input image to a proposed distribution over LSTM and Dense layers for that image. This distribution is called posterior in the network.
- Implementing a convolutional decoder with transpose convolutional layers
- This decoder takes a random vector sampled from the distribution that was outputted by the encoder and decodes it to an 28 × 28 grayscale image. Since I go to an image from a random vector, I needed transpose convolution.
- See decoder() in Network class of model.py. Dense layers are used before transpose convolutional layers. The decoder basically takes a posterior sample and maps it back to a distribution of images that are plausible for the sample. It allows us to generate new images for any posterior sample we choose. I use a Bernoulli distribution. It can be modeled in a different way, for example as a Normal distribution.
- Implementing the reconstruction loss with binary cross-entropy and the regularization term with KL-divergence
- See optimization() in Network class of model.py. I train the model using the evidence lower bound (ELBO) which is an approximation to the data likelihood. The important point is that ELBO only uses the likelihood of a data point given our current estimate of its posterior, which we can sample. I just maximize the ELBO using gradient descent (important note: I printed out the negative of ELBO for loss track). Sampling from posterior are implemented using the reparameterization internally so that TensorFlow can backpropagate through them.
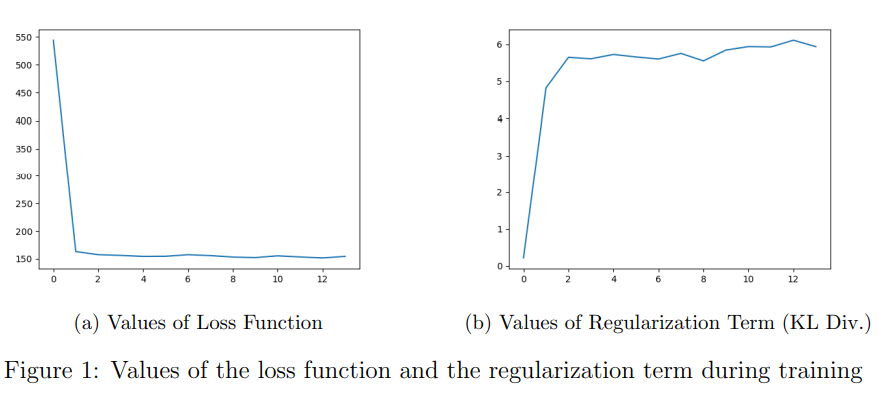
The value of loss function decreases at first epoches, then there was no much improvement in decreasing loss value. On the other hand, the value of regularization term (that makes the latent space regular) increased at first epoches then stayed still. We come up with regularization term since two close points in the latent space should not give two completely different contents once decoded and for a chosen distribution, a point sampled from the latent space should give meaningful content once decoded. In order to do that regularisation is done by enforcing distributions to be close to a standard normal distribution. See Figure 1. Through training (especially at first epoches), model is forced to regularize latent space more.