A high-performance asynchronous request library based on Rust and Python, suitable for scenarios that require high-throughput concurrent HTTP requests. It implements the core concurrent logic in Rust and packages it into a Python module using PyO3 and maturin, combining Rust's performance with Python's ease of use.
- Dual Request Modes: Supports both batch concurrent requests (
fetch_requests) and single asynchronous requests (fetch_single). - High Performance: Built with Rust, Tokio, and a shared
reqwestclient for maximum throughput. - Highly Customizable: Allows custom headers, parameters/body, per-request timeouts, and tags.
- Flexible Concurrency Modes: Choose between
SELECT_ALL(default, get results as they complete) andJOIN_ALL(wait for all requests to finish) to fit your use case. - Smart Response Handling: Automatically decompresses
gzip,brotli, anddeflateencoded responses. - Global Timeout Control: Use
total_timeoutin batch requests to prevent hangs. - Detailed Results: Each response includes the HTTP status, body, metadata (like processing time), and any exceptions.
- Debug Mode: An optional debug mode (
set_debug(True)) prints detailed request/response information.
pip install rusty-reqOr build from source:
# This will compile the Rust code and create a .whl file
maturin build --release
# Install from the generated wheel
pip install target/wheels/rusty_req-*.whl
cargo watch -s "maturin develop"
If you need to access external networks through a proxy, create a ProxyConfig object and set it as a global proxy:
import asyncio
import rusty_req
async def proxy_example():
# Create ProxyConfig object
proxy = rusty_req.ProxyConfig(
http="http://127.0.0.1:7890",
https="http://127.0.0.1:7890"
)
# Set global proxy (all requests will use this proxy)
await rusty_req.set_global_proxy(proxy)
# Send request (will go through proxy automatically)
resp = await rusty_req.fetch_single(url="https://httpbin.org/get")
print(resp)
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(proxy_example())set_debug enables debug mode, supporting console output and log file writing:
import rusty_req
# Print debug logs to console only
rusty_req.set_debug(True)
# Print to console and write to log file
rusty_req.set_debug(True, "logs/debug.log")
# Disable debug mode
rusty_req.set_debug(False)Perfect for making a single asynchronous call and awaiting its result.
import asyncio
import pprint
import rusty_req
async def single_request_example():
"""Demonstrates how to use fetch_single for a POST request."""
print("🚀 Fetching a single POST request to httpbin.org...")
# Enable debug mode to see detailed logs in the console
rusty_req.set_debug(True)
response = await rusty_req.fetch_single(
url="https://httpbin.org/post",
method="POST",
params={"user_id": 123, "source": "example"},
headers={"X-Client-Version": "1.0"},
tag="my-single-post"
)
print("\n✅ Request finished. Response:")
pprint.pprint(response)
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(single_request_example())The core feature for handling a large number of requests concurrently. This example simulates a simple load test.
import asyncio
import time
import rusty_req
from rusty_req import ConcurrencyMode
async def batch_requests_example():
"""Demonstrates 100 concurrent requests with a global timeout."""
requests = [
rusty_req.RequestItem(
url="https://httpbin.org/delay/2", # This endpoint waits 2 seconds
method="GET",
timeout=2.9, # Per-request timeout, should succeed
tag=f"test-req-{i}",
)
for i in range(100)
]
# Disable debug logs for cleaner output
rusty_req.set_debug(False)
print("🚀 Starting 100 concurrent requests...")
start_time = time.perf_counter()
# Set a global timeout of 3.0 seconds. Some requests will be cut off.
responses = await rusty_req.fetch_requests(
requests,
total_timeout=3.0,
mode=ConcurrencyMode.SELECT_ALL # Explicitly use SELECT_ALL mode
)
total_time = time.perf_counter() - start_time
# --- Process results ---
success_count = 0
failed_count = 0
for r in responses:
# Check the 'exception' field to see if the request was successful
if r.get("exception") and r["exception"].get("type"):
failed_count += 1
else:
success_count += 1
print("\n📊 Load Test Summary:")
print(f"⏱️ Total time taken: {total_time:.2f}s")
print(f"✅ Successful requests: {success_count}")
print(f"⚠️ Failed or timed-out requests: {failed_count}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(batch_requests_example())The fetch_requests function supports two powerful concurrency strategies. Choosing the right one is key to building robust applications.
-
ConcurrencyMode.SELECT_ALL(Default): Best-Effort Collector This mode operates on a "first come, first served" or "best-effort" basis. It aims to collect as many successful results as possible within the giventotal_timeout.- It returns results as soon as they complete.
- If the
total_timeoutis reached, it gracefully returns all the requests that have already succeeded, while marking any still-pending requests as timed out. - A failure in one request does not affect others.
-
ConcurrencyMode.JOIN_ALL: Transactional (All-or-Nothing) This mode treats the entire batch of requests as a single, atomic transaction. It is much stricter.- It waits for all submitted requests to complete first.
- It then inspects the results.
- Success Case: Only if every single request was successful will it return the complete list of successful results.
- Failure Case: If even one request fails for any reason (e.g., its individual timeout, a network error, or a non-2xx status code), this mode will discard all results and return a list where every request is marked as a global failure.
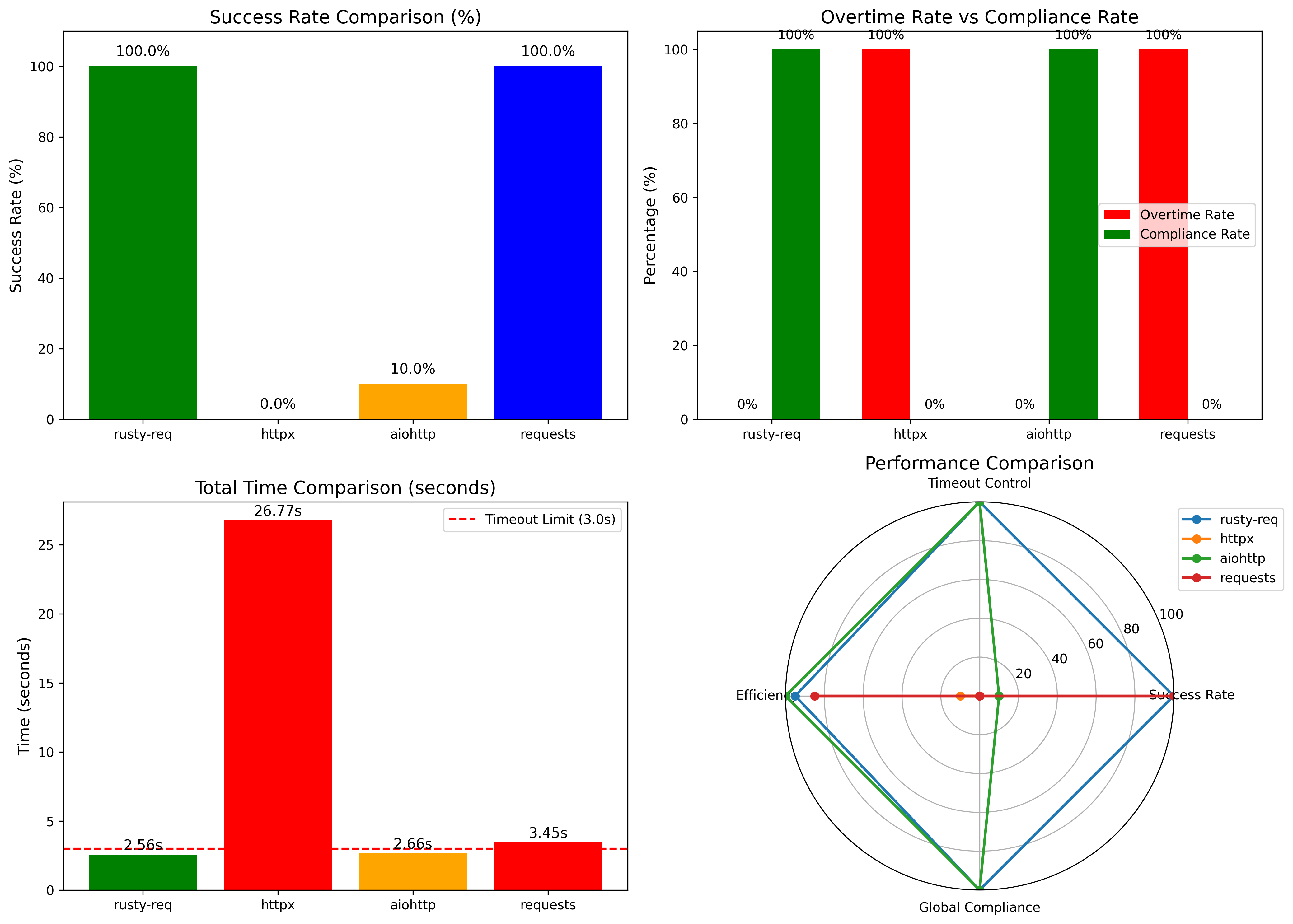
Under the same test conditions (global timeout 3s, per-request timeout 2.6s, httpbin delay 2.3s), we compared the performance of different libraries:
| Library / Framework | Total Requests | Successful | Timed Out | Success Rate | Actual Total Time | Notes / Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rusty-req | 1000 | 1000 | 0 | 100.0% | 2.56s | Stable performance under high concurrency; precise control of per-request and total timeouts |
| httpx | 1000 | 0 | 0 | 0.0% | 26.77s | Timeout parameters did not take effect; overall performance abnormal |
| aiohttp | 1000 | 100 | 900 | 10.0% | 2.66s | Per-request timeout effective, but global timeout control insufficient |
| requests | 1000 | 1000 | 0 | 100.0% | 3.45s | Synchronous blocking mode; not suitable for large-scale concurrent requests |
Key takeaways:
- Rusty-req can complete tasks within strict global timeout limits while maintaining high concurrency and stability.
- Traditional asynchronous libraries struggle with global timeout enforcement and extreme concurrency scenarios.
- Synchronous libraries like
requestsproduce correct results but are not scalable for large-scale concurrent requests.
| Aspect | ConcurrencyMode.SELECT_ALL (Default) |
ConcurrencyMode.JOIN_ALL |
|---|---|---|
| Failure Handling | Tolerant. One failure does not affect other successful requests. | Strict / Atomic. One failure causes the entire batch to fail. |
| Primary Use Case | Maximizing throughput; getting as much data as possible. | Tasks that must succeed or fail as a single unit (e.g., transactions). |
| Result Order | By completion time (fastest first). | By original submission order. |
| "When do I get results?" | As they complete, one by one. | All at once, only after every request has finished and been validated. |
The example below clearly demonstrates the difference in behavior.
import asyncio
import rusty_req
from rusty_req import ConcurrencyMode
async def concurrency_modes_example():
"""Demonstrates the difference between SELECT_ALL and JOIN_ALL modes."""
# Note: We are using an endpoint that returns 500 to force a failure.
requests = [
rusty_req.RequestItem(url="https://httpbin.org/delay/2", tag="should_succeed"),
rusty_req.RequestItem(url="https://httpbin.org/status/500", tag="will_fail"),
rusty_req.RequestItem(url="https://httpbin.org/delay/1", tag="should_also_succeed"),
]
# --- 1. Test SELECT_ALL ---
print("--- 🚀 Testing SELECT_ALL (Best-Effort) ---")
results_select = await rusty_req.fetch_requests(
requests,
mode=ConcurrencyMode.SELECT_ALL,
total_timeout=3.0
)
print("Results:")
for res in results_select:
tag = res.get("meta", {}).get("tag")
status = res.get("http_status")
err_type = res.get("exception", {}).get("type")
print(f" - Tag: {tag}, Status: {status}, Exception: {err_type}")
print("\n" + "="*50 + "\n")
# --- 2. Test JOIN_ALL ---
print("--- 🚀 Testing JOIN_ALL (All-or-Nothing) ---")
results_join = await rusty_req.fetch_requests(
requests,
mode=ConcurrencyMode.JOIN_ALL,
total_timeout=3.0
)
print("Results:")
for res in results_join:
tag = res.get("meta", {}).get("tag")
status = res.get("http_status")
err_type = res.get("exception", {}).get("type")
print(f" - Tag: {tag}, Status: {status}, Exception: {err_type}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(concurrency_modes_example())The expected output from the script above:
--- 🚀 Testing SELECT_ALL (Best-Effort) ---
Results:
- Tag: should_also_succeed, Status: 200, Exception: None
- Tag: will_fail, Status: 500, Exception: HttpStatusError
- Tag: should_succeed, Status: 200, Exception: None
==================================================
--- 🚀 Testing JOIN_ALL (All-or-Nothing) ---
Results:
- Tag: should_succeed, Status: 0, Exception: GlobalTimeout
- Tag: will_fail, Status: 0, Exception: GlobalTimeout
- Tag: should_also_succeed, Status: 0, Exception: GlobalTimeout
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
url |
str |
✅ | The target URL. |
method |
str |
✅ | The HTTP method. |
params |
dict / None |
No | For GET/DELETE, converted to URL query parameters. For POST/PUT/PATCH, sent as a JSON body. |
headers |
dict / None |
No | Custom HTTP headers. |
tag |
str |
No | An arbitrary tag to help identify or index the response. |
http_version |
str |
No | The default behavior when the HTTP version is set to “Auto” is to attempt HTTP/2 first, and fall back to HTTP/1.1 if HTTP/2 is not supported. |
ssl_verify |
bool |
No | SSL certificate verification (default True, set False to disable for self-signed certificates) |
timeout |
float |
✅ | Timeout for this individual request in seconds. Defaults to 30s. |
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
http |
str / None |
No | Proxy URL for HTTP requests (e.g. http://127.0.0.1:8080). |
https |
str / None |
No | Proxy URL for HTTPS requests. |
all |
str / None |
No | A single proxy URL applied to all schemes (overrides http/https). |
no_proxy |
List[str] / None |
No | List of hostnames/IPs to exclude from proxying. |
username |
str / None |
No | Optional proxy authentication username. |
password |
str / None |
No | Optional proxy authentication password. |
trust_env |
bool / None |
No | Whether to respect system environment variables (HTTP_PROXY, NO_PROXY). |
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
requests |
List[RequestItem] |
✅ | A list of RequestItem objects to be executed concurrently. |
total_timeout |
float |
No | A global timeout in seconds for the entire batch operation. |
mode |
ConcurrencyMode |
No | The concurrency strategy. SELECT_ALL (default) for best-effort collection. JOIN_ALL for atomic (all-or-nothing) execution. See Section 3 for a detailed comparison. |
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
url |
str |
✅ | The target request URL. |
method |
str / None |
No | HTTP method, e.g., "GET", "POST". If not provided, the client may handle defaults. |
params |
dict / None |
No | Request parameters. For GET/DELETE, converted to URL query parameters; for POST/PUT/PATCH, sent as JSON body. |
timeout |
float / None |
No | Timeout for this request in seconds. Defaults to 30s. |
headers |
dict / None |
No | Custom HTTP request headers. |
tag |
str / None |
No | Arbitrary tag to help identify or index the response. |
proxy |
ProxyConfig / None |
No | Optional proxy configuration. Applied to this request if provided. |
http_version |
HttpVersion / None |
No | HTTP version choice, usually supports "Auto" (try HTTP/2, fallback to HTTP/1.1), "1.1", "2", etc. |
ssl_verify |
bool / None |
No | Whether to verify SSL certificates. Defaults to True; set False to ignore self-signed certificates. |
Both fetch_single and fetch_requests return a dictionary (or a list of dictionaries) with a consistent structure.
{
"http_status": 200,
"response": {
"headers": {
"access-control-allow-credentials": "true",
"access-control-allow-origin": "*",
"connection": "keep-alive",
"content-length": "314",
"content-type": "application/json",
"date": "Wed, 10 Sep 2025 03:15:31 GMT",
"server": "gunicorn/19.9.0"
},
"content": "{\"data\":\"...\", \"headers\":{\"...\"}}"
},
"meta": {
"process_time": "2.0846",
"request_time": "2025-09-10 11:22:46 -> 2025-09-10 11:22:48",
"tag": "req-0"
},
"exception": {}
}{
"http_status": 0,
"response": {
"headers": {
"access-control-allow-credentials": "true",
"access-control-allow-origin": "*",
"connection": "keep-alive",
"content-length": "314",
"content-type": "application/json",
"date": "Wed, 10 Sep 2025 03:15:31 GMT",
"server": "gunicorn/19.9.0"
},
"content": ""
},
"meta": {
"process_time": "3.0012",
"request_time": "2025-08-08 03:15:05 -> 2025-08-08 03:15:08",
"tag": "test-req-50"
},
"exception": {
"type": "Timeout",
"message": "Request timeout after 3.00 seconds"
}
}For a detailed list of changes, see the CHANGELOG
This project is licensed under the MIT License.