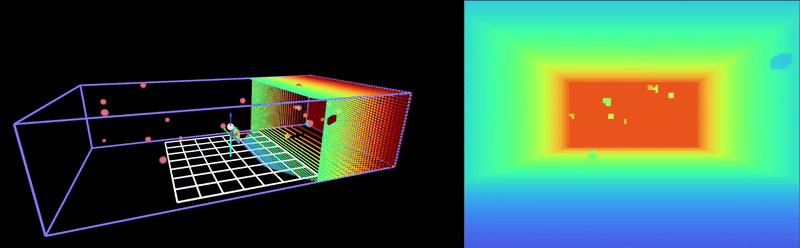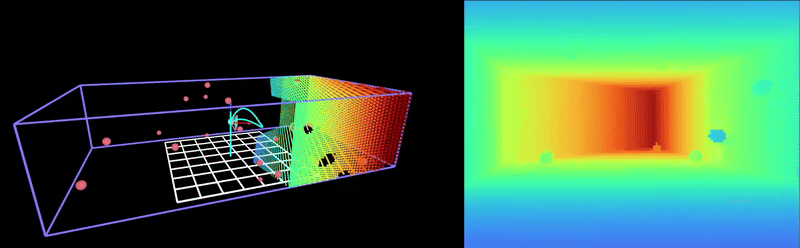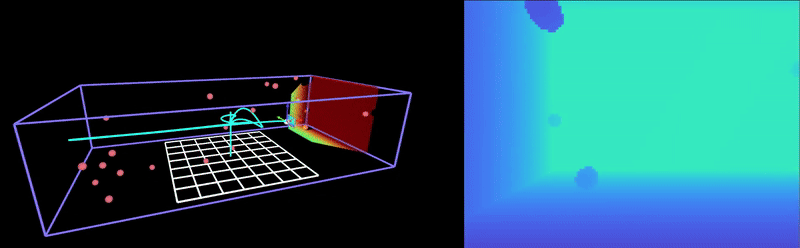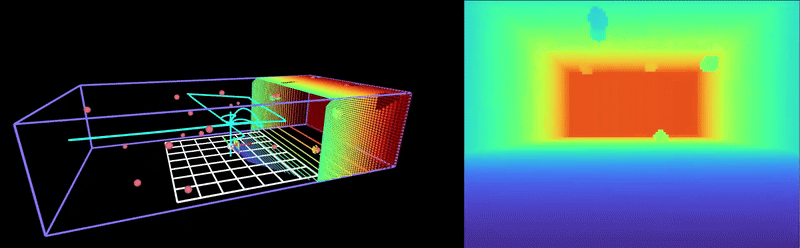
This repository is a fork of Peng, a minimal quadrotor autonomy framework written in Rust. Peng implements a real-time dynamics simulation, trajectory planning, and control with modern visualization capabilities. This fork integrates with HyRL, an obstacle avoidance RL model that is robust to adversarial noise in the position estimate. For information on the Peng framework, please refer to the original repository here.
- You can configure the simulation through config file, see quad.yaml for example.
- Configure simulation parameters such as mass, inertia, and control gains.
- Configure control parameters such as PID gains.
- Configure trajectory planner parameters such as waypoints, obstacles, and trajectory type.
- Configure visualization parameters such as camera intrinsics and depth rendering.
Configuration files contain a high-level mission description, along with a set of simulation parameters. These files are designed to be modified and copied to suit your desired simulation scenario. These simulation files are provided as input to the main program when running the simulation.
This repository leverages Nix to provide declarative, and reproducible environment for software builds. The easiest way to get started is to use the determinate systems installer to install Nix:
curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSf -L https://install.determinate.systems/nix | sh -s -- install --determinateOnce Nix is installed, you can clone this repo, and enter a development shell with all dependencies installed by running:
- Clone this repo:
git clone git@github.com:HSL-UCSC/Peng.git- Enter a Nix shell at the root of this repo:
nix developIf successful, you should see your shell prompt prefixed with (nix-shell) indicating you are in a Nix development shell.
In a Nix development shell, you can build and run the basic Peng SITL by executing:
cargo run config/quad.yamlThis command runs the main program with the standard configuration file as input.
The HyRL obstacle avoidance integration requires a server to be running. You have several options:
Option 1: Manual server control
# Terminal A - Start server
nix develop
hyrl-server
# Terminal B - Run simulation
nix develop
cargo run config/quad_hyrl.yamlOption 2: Auto-background server
# Single terminal - server runs in background
nix develop .#withServer
cargo run config/quad_hyrl.yamlOption 3: Standalone server from source
# Terminal A - Clone and start server from source
git clone https://github.com/friend0/ObstacleAvoidanceHyRL
cd ObstacleAvoidanceHyRL
nix develop
hyrl-server
# Terminal B - Run simulation
cd /path/to/PengHSL
nix develop
cargo run config/quad_hyrl.yamlThe server runs on localhost:50051 and will be automatically cleaned up when you exit the shell.
This fork of Peng for the Hybrid Systems Lab supports interfaces to external simulators, namely Liftoff®: FPV Drone Racing. Liftoff is a realistic FPV drone simulation designed to give hobbyists and enthusiasts flight experience that is transferrable to flying a real vehicle. Liftoff provides a means for retrieving detailed state feedback from the simulation from commands on a UDP port. With the addition of a CyberRC device, we can close the loop and fly in Liftoff with automatic control.
To run Peng with Liftoff, follow these steps:
-
Install Liftoff: FPV Drone Racing from Steam.
-
Configure Liftoff telemetry so that the controller can get feedback from the drone. See the guide here. Liftoff provides feedback from the internal drone simulation at roughly 100Hz, which is quite good for position control. The configuration values specified in this file influence what is included in the feedback packet we get from Liftoff. By extension, this also influences how we need to parse the binary payload. The binary parser is currently implemented to read data from this configuration:
{ "EndPoint": "127.0.0.1:9001", "StreamFormat": [ "Timestamp", "Position", "Attitude", "Gyro", "Input", "MotorRPM" ] }If you need to add or remove items from telemetry, you will also need to modify the LiftoffPacket struct in
src/liftoff_quadrotor.rs. Remote endpoints can also be specified, with the caveat that you will need to configure your network and interfaces to support such a setup. -
Attach a CyberRC device to the host PC that is running Peng. This device will be used to send control signals to Liftoff. The device should be connected to the host PC via USB. You will also need a USB to serial UART adapter to communicate with the device.
-
Run Peng with a configuration file set up to run with Liftoff. This configuration file will be quite similar to the stock configuration file used to run self contained simulations with Peng, with some minor additional configuration for the port to retrieve feedback from Liftoff, which serial interface the CyberRC is connected to, and what baud rate to use to send serial commands to the device.
If you encountered any issue with the rerun:
- Verify rerun-cli version matches rerun version in Cargo.toml:
rerun --version- For Linux/WSL2 users, consult the rerun troubleshooting.
Peng is free, open source and permissively licensed! Except where noted (below and/or in individual files), all code in this repository is dual-licensed under either:
- MIT License (LICENSE-MIT or http://opensource.org/licenses/MIT)
- Apache License, Version 2.0 (LICENSE-APACHE or http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0) at your option.
This means you can select the license you prefer!
If you use this project in your research or work, please cite it as follows:
@software{peng_quad,
author = {Yang Zhou},
title = {Peng: A Minimal Quadrotor Autonomy Framework in Rust},
year = {2024},
publisher = {GitHub},
journal = {GitHub repository},
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/makeecat/peng}},
}