What Matters for Representation Alignment: Global Information or Spatial Structure?
Official PyTorch Implementation: Improved REPA in just 3 lines of code
What Matters for Representation Alignment: Global Information or Spatial Structure?
Jaskirat Singh1,*, Xingjian Leng2, Zongze Wu1, Liang Zheng2, Richard Zhang1,
Eli Shechtman1, Saining Xie3
1Adobe Research, 2ANU, 3New York University
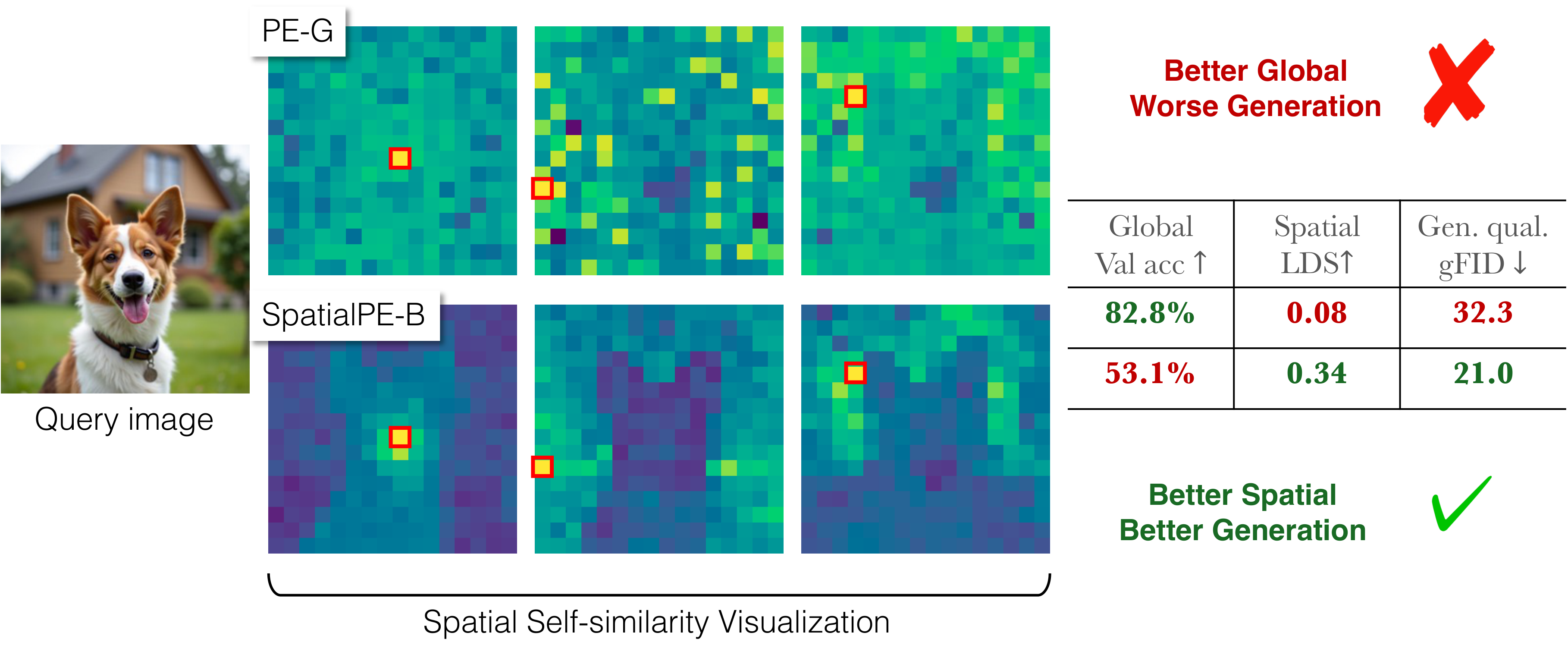
Representation matters for generation. But what truly drives its effectiveness: global semantic information or spatial structure? Prevailing wisdom says global semantics. We reveal a surprising finding: spatial structure, not global semantic information, drives generation performance of a representation.
Building on this finding, we introduce iREPA, a simple three lines of code change which consistently improves convergence speed with REPA across diverse training recipes (REPA, REPA-E, Meanflow, JiT etc).
iREPA: Improved REPA in just 3 lines of code
# 1. Conv projection instead of MLP
proj_layer = nn.Conv2d(D_in, D_out, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
# 2. Spatial normalization on encoder features [B, T, D]
x = x - gamma * x.mean(dim=1, keepdim=True)
x = x / (x.std(dim=1, keepdim=True) + 1e-6)git clone https://github.com/End2End-Diffusion/iREPA.git
cd iREPA
# Create environment (Python 3.10+)
conda create -n irepa python=3.10 -y && conda activate irepa
# Install dependencies
pip install -r environment/requirements.txt- Option A – Quick Start (Recommended): Download the full pre-processed dataset:
hf download REPA-E/iREPA-collections \ --include "data/**" \ --local-dir "."
- Option B – Bring Your Own ImageNet: Ensure your data resides at
data/imagenet/and containstrain/andval/subfolders. Then, download only the cached latents:hf download REPA-E/iREPA-collections \ --include "data/imagenet-latents-sdvae-ft-mse-f8d4/**" \ --local-dir "."
Download pre-trained vision encoders and install the DINOv3 dependency.
# Step 1: Download pre-trained vision encoders
hf download REPA-E/iREPA-collections \
--include "pretrained_models/**" \
--local-dir "."
# Step 2: Clone DINOv3 repository
git clone https://github.com/facebookresearch/dinov3.git
cd dinov3
git checkout 94a96ac83c2446f15f9bdcfae23cad3c6a9d4988
cd ..This repository provides REPA/iREPA for both latent and pixel-space diffusion:
| Approach | Description | Directory |
|---|---|---|
| LDM | Latent Diffusion (SiT) | ldm/ |
| JiT | Pixel-space diffusion (JiT) | jit/ |
Note: We provide all model checkpoints with REPA and iREPA across all vision encoders: here.
- SiT + REPA (using
pe-vit-gencoder)
cd ldm
accelerate launch train.py --config configs/repa.yaml \
--model="SiT-B/2" \
--enc-type="pe-vit-g" \
--encoder-depth=4 \
--data-dir=../data \
--exp-name="sitb2-pe-vit-g-repa"- SiT + iREPA (using
pe-vit-gencoder)
cd ldm
accelerate launch train.py --config configs/irepa.yaml \
--model="SiT-B/2" \
--enc-type="pe-vit-g" \
--encoder-depth=4 \
--data-dir=../data \
--exp-name="sitb2-pe-vit-g-irepa"- JiT + REPA (using
pe-vit-gencoder)
cd jit
torchrun --nproc_per_node=4 main_jit.py --config configs/irepa.yaml \
--model JiT-B/16 \
--enc_type="pe-vit-g" \
--encoder_depth=4 \
--data_path=../data \
--output_dir="exps/jit-pe-vit-g-repa"- JiT + iREPA (using
pe-vit-gencoder)
cd jit
torchrun --nproc_per_node=4 main_jit.py --config configs/irepa.yaml \
--model JiT-B/16 \
--enc_type="pe-vit-g" \
--encoder_depth=4 \
--data_path=../data \
--output_dir="exps/jit-pe-vit-g-irepa"LDM:
cd ldm
torchrun --nproc_per_node=8 generate.py \
--model="SiT-B/2" \
--ckpt="exps/<exp_name>/checkpoints/<step>.pt" \
--num-fid-samples=50000 \
--sample-dir=samplesJiT: Online evaluation is enabled by default with --online_eval.
We use the ADM evaluation suite to compute image generation quality metrics, including gFID, sFID, Inception Score (IS), Precision, and Recall.
We provide spatial metrics (LDS, CDS, SRSS, RMSC) for evaluating vision encoder feature representations. Download pre-computed features and stats:
cd metrics
# Download spatial metrics data (~20GB)
huggingface-cli download REPA-E/iREPA-collections \
--include "spatial-metrics-data/**" \
--local-dir "." \
--repo-type model
mv spatial-metrics-data dataPlot correlation with FID across all vision encoders (Linear Probing vs Spatial Metrics):
cd metrics
python spatial_metrics_comparison.py --device cudaVisualize spatial normalization effects across different encoders:
python scripts/viz_spatialnorm.py \
--encoders dinov3-vit-b16 mocov3-vit-l \
--device cuda \
--image_path assets/image1.png \
--seed 0 \
--output_dir assets \
--output_index 1- DINOv1:
dino-vit-b - DINOv2:
dinov2-vit-b,dinov2-vit-l,dinov2-vit-g - DINOv3:
dinov3-vit-b16,dinov3-vit-l16,dinov3-vit-h16plus,dinov3-vit-7b16 - WebSSL:
webssl-vit-dino300m_full2b_224,webssl-vit-dino1b_full2b_224,webssl-vit-dino2b_full2b_224,webssl-vit-dino3b_full2b_224,webssl-vit-dino5b_full2b_224,webssl-vit-dino7b_full8b_224 - MoCoV3:
mocov3-vit-b,mocov3-vit-l - CLIP:
clip-vit-L - I-JEPA:
jepa-vit-h - MAE:
mae-vit-l - SigLIP:
siglip-vit-b,siglip-vit-l,siglip-vit-so400m - SigLIP2:
siglip2-vit-b,siglip2-vit-l,siglip2-vit-so400m,siglip2-vit-g - PE:
pe-vit-b,pe-vit-l,pe-vit-g - LangPE:
langpe-vit-l,langpe-vit-g - SpatialPE:
spatialpe-vit-b,spatialpe-vit-l,spatialpe-vit-g - SAM2:
sam2-vit-s,sam2-vit-b,sam2-vit-l
The codebase is built upon some amazing projects:
We thank the authors for making their work publicly available!
@article{singh2025matters,
title={What matters for Representation Alignment: Global Information or Spatial Structure?},
author={Singh, Jaskirat and Leng, Xingjian and Wu, Zongze and Zheng, Liang and Zhang, Richard and Shechtman, Eli and Xie, Saining},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2512.10794},
year={2025}
}