Task - Constructors and Encapsulation - An Student #9
Replies: 63 comments
-
|
`class Student { } class C202 { |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
class Student{ } public class Constructor { } |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
`class Student{ } } ` |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
`class Student { } public class StudentDetails { } |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
` } public class StudentInfo { } |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
Student class-- } ` Student Driver Class-- ` } |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
`public class Student { }` |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
class Student { } class Main { |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
` package Day5; } { } |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
class Student public Student() public Student(int roll_no) public Student(String name,int roll_no) public int getRollNo() public String getName() { public void display() public class MyClass { |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
` } ` |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
class Student { } public class ClassStudent { } |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
class Student { } public class Students { |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
` class Student { } public class Constructors { } ` |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
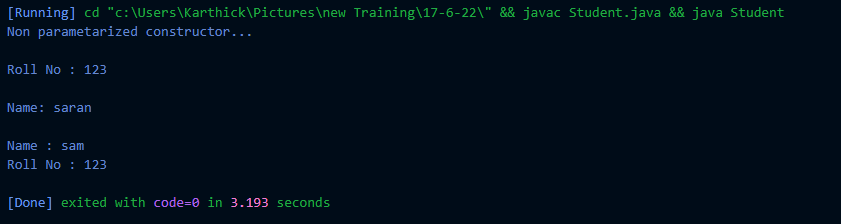
Student Details in Constructorclass Details{
int rollno=0;
String name=" ";
public Details() {
}
public Details(int rollno) {
this.rollno = rollno;
}
public Details(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Details(int rollno, String name) {
this.rollno = rollno;
this.name = name;
}
public int getRollno() {
return rollno;
}
public void setRollno(int rollno) {
this.rollno = rollno;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
void display(){
if(rollno==0){
if(name.equals(" ")){
System.out.println("Non parametarized constructor...");
}
else{
System.out.println("Name: " + name);
}
}
else{
if(name.equals(" ")){
System.out.println("Roll No : " + rollno);
}
else {
System.out.printf("Name : %s%nRoll No : %d",name,rollno);
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public class Student{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Details d1=new Details();
Details d2=new Details(123);
Details d3=new Details("saran");
Details d4=new Details(123,"sam");
d1.display();
d2.display();
d3.display();
d4.display();
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
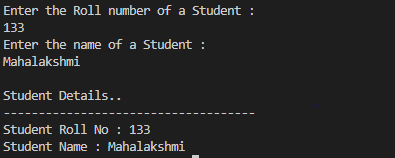
TASK-CONSTRUCTOR AND ENCAPSULATIONStudent.javaimport java.util.Scanner;
public class Student {
private int rollNo;
private String name;
public Student() //non parameterized constructor
{
System.out.println("Student Details..");
}
public Student(int rollNo, String name) // parameterized constructor
{
super();
this.rollNo = rollNo;
this.name = name;
}
//getter and setter methods for accessing the private data members
public int getRollNo()
{
return rollNo;
}
public void setRollNo(int rollNo) {
this.rollNo = rollNo;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void display()
{
System.out.println("Student Roll No : "+getRollNo());
System.out.println("Student Name : "+getName());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc =new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the Roll number of a Student :");
int n=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter the name of a Student :");
String name=sc.next();
System.out.println();
Student ob=new Student(); //calling non parameterized constructor
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
Student ob1=new Student(n,name); //calling parameterized constructor
ob1.display(); //calling the method
}
}Output |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
StudentDriver.javaclass Student{
int rollno;
String name;
Student(){
rollno = 10;
String name = "Tony";
}
Student(int rollno){
this.rollno = rollno;
}
Student(String name){
this.name = name;
}
Student(int rollno, String name){
this.rollno = rollno;
this.name = name;
}
int getRollNo(){
return this.rollno;
}
public void setRollNo(int rollno){
this.rollno = rollno;
}
String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public void setName(String name){
this.name = name;
}
void display(){
System.out.println("RollNo: " + rollno);
System.out.println("Name: " + name);
}
}
public class StudentDriver{
public static void main(String[] args){
Student s1=new Student();
Student s2=new Student(30);
Student s3=new Student("Nancy");
Student s4=new Student(10,"Steve");
s1.display();
s2.display();
s3.display();
s4.display();
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
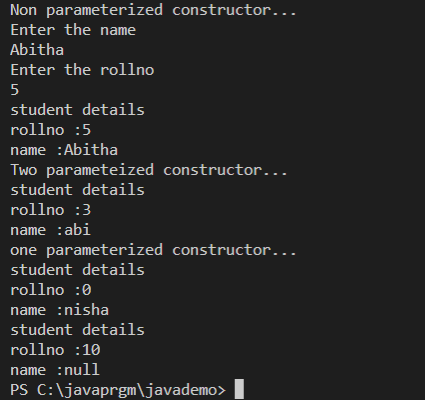
Constructorpackage constructdemo;
import java.util.Scanner;
class student{
private int rollno;
private String name;
student(){ // non-parameterized constructor
}
student(int rollno){ //one parameterized constructor
this.rollno=rollno;
}
student(String name){
this.name=name;
}
student(int rollno, String name){ // two parameterized constructor
this.rollno=rollno;
this.name=name;
}
public int getRollno() { // getter and setter
return rollno;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setRollno(int rollno) {
this.rollno = rollno;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void display(){
System.out.println("student details");
System.out.println("rollno :"+rollno+"\n"+"name :"+name);
}}
public class StudentDriver {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Non parameterized constructor...");
student obj1=new student();
System.out.println("Enter the name");
obj1.setName(sc.nextLine());
System.out.println("Enter the rollno");
obj1.setRollno(sc.nextInt());
obj1.display();
System.out.println("Two parameteized constructor...");
student obj2=new student(3,"abi");
obj2.display();
System.out.println("one parameterized constructor...");
student obj3=new student("nisha");
obj3.display();
student obj4=new student(10);
obj4.display();
}
}output: |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
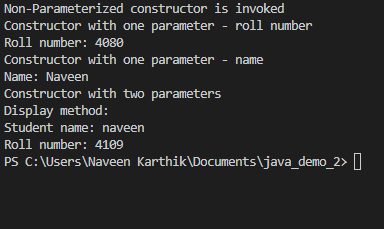
ConstructorsTask.javaclass Student {
private int rollNo;
private String name;
// defining constructors
Student() {
System.out.println("Non-Parameterized constructor is invoked");
}
Student(int rollNo) {
System.out.println("Constructor with one parameter - roll number");
this.rollNo = rollNo;
System.out.println("Roll number: " + this.rollNo);
}
Student(String name) {
System.out.println("Constructor with one parameter - name");
this.name = name;
System.out.println("Name: " + this.name);
}
Student(int rollNo, String name) {
System.out.println("Constructor with two parameters");
}
// getters and setters method
public int getRollNo() {
return rollNo;
}
public void setRollNo(int rollNo) {
this.rollNo = rollNo;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void display() {
System.out.println("Display method:");
System.out.println("Student name: " + getName());
System.out.println("Roll number: " + getRollNo());
}
}
public class ConstructorsTask {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 = new Student(); // non parameterized constructor is invoked
Student s2 = new Student(4080); // parameterized constructor is invoked
s2.setRollNo(4080);
Student s3 = new Student("Naveen"); // parameterized constructor is invoked
s3.setName("Naveen");
Student s4 = new Student(4112, "Karthik"); // parameterized constructor is invoked
String name = "naveen";
int rollNo = 4109;
s4.setName(name);
s4.setRollNo(rollNo);
s4.display();
}
}Output: |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
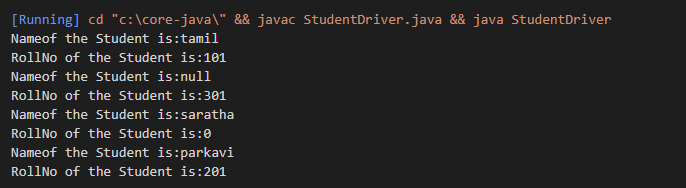
Studentclass Student{
private int rollNo;
private String Name;
public int getRollNo() {
return rollNo;
}
public void setRollNo(int rollNo) {
this.rollNo = rollNo;
}
public String getName() {
return Name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
Name = name;
}
Student(){}
Student(int rollNo){
this.rollNo = rollNo;
}
Student(String name){
this.Name = name;
}
Student(int rollNo,String name){
this.rollNo=rollNo;
this.Name = name;
}
public void display(){
System.out.println("Nameof the Student is:"+getName());
System.out.println("RollNo of the Student is:"+getRollNo());
}
}
public class StudentDriver{
public static void main(String[] args){
Student student1= new Student();
student1.setName("tamil");
student1.setRollNo(101);
Student student2= new Student(301);
Student student3= new Student("saratha");
Student student4= new Student(201,"parkavi");
student1.display();
student2.display();
student3.display();
student4.display();
}
}Output: |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
studnew.javaclass student
{
private int roll_no;
private String name;
public student() //user defined constructor with no parameters passed
{
}
public student(int roll_no)//Parameterized constructor for roll no
{
this.roll_no=roll_no;
}
public student(String name)//Parameterized constructor for name
{
this.name=name;
}
public void setname(String name)//assigning name using set method
{
this.name=name;
}
public void setrollno(int roll_no) //assigning roll_no using set method
{
this.roll_no=roll_no;
}
public int getroll_no() // used to get the value of roll no
{
return roll_no;
}
public String getname() //used to get the value of name using getter method
{
return name;
}
public String Display() // Displays both name and roll no which has been passed from driver class and gets assigned in the current occurence
{
return "Name: "+name+"\nRollNo: "+roll_no;
}
}
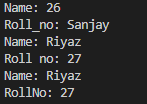
public class studnew {
public static void main(String args[])
{
student s1=new student();//invokes user defined constructors with no parameters
student s2=new student(26);//invokes user defined parameterized constructors with integer argument
student s3=new student("Sanjay");//invokes user defined parameterized constructors with String argument
System.out.println("Name: "+s2.getroll_no()+"\nRoll_no: "+s3.getname());
s1.setname("Riyaz");//using setter to pass the value for name
s1.setrollno(27);//using setter to pass the value for roll number
System.out.println("Name: "+s1.getname()+"\nRoll no: "+s1.getroll_no());//getting value using getter method
System.out.println(s1.Display());
}
}Output |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
1class Student{
private int rollNo;
private String name;
Student(){
System.out.println("No args constructor");
}
public Student(int rollNo) {
this.rollNo = rollNo;
}
public Student(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Student(int rollNo, String name) {
this.rollNo = rollNo;
this.name = name;
}
public int getRollNo() {
return rollNo;
}
public void setRollNo(int rollNo) {
this.rollNo = rollNo;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [name=" + name + ", rollNo=" + rollNo + "]";
}
public void display(){
System.out.println("Student [name=" + name + ", rollNo=" + rollNo );
}
}
public class StudentDriver{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 =new Student();
s1.setName("Raj");
s1.setRollNo(7777);
Student s2 =new Student(77);
Student s3 =new Student("Roshan");
Student s4 =new Student(77,"Rajkapoor");
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(s2);
System.out.println(s3);
System.out.println(s4);
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
class Student{
private int rollNo;
private String Name;
public int getRollNo() {
return rollNo;
}
public void setRollNo(int rollNo) {
this.rollNo = rollNo;
}
public String getName() {
return Name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
Name = name;
}
Student(){}
Student(int rollNo){
this.rollNo = rollNo;
}
Student(String name){
this.Name = name;
}
Student(int rollNo,String name){
this.rollNo=rollNo;
this.Name = name;
}
public void display(){
System.out.println("Name of the Student is:"+getName());
System.out.println("RollNo of the Student is:"+getRollNo());
}
}
public class StudentMain{
public static void main(String[] args){
Student student1= new Student();
student1.setName("saratha");
student1.setRollNo(1);
Student student2= new Student(2);
Student student3= new Student("parkavi");
Student student4= new Student(3,"lakshmi");
student1.display();
student2.display();
student3.display();
student4.display();
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
class Student{
int rollNo;
String name;
Student(){
}
Student(int rollNo){
this.rollNo=rollNo;
this.name = "Default";
}
Student(String name){
this.name = name;
this.rollNo=0;
}
Student(int rollNo,String name){
this.rollNo = rollNo;
this.name = name;
}
protected void display(){
System.out.println("RollNo: "+this.rollNo);
System.out.println("Name: "+this.name);
}
int getRollNo(){
return this.rollNo;
}
String getName(){
return this.name;
}
void setRollNo(int rollNo){
this.rollNo=rollNo;
}
void setName(String name){
this.name=name;
}
}
public class MainClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1=new Student(10,"saratha");
Student s2=new Student(20);
Student s3=new Student("selvam");
Student s4=new Student();
s1.display();
System.out.println();
s2.display();
System.out.println();
s3.display();
System.out.println();
s4.display();
System.out.println();
s2.setName("saranya");
s3.setRollNo(339);
s2.display();
System.out.println();
s3.display();
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
class Student{
int rollNo;
String name;
Student(){
rollNo=110;
String name="ABC";
}
Student(int rollNo){
this.rollNo=rollNo;
this.name = "Default";
}
Student(String name){
this.name = name;
this.rollNo=0;
}
Student(int rollNo,String name){
this.rollNo = rollNo;
this.name = name;
}
protected int getRollNo(){
return this.rollNo;
}
protected String getName(){
return this.name;
}
protected void setRollNo(int rollNo){
this.rollNo=rollNo;
}
protected void setName(String name){
this.name=name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [name=" + name + ", rollNo=" + rollNo + "]";
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1=new Student(1, "Shalini");
Student s2=new Student(2, "Kamini");
Student s3=new Student("Stranger");
Student s4=new Student();
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(s2);
System.out.println(s3);
System.out.println(s4);
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
class Student {
private int rollNo;
private String name;
public Student() {
super();
}
public Student(int rollNo) {
super();
this.rollNo = rollNo;
}
public Student(String name) {
super();
this.name = name;
}
public Student(int rollNo, String name) {
super();
this.rollNo = rollNo;
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getRollNo() {
return rollNo;
}
public void setRollNo(int rollNo) {
this.rollNo = rollNo;
}
public void display() {
System.out.println("name: " + this.getName() + " roll no: " + this.getRollNo());
}
}
public class StudentDetails {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Student studentOne = new Student();
studentOne.display();
Student studentTwo = new Student(12);
studentTwo.display();
Student studentThree = new Student("test");
studentThree.display();
Student studentFour = new Student(12, "testing");
studentFour.display();
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
class Student{
private int rollno;
private String name;
public Student(int rollno, String name) {
this.rollno = rollno;
this.name = name;
}
public Student(int rollno) {
this.rollno = rollno;
}
public Student(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Student(){
rollno=1;
name="Kane";
}
public int getRollno() {
return rollno;
}
public void setRollno(int rollno) {
this.rollno = rollno;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
void display(){
System.out.println("RollNo: " + rollno+" Name: " + name);
}
}
public class StudentDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student1=new Student(10,"Peter");
Student student2=new Student(12);
Student student3=new Student("Ram");
System.out.println("Name of student 3 :");
System.out.println(student3.getName());
System.out.println("RollNo of student 2 :");
System.out.println(student2.getRollno());
System.out.println("Student 1 details");
student1.display();
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
// Student.java
public class Student {
private int rollNo;
private String name;
public Student() {}
public Student(int rollNo, String name) {
this.rollNo = rollNo;
this.name = name;
}
public int getRollNo() {
return rollNo;
}
public void setRollNo(int rollNo) {
this.rollNo = rollNo;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void display() {
System.out.println("Roll no :" + this.rollNo + " and Name : " + this.name);
}
}// StudentDriver.java
public class StudentDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student_1 = new Student();
student_1.display();
Student student_2 = new Student(1, "Ram");
student_2.display();
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
Task 1 - Sayan Dey class Student{ } } |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading. Please reload this page.
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading. Please reload this page.
-
Create a class Student with the following data members:
Implement the following in the Student class:
Create a driver class StudentDriver with the main() method to implement the above features.
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
All reactions