Task - Functional Programming - Lambda Expressions - Animal Noises #68
Replies: 32 comments 1 reply
-
interface Animal {
void makeSound();
}
class Dog implements Animal {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Bow Bow");
}
}
class Cat implements Animal {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Meow Meow");
}
}
class Lion implements Animal {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Roar");
}
}
public class LambdaExpressionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// traditional implementation
Animal dog = new Dog();
dog.makeSound();
Animal cat = new Cat();
cat.makeSound();
Animal lion = new Lion();
lion.makeSound();
// using Anonymous class
Animal anonymousDog = new Animal() {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Bow Bow");
}
};
anonymousDog.makeSound();
Animal anonymousCat = new Animal() {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Meow Meow");
}
};
anonymousCat.makeSound();
Animal anonymousLion = new Animal() {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Roar");
}
};
anonymousLion.makeSound();
// using Lambda Expression
Animal lambdaDog = () -> {
System.out.println("Bow Bow");
};
lambdaDog.makeSound();
Animal lambdaCat = () -> {
System.out.println("Meow Meow");
};
lambdaCat.makeSound();
Animal lambdaLion = () -> {
System.out.println("Roar");
};
lambdaLion.makeSound();
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
@FunctionalInterface
interface Animal {
String makeSound();
}
public class AnimalNoises {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* START - Implement the interface using Anonymous classes
*/
Animal animalDogs = new Animal() {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Bow Bow!!!";
}
};
Animal animalBirds = new Animal() {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "chirp chirp !!!";
}
};
Animal animalCats = new Animal() {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Mew Mew !!!";
}
};
Animal animaHorses = new Animal() {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "neigh !!!";
}
};
Animal animalMonkeys = new Animal() {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "ooh-ooh-ahh-ahh !!!";
}
};
Animal animalLions = new Animal() {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "growl !!!";
}
};
Animal animalElephants = new Animal() {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "trumpeting !!!";
}
};
/**
* END - Implement the interface using Anonymous classes
*/
/**
* START - Implement the interface using Lambda Expression
*/
Animal animalDogsL = () -> "Bow Bow!!!";
Animal animalBirdsL = () -> "chirp chirp !!!";
Animal animalCatsL = () -> "Mew Mew !!!";
Animal animalHorsesL = () -> "neigh !!!";
Animal animalMonkeysL = () -> "ooh-ooh-ahh-ahh !!!";
Animal animalLionsL = () -> "growl !!!";
Animal animalElephantsL = () -> "trumpeting !!!";
/**
* END - Implement the interface using Lambda Expression
*/
System.out.println("Dog Sound (using traditional way): " + new Dogs().makeSound());
System.out.println("Cat Sound (using Anonymous class): " + animalCats.makeSound());
System.out.println("Bird Sound (using Lambda): " + animalBirdsL.makeSound());
}
}
/**
* Class for Traditional Use case
*/
class Dogs implements Animal {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Bow Bow!!!";
}
}
class Birds implements Animal {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "chirp chirp !!!";
}
}
class Cats implements Animal {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Mew Mew !!!";
}
}
class Horses implements Animal {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "neigh !!!";
}
}
class Monkeys implements Animal {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "ooh-ooh-ahh-ahh !!!";
}
}
class Lions implements Animal {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "growl !!!";
}
}
class Elephants implements Animal {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "trumpeting !!!";
}
}
/*
Below is an example of an Anonymous class that will be automatically created by Java at Runtime.
If class_name already exist then it will have class_names$1,class_names$2 etc.
class AnimalNoises$Animal implements Animal{
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Bow Bow!!!";
}
}*/ |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
package com.java.lamda;
interface Animal{
String makeSound();
}
class Dogs implements Animal{
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Dogs Sounds";
}
}
class Birds implements Animal{
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Birds Sound";
}
}
class Cats implements Animal{
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Cats Sound";
}
}
class Horses implements Animal{
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Horses Sound";
}
}
class Monkeys implements Animal{
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Monkeys Sound";
}
}
class Lions implements Animal{
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Lions Sounds";
}
}
class Elephants implements Animal{
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Elephants Sound";
}
}
public class TraditionalClasses {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("TraditionalClasses =============================================");
Animal elephants=new Elephants();
System.out.println(new Dogs().makeSound());
System.out.println(new Birds().makeSound());
System.out.println(new Cats().makeSound());
System.out.println(new Horses().makeSound());
System.out.println(new Monkeys().makeSound());
System.out.println(elephants.makeSound());
System.out.println(new Lions().makeSound());
//anonymous
Animal elephant=new Animal() {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Anonymous elephent";
}
};
System.out.println(elephant.makeSound());
//Lamda
Animal dogs =() -> "Lamba dogs";
System.out.println(dogs.makeSound());
Animal cats =() -> "Lamba Cat";
System.out.println(cats.makeSound());
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
interface Animal {
void makeSound();
}
class dogs implements Animal {
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("bow wow");
}
}
class cats implements Animal {
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("meow meow");
}
}
class birds implements Animal {
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("kee kee");
}
}
class horses implements Animal {
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("a neigh");
}
}
class monkeys implements Animal {
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("whoop");
}
}
class lions implements Animal {
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("roar");
}
}
class elephants implements Animal {
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("trumpet");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal dogsSound = new dogs();
dogsSound.makeSound();
Animal catsSound = new cats();
catsSound.makeSound();
Animal monkey = new Animal() {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("whoop");
}
};
monkey.makeSound();
Animal horses = new Animal() {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("a neigh");
}
};
horses.makeSound();
Animal birds = ()->System.out.println("kee kee");
birds.makeSound();
Animal lions = ()->System.out.println("roar");
lions.makeSound();
Animal elephant = ()->System.out.println("trumpet");
elephant.makeSound();
}
}
`` |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
Interfacepublic interface Animal {
public String makeNoise();
}Dog and Cat Classpublic class Dog implements Animal {
@Override
public String makeNoise() {
return "Bow Bow";
}
}
public class Cat implements Animal {
@Override
public String makeNoise() {
return "Meow Meow";
}
}Main Classpublic class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal dog = new Dog();
System.out.println(dog.makeNoise());
Animal cat = new Cat();
System.out.println(cat.makeNoise());
//Anonymous Classes
Animal dogAC = new Animal() {
@Override
public String makeNoise() {
return "Bow Bow";
}
};
System.out.println(dogAC.makeNoise() + " using Anonymous Classes");
Animal catAC = new Animal() {
@Override
public String makeNoise() {
return "Meow Meow";
}
};
System.out.println(catAC.makeNoise() + " using Anonymous Classes");
//Lambda Expressions
Animal dogLE = () -> "Bow Bow";
System.out.println(dogLE.makeNoise() + " using Lambda Expressions");
Animal catLE = () -> "Meow Meow";
System.out.println(catLE.makeNoise() + " using Lambda Expressions");
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
// Ramprasad |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
interface Animal{
String makeSound();
}
class Dog implements Animal {
@Override
public String makeSound(){
return "Bark";
}
}
class Bird implements Animal {
@Override
public String makeSound(){
return "Chirp";
}
}
public class FunctionalProgrammingDemo {
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println("-----Using traditional classes-----");
Animal dog = new Dog();
Animal bird = new Bird();
System.out.println("Dog Sound:- " + dog.makeSound());
System.out.println("Bird Sound:- " + bird.makeSound());
System.out.println();
System.out.println("-----Using anonymous classes-----");
Animal anonymousDog = new Dog() {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Bark";
}
};
System.out.println("Dog Sound:- " + anonymousDog.makeSound());
Animal anonymousBird = new Bird() {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Chirp";
}
};
System.out.println("Bird Sound:- " + anonymousBird.makeSound());
System.out.println();
System.out.println("-----Using lambda expressions-----");
Animal lambdaDog = () -> "Bark";
Animal lambdaBird = () -> "Chirp";
System.out.println("Dog Sound:- " + lambdaDog.makeSound());
System.out.println("Bird Sound:- " + lambdaBird.makeSound());
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
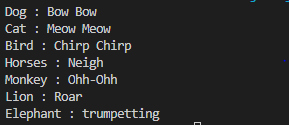
Task - Functional Programming - Lambda Expressions - Animal NoisesAnimalInterface.javapackage Interface;
interface Animal
{
String makeSound();
}Traditional Methodclass Dog implements Animal
{
public String makeSound()
{
return "Dog : Bow Bow";
}
}
class Bird implements Animal
{
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Bird : Chirp Chirp";
}
}
class Cat implements Animal
{
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Cat : meow meow";
}
}
class Horses implements Animal
{
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Horse : neigh ";
}
}
class Monkeys implements Animal
{
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Monkey : ooh-ohh-ahh-ahh";
}
}
class Lions implements Animal
{
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Lion : roar";
}
}
class Elephant implements Animal
{
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Elepant : trumpetting";
}
}
public class AnimalInterface {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal dog=new Dog();
Animal bird=new Bird();
Animal cat=new Cat();
Animal Horses=new Horses();
Animal Monkeys=new Monkeys();
Animal Lions=new Lions();
Animal Elephant=new Elephant();
System.out.println(dog.makeSound());
System.out.println(bird.makeSound());
System.out.println(cat.makeSound());
System.out.println(Horses.makeSound());
System.out.println(Monkeys.makeSound());
System.out.println(Lions.makeSound());
System.out.println(Elephant.makeSound());
}
}Using Anonymous Classpublic class AnimalInterface {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal dogAnonymus=new Animal()
{
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Dog : Bow Bow";
}
};
System.out.println(dogAnonymus.makeSound());
Animal birdAnonymus=new Animal()
{
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Bird : chirp chirp";
}
};
System.out.println(birdAnonymus.makeSound());
Animal catAnonymus=new Animal()
{
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Cat : Meow Meow";
}
};
System.out.println(catAnonymus.makeSound());
Animal horseAnonymus=new Animal()
{
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Horses : neigh";
}
};
System.out.println(horseAnonymus.makeSound());
Animal monkeyAnonymus=new Animal()
{
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Monkey : ooh-ooh-ahh-ah";
}
};
System.out.println(monkeyAnonymus.makeSound());
Animal lionAnonymus=new Animal()
{
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Lion : roar";
}
};
System.out.println(lionAnonymus.makeSound());
Animal elephantAnonymus=new Animal()
{
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Elephant : trumpetting";
}
};
System.out.println(elephantAnonymus.makeSound());
}}Using Lambda Expression public class AnimalInterface {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal dog=()->{return "Dog : Bow Bow";};
Animal cat=()->{return "Cat : Meow Meow";};
Animal bird=()->{return "Bird : Chirp Chirp";};
Animal horse=()->{return "Horses : Neigh";};
Animal monkey=()->{return "Monkey : Ohh-Ohh";};
Animal lion=()->{return "Lion : Roar";};
Animal elephant=()->{return "Elephant : trumpetting";};
System.out.println(dog.makeSound());
System.out.println(cat.makeSound());
System.out.println(bird.makeSound());
System.out.println(horse.makeSound());
System.out.println(monkey.makeSound());
System.out.println(lion.makeSound());
System.out.println(elephant.makeSound());
}
}Output |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
Interfaceinterface Animal{
String makeSound();
}Traditional Methodclass Dogs implements Animal{
public String makeSound(){
return "Bow Bow...";
}
}
class Birds implements Animal{
public String makeSound(){
return "Chirp Chirp...";
}
}
class Cats implements Animal{
public String makeSound(){
return "Meow Meow...";
}
}
class Horses implements Animal{
public String makeSound(){
return "Neigh Neigh...";
}
}
class Monkeys implements Animal{
public String makeSound(){
return "Whoop Whoop...";
}
}
class Lions implements Animal{
public String makeSound(){
return "Roar Roar...";
}
}
class Elephants implements Animal{
public String makeSound(){
return "Trumpeting...";
}
}
public class LambdaExp{
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Traditional Method
Animal dog = new Dogs();
System.out.println(dog.makeSound());
Animal bird = new Birds();
System.out.println(bird.makeSound());
Animal cat = new Cats();
System.out.println(cat.makeSound());
Animal horse = new Horses();
System.out.println(horse.makeSound());
Animal monkey = new Monkeys();
System.out.println(monkey.makeSound());
Animal lion = new Lions();
System.out.println(lion.makeSound());
Animal elephant = new Elephants();
System.out.println(elephant.makeSound());
}
}Anonymous Methodpublic class LambdaExp{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal adog = new Animal(){
public String makeSound(){
return "Bow Bow...";
}
};
System.out.println(adog.makeSound());
Animal abird = new Animal(){
public String makeSound(){
return "Chirp Chirp...";
}
};
System.out.println(abird.makeSound());
Animal acat = new Animal(){
public String makeSound(){
return "Meow Meow...";
}
};
System.out.println(acat.makeSound());
Animal ahorse = new Animal(){
public String makeSound(){
return "Neigh Neigh...";
}
};
System.out.println(ahorse.makeSound());
Animal amonkey = new Animal(){
public String makeSound(){
return "Whoop Whoop...";
}
};
System.out.println(amonkey.makeSound());
Animal alion = new Animal(){
public String makeSound(){
return "Roar Roar...";
}
};
alion.makeSound();
Animal aelephant = new Animal(){
public String makeSound(){
return "Trumpeting...";
}
};
System.out.println(aelephant.makeSound());
}
}Lambda Expressionpublic class LambdaExp{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal ldog = () ->"Bow Bow...";
ldog.makeSound();
Animal lbird = () ->"Chirp Chirp...";
lbird.makeSound();
Animal lcat = () -> "Meow Meow...";
lcat.makeSound();
Animal lhorse = () ->"Neigh Neigh...";
lhorse.makeSound();
Animal lmonkey = () ->"Whoop...";
lmonkey.makeSound();
Animal llion = () -> "Roar...";
llion.makeSound();
Animal lelephant = () ->"Trumpeting...";
lelephant.makeSound();
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
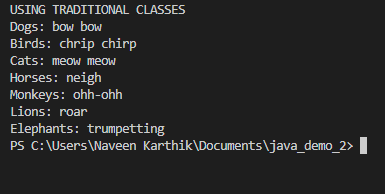
Using traditional classesinterface Animal {
String makeSound();
}
class Dogs implements Animal {
public String makeSound() {
String d = "Dogs: bow bow";
return d;
}
}
class Birds implements Animal {
public String makeSound() {
String b = "Birds: chrip chirp";
return b;
}
}
class Cats implements Animal {
public String makeSound() {
String c = "Cats: meow meow";
return c;
}
}
class Horses implements Animal {
public String makeSound() {
String h = "Horses: neigh";
return h;
}
}
class Monkeys implements Animal {
public String makeSound() {
String m = "Monkeys: ohh-ohh";
return m;
}
}
class Lions implements Animal {
public String makeSound() {
String l = "Lions: roar";
return l;
}
}
class Elephants implements Animal {
public String makeSound() {
String e = "Elephants: trumpetting";
return e;
}
}
public class FuncInterf1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("USING TRADITIONAL CLASSES");
Animal d = new Dogs();
System.out.println(d.makeSound());
Animal b = new Birds();
System.out.println(b.makeSound());
Animal c = new Cats();
System.out.println(c.makeSound());
Animal h = new Horses();
System.out.println(h.makeSound());
Animal m = new Monkeys();
System.out.println(m.makeSound());
Animal l = new Lions();
System.out.println(l.makeSound());
Animal e = new Elephants();
System.out.println(e.makeSound());
}
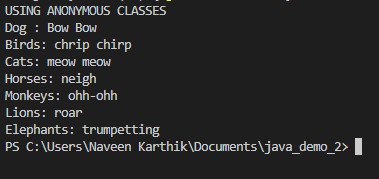
}Output:Using anonymous classesinterface Animal {
String makeSound();
}
public class FuncInterf2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("USING ANONYMOUS CLASSES");
Animal d = new Animal() {
public String makeSound() {
return "Dog : Bow Bow";
}
};
Animal b = new Animal() {
public String makeSound() {
return "Birds: chrip chirp";
}
};
Animal c = new Animal() {
public String makeSound() {
return "Cats: meow meow";
}
};
Animal h = new Animal() {
public String makeSound() {
return "Horses: neigh";
}
};
Animal m = new Animal() {
public String makeSound() {
return "Monkeys: ohh-ohh";
}
};
Animal l = new Animal() {
public String makeSound() {
return "Lions: roar";
}
};
Animal e = new Animal() {
public String makeSound() {
return "Elephants: trumpetting";
}
};
System.out.println(d.makeSound());
System.out.println(b.makeSound());
System.out.println(c.makeSound());
System.out.println(h.makeSound());
System.out.println(m.makeSound());
System.out.println(l.makeSound());
System.out.println(e.makeSound());
}
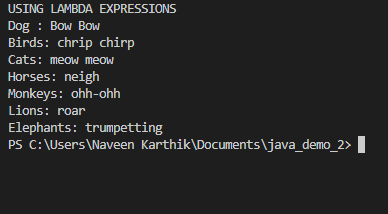
}Output:Using lambda expressionsinterface Animal {
String makeSound();
}
public class FuncInterf3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("USING LAMBDA EXPRESSIONS");
Animal d = () -> {
return "Dog : Bow Bow";
};
System.out.println(d.makeSound());
Animal b = () -> {
return "Birds: chrip chirp";
};
System.out.println(b.makeSound());
Animal c = () -> {
return "Cats: meow meow";
};
System.out.println(c.makeSound());
Animal h = () -> {
return "Horses: neigh";
};
System.out.println(h.makeSound());
Animal m = () -> {
return "Monkeys: ohh-ohh";
};
System.out.println(m.makeSound());
Animal l = () -> {
return "Lions: roar";
};
System.out.println(l.makeSound());
Animal e = () -> {
return "Elephants: trumpetting";
};
System.out.println(e.makeSound());
}
}Output: |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
1Ani.javainterface Animal
{
public String makeSound();
}
class dogs implements Animal
{
public String makeSound()
{
return "Barks";
}
}
class birds implements Animal
{
public String makeSound()
{
return "Chirping";
}
}
class cats implements Animal
{
public String makeSound()
{
return "Meow";
}
}
class horses implements Animal
{
public String makeSound()
{
return "neigh";
}
}
class monkey implements Animal
{
public String makeSound()
{
return "Screech";
}
}
class lions implements Animal
{
public String makeSound()
{
return "Roar";
}
}
class elephants implements Animal
{
public String makeSound()
{
return "Trumpets";
}
}
public class ani {
public static void main(String args[])//Traditional method using overriding
{
Animal dog=new dogs();
Animal bird=new birds();
Animal cat=new cats();
Animal horse=new horses();
Animal monkey=new monkey();
Animal lion=new lions();
Animal elephant=new elephants();
System.out.println("dog: "+dog.makeSound());
System.out.println("Birds: "+bird.makeSound());
System.out.println("Cats: "+cat.makeSound());
System.out.println("Horses: "+horse.makeSound());
System.out.println("Monkeys: "+monkey.makeSound());
System.out.println("Lions: "+lion.makeSound());
System.out.println("Elephants: "+elephant.makeSound());
}
}Output2Anim.javainterface Animal
{
public String makeSound();
}
public class Anim
{
public static void main(String args[])//Using anonymous class and overriding the interface method
{
Animal dog=new dogs(){
public String makeSound()
{
return "Barks";
}};
Animal bird=new birds(){
public String makeSound()
{
return "Chirping";
}};
Animal cat=new cats(){
public String makeSound()
{
return "Meow";
}};
Animal horse=new horses(){
public String makeSound()
{
return "neigh";
}};
Animal monkey=new monkey(){
public String makeSound()
{
return "Screech";
}};
Animal lion=new lions(){
public String makeSound()
{
return "Roar";
}};
Animal elephant=new elephants(){
public String makeSound()
{
return "Trumpets";
}};
System.out.println("dog: "+dog.makeSound());
System.out.println("Birds: "+bird.makeSound());
System.out.println("Cats: "+cat.makeSound());
System.out.println("Horses: "+horse.makeSound());
System.out.println("Monkeys: "+monkey.makeSound());
System.out.println("Lions: "+lion.makeSound());
System.out.println("Elephants: "+elephant.makeSound());
}
}Output3.Anima.javainterface Animal
{
public String makeSound();
}
public class Anima
{
public static void main(String args[])//Using lambda expression and passing the statements into the interface makeSound method
{
Animal dog=()->{
return "Barks";
};
Animal bird=()->{
return "Chirping";
};
Animal cat=()->{
return "Meow";
};
Animal horse=()->{
return "neigh";
};
Animal monkey=()->{
return "Screech";
};
Animal lion=()->{
return "Roar";
};
Animal elephant=()->{
return "Trumpets";
};
System.out.println("dog: "+dog.makeSound());
System.out.println("Birds: "+bird.makeSound());
System.out.println("Cats: "+cat.makeSound());
System.out.println("Horses: "+horse.makeSound());
System.out.println("Monkeys: "+monkey.makeSound());
System.out.println("Lions: "+lion.makeSound());
System.out.println("Elephants: "+elephant.makeSound());
}
}Output |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
Interface1_TraditionalClassespackage Interface.TraditionalClasses;
interface Animal {
String makeSound();
}
class Dog implements Animal {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Dog: Barks";
}
}
class Birds implements Animal {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Bird: Chirp";
}
}
class Cats implements Animal {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Cat: Meow";
}
}
class Horses implements Animal {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Horse: Neigh";
}
}
class Monkey implements Animal {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Monkey: Screech";
}
}
class Lions implements Animal {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Lion: Roar";
}
}
class Elephants implements Animal {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Elephant: Trumpets";
}
}
public class TraditionalClass {
public static void main(String args[]) { // Using Traditional method
Animal dog = new Dog();
Animal bird = new Birds();
Animal cat = new Cats();
Animal horse = new Horses();
Animal monkey = new Monkey();
Animal lion = new Lions();
Animal elephant = new Elephants();
System.out.println(dog.makeSound());
System.out.println(bird.makeSound());
System.out.println(cat.makeSound());
System.out.println(horse.makeSound());
System.out.println(monkey.makeSound());
System.out.println(lion.makeSound());
System.out.println(elephant.makeSound());
}
}2_AnonymousClasspackage Interface.AnonymousClasses;
interface Animal {
String makeSound();
}
public class AnonymousClass {
public static void main(String[] args) { //Using Anonymous method
Animal dog = new Animal() {
@Override public String makeSound() {
return "Dog: Barks";
}
};
Animal bird = new Animal() {
@Override public String makeSound() {
return "Bird: Chrip";
}
};
Animal cat = new Animal() {
@Override public String makeSound() {
return "Cat: Meow";
}
};
Animal horse = new Animal() {
@Override public String makeSound() {
return "Horse: Neigh";
}
};
Animal monkey = new Animal() {
@Override public String makeSound() {
return "Monkey: Screech";
}
};
Animal lion = new Animal() {
@Override public String makeSound() {
return "Lion: Roar";
}
};
Animal elephant = new Animal() {
@Override public String makeSound() {
return "Elephant: Trumpets";
}
};
System.out.println(dog.makeSound());
System.out.println(bird.makeSound());
System.out.println(cat.makeSound());
System.out.println(horse.makeSound());
System.out.println(monkey.makeSound());
System.out.println(lion.makeSound());
System.out.println(elephant.makeSound());
}
}3_LambdaExpressionspackage Interface.LambdaExpression;
interface Animal {
String makeSound();
}
public class LambdaExpression { // Lambda expression for Functional Interface
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal dog = () -> { return "Dog: Barks"; };
Animal bird = () -> { return "Bird: Chrip"; };
Animal cat = () -> { return "Cat: Meow"; };
Animal horse = () -> { return "Horse: Neigh"; };
Animal monkey = () -> { return "Monkey: Screech"; };
Animal lion = () -> { return "Lion: Roar"; };
Animal elephant = () -> { return "Elephant: Trumpets"; };
System.out.println(dog.makeSound());
System.out.println(bird.makeSound());
System.out.println(cat.makeSound());
System.out.println(horse.makeSound());
System.out.println(monkey.makeSound());
System.out.println(lion.makeSound());
System.out.println(elephant.makeSound());
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
Traditional classes , Anonymous Classes and Lambda Expressioninterface Animal{
String makeSound();
}
class Dog implements Animal{
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "bow-bow";
}
}
class Birds implements Animal{
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Chirp";
}
}
public class LambdaExp{
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Trditional Classes...");//Traditional classes
Animal dog=new Dog();
Animal birds=new Birds();
System.out.println("Dog : "+dog.makeSound());
System.out.println("Birds : "+birds.makeSound());
System.out.println("Anonymos Classes...");// Anonymous Classes
Animal cat=new Animal(){
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "meow";
}
};
System.out.println("Cat : "+cat.makeSound());
System.out.println("Lambda Expression...");//Lambda Expression
Animal lion =()->{
return "Roar";
};
System.out.println("Lion : "+lion.makeSound());
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
Task 1interface Animal{
String makeSound();
}
class Dog implements Animal{
public String makeSound(){
return "Bow Bow";
}
}
class Birds implements Animal{
public String makeSound(){
return "chirp chirp";
}
}
class Cat implements Animal{
public String makeSound(){
return "Meow Meow";
}
}
class Horse implements Animal{
public String makeSound(){
return "Neigh Neigh";
}
}
class Monkey implements Animal{
public String makeSound(){
return "Ooh ooh ";
}
}
class Lion implements Animal{
public String makeSound(){
return "growl growl";
}
}
class Elephant implements Animal{
public String makeSound(){
return "trumpeting";
}
}
public class AnimalDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal dog = new Dog();
Animal birds=new Birds();
Animal cat = new Cat();
Animal horse = new Horse();
Animal monkey=new Elephant();
Animal lion= new Lion();
Animal elephant = new Cat();
System.out.println(dog.makeSound());
System.out.println(birds.makeSound());
System.out.println(cat.makeSound());
System.out.println(horse.makeSound());
System.out.println(monkey.makeSound());
System.out.println(lion.makeSound());
System.out.println(elephant.makeSound());
}
}2 Anonymous classinterface Animal{
String makeSound();
}
public class AnonymousInner {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal dog =new Dog(){
public String makeSound(){
return "Bow Bow";
}
};
System.out.println(dog.makeSound());
Animal birds =new Birds(){
public String makeSound(){
return "chirp chirp";
}
};
System.out.println(birds.makeSound());
Animal cat =new Cat(){
public String makeSound(){
return "Meow Meow";
}
};
System.out.println(cat.makeSound());
Animal horse =new Horse(){
public String makeSound(){
return "Niegh Niegh";
}
};
System.out.println(horse.makeSound());
Animal monkey =new Monkey(){
public String makeSound(){
return "Ooh Ooh";
}
};
System.out.println(monkey.makeSound());
Animal lion =new Lion(){
public String makeSound(){
return "growl growl";
}
};
System.out.println(lion.makeSound());
Animal elephant =new Elephant(){
public String makeSound(){
return "trumpeting";
}
};
System.out.println(elephant.makeSound());
}
}3 Lambda Expression/*Implement the interface using lambda expressions to return the noise made by dogs, birds, cats, horses, monkeys, lions, and elephants. */
interface Animal{
String makeSound();
}
public class LambdaExpression implements Animal{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal cat =()-> "Meow Meow";
System.out.println("Cat makes noise: " + cat.makeSound());
Animal birds =()-> "Swirp swirp";
System.out.println("birds makes noise: " +birds.makeSound());
Animal dog =()-> "bow bow";
System.out.println("dog makes noise: " + dog.makeSound());
Animal horses =()-> "Neigh Neigh";
System.out.println("horses makes noise: "+horses.makeSound());
Animal monkeys =()-> "Ooh Ooh";
System.out.println("monkeys makes noise: "+monkeys.makeSound());
Animal lions =()-> "growl growl";
System.out.println("lions makes noise:"+lions.makeSound());
Animal elephants =()-> "trumps";
System.out.println("elephants makes noise:"+elephants.makeSound());
}
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return null;
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
1.Traditionalinterface Animal {
String makeSound();
}
class Dogs implements Animal {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "bow bow";
}
}
class Birds implements Animal {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "chirrup chirrup";
}
}
class Cats implements Animal {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "meow meow";
}
}
class Horses implements Animal {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "neigh neigh";
}
}
class Monkeys implements Animal {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "whoop whoop";
}
}
class Lions implements Animal {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "roar";
}
}
class Elephants implements Animal {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "trumpet";
}
}
public class Animals {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal animal1=new Dogs();
System.out.println("Dogs:"+animal1.makeSound());
Animal animal2=new Birds();
System.out.println("Birds:"+animal2.makeSound());
Animal animal3=new Cats();
System.out.println("Cats:"+animal3.makeSound());
Animal animal4=new Horses();
System.out.println("Horses:"+animal4.makeSound());
Animal animal5=new Monkeys();
System.out.println("Monkeys:"+animal5.makeSound());
Animal animal6=new Lions();
System.out.println("Lions:"+animal6.makeSound());
Animal animal7=new Elephants();
System.out.println("Elepants:"+animal7.makeSound());
}
}2.Anonymousinterface Animal {
String makeSound();
}
public class Anonymous {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal dog=new Dogs(){
public String makeSound() {
return "bow bow";
}
};
Animal cat=new Cats(){
public String makeSound() {
return "meow meow";
}
};
Animal bird=new Birds(){
public String makeSound() {
return "chirrup chirrup";
}
};
Animal horse =new Horses(){
public String makeSound() {
return "neigh";
}
};
Animal monkey=new Monkeys(){
public String makeSound() {
return "whoop";
}
};
Animal lion=new Lions(){
public String makeSound() {
return "Roar";
}
};
Animal elephant = new Elephants(){
public String makeSound() {
return "trumpet";
}
};
System.out.println("Dog Sound:" + dog.makeSound());
System.out.println("Cat Sound:" + cat.makeSound());
System.out.println("Bird Sound:" + bird.makeSound());
System.out.println("Monkey Sound:" + monkey.makeSound());
System.out.println("Horse Sound:" + horse.makeSound());
System.out.println("Lion Sound:" + lion.makeSound());
System.out.println("Elephant Sound:" + elephant.makeSound());
}
}
3.Lambda Expressionsinterface Animal {
String makeSound();
}
public class Lambdas {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal dog=()->"wow wow";
Animal cat=()->"meow meow";
Animal bird=()->"chirrup ";
Animal horse=()->"neigh";
Animal monkey=()->"ooh";
Animal lion=()->"roar";
Animal elephant=()->"trumpet";
System.out.println("dog sound : " + dog.makeSound());
System.out.println("cat sound : " + cat.makeSound());
System.out.println("bird sound : " + bird.makeSound());
System.out.println("horse sound : " + horse.makeSound());
System.out.println("monkey sound : " + monkey.makeSound());
System.out.println("lion sound : " + lion.makeSound());
System.out.println("elephant sound : " + elephant.makeSound());
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
interface Animal {
String makeSound();
}
class Dogs implements Animal {
public String makeSound() {
return ("Bhow Bhow");
}
}
class Cats implements Animal {
public String makeSound() {
return ("Meow Meow");
}
}
public class Discussion68 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("\nBy using traditional class: ");
Animal D = new Dogs();
System.out.println(D.makeSound());
Animal C = new Cats();
System.out.println(C.makeSound());
System.out.println("\nBy using Anonymous class: ");
Animal cat = new Animal() {
public String makeSound() {
return ("Meow Meow");
}
};
System.out.println(cat.makeSound());
Animal dog = new Animal() {
public String makeSound() {
return ("Bhow Bhow");
}
};
System.out.println(dog.makeSound());
System.out.println("\nBy using Lambda expressions: ");
Animal d = () -> "Bhow Bhow";
Animal c = () -> "Meow Meow";
System.out.println(d.makeSound());
System.out.println(c.makeSound());
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
public class D68
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Animal dog = new Dog();
dog.makeSound();
Animal cat = new Cat();
cat.makeSound();
Animal lion = new Lion();
lion.makeSound();
Animal anonymousDog = new Animal() {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Bow Bow!");
}
};
anonymousDog.makeSound();
Animal anonymousCat = new Animal() {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Meow Meow!");
}
};
anonymousCat.makeSound();
Animal anonymousLion = new Animal() {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Roar!");
}
};
anonymousLion.makeSound();
Animal lambdaDog = () -> {
System.out.println("Bow Bow");
};
lambdaDog.makeSound();
Animal lambdaCat = () -> {
System.out.println("Meow Meow");
};
lambdaCat.makeSound();
Animal lambdaLion = () -> {
System.out.println("Roar");
};
lambdaLion.makeSound();
}
}
interface Animal {
void makeSound();
}
class Dog implements Animal {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Bow Bow!");
}
}
class Cat implements Animal {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Meow Meow!");
}
}
class Lion implements Animal {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Roar!");
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
interface Animal {
void makeSound();
}
class Dog implements Animal {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Bow Bow");
}
}
class Cat implements Animal {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Meow Meow");
}
}
class Lion implements Animal {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Roar");
}
}
public class discussion68 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// traditional implementation
Animal dog = new Dog();
dog.makeSound();
Animal cat = new Cat();
cat.makeSound();
Animal lion = new Lion();
lion.makeSound();
// using Anonymous class
Animal anonymousDog = new Animal() {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Bow Bow too");
}
};
anonymousDog.makeSound();
Animal anonymousCat = new Animal() {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Meow Meow too ");
}
};
anonymousCat.makeSound();
Animal anonymousLion = new Animal() {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Roar too");
}
};
anonymousLion.makeSound();
// using Lambda Expression
Animal lambdaDog = () -> {
System.out.println("Bow Bow");
};
lambdaDog.makeSound();
Animal lambdaCat = () -> {
System.out.println("Meow Meow");
};
lambdaCat.makeSound();
Animal lambdaLion = () -> {
System.out.println("Roar");
};
lambdaLion.makeSound();
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
import java.util.*;
public class task68 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal dog = new Dog();
dog.makeSound();
Animal bird = new Bird();
bird.makeSound();
Animal cat = new Cat();
cat.makeSound();
Animal horse = new Horse();
horse.makeSound();
Animal monkey = new Monkey();
monkey.makeSound();
Animal lion = new Lion();
lion.makeSound();
Animal elephant = new Elephant();
elephant.makeSound();
Animal anonymousDog = new Animal() {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Dog sounds are Bow Bow");
}
};
anonymousDog.makeSound();
Animal anonymousCat = new Animal() {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Cat sounds are Meow Meow");
}
};
anonymousCat.makeSound();
Animal lambdaDog = () -> {
System.out.println("Dogs bark");
};
lambdaDog.makeSound();
Animal lambdaLion = () -> {
System.out.println("Lions roar");
};
lambdaLion.makeSound();
}
}
interface Animal {
void makeSound();
}
class Dog implements Animal {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Dog sounds");
}
}
class Bird implements Animal {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Bird sounds");
}
}
class Cat implements Animal {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Cat sounds");
}
}
class Horse implements Animal {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Horse sounds");
}
}
class Monkey implements Animal {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Monkey sounds");
}
}
class Lion implements Animal {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Lion sounds");
}
}
class Elephant implements Animal {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Elephant sounds");
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
interface Animal {
String makeSound();
}
class dog implements Animal {
public String makeSound() {
return "bhaw-bhaw";
}
}
class cat implements Animal {
public String makeSound() {
return "meow-meow";
}
}
class bird implements Animal {
public String makeSound() {
return "Chirp- Chirp";
}
}
public class animals {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Traditional
Animal a = new dog();
System.out.println(a.makeSound());
Animal b = new cat();
System.out.println(b.makeSound());
Animal c = new bird();
System.out.println(c.makeSound());
// Anonymous
Animal dogobj = new Animal() {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Bhaw Bhaw";
}
};
System.out.println(dogobj.makeSound());
Animal catobj = new cat() {
public String makeSound() {
return "Meow- meow";
}
};
System.out.println(catobj.makeSound());
Animal birdobj = new bird() {
public String makeSound() {
return "Chirp-Chirp";
}
};
System.out.println(birdobj.makeSound());
// Lambda expression
Animal ldog = () -> "bhaw bhaw";
System.out.println(ldog.makeSound());
Animal cata = () -> "Meow- meow";
System.out.println(cata.makeSound());
Animal bird = () -> "Chirp-Chirp";
System.out.println(bird.makeSound());
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
class Dog implements Animal{
@Override
public String makeSound() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return "Bow Bow";
}
}
class Bird implements Animal{
@Override
public String makeSound() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return "Birds making noise";
}
}
class Cat implements Animal{
@Override
public String makeSound() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return "Meow Meow";
}
}
public class Driver {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Implementing
Dog dog = new Dog();
System.out.println(dog.makeSound());
Bird bird = new Bird() ;
System.out.println(bird.makeSound());
Cat cat = new Cat() ;
System.out.println(cat.makeSound());
//Anonymous Class
Animal d = new Animal() {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return "Bow Bow Bow" ;
}
};
System.out.println(d.makeSound());
Animal b = new Animal() {
public String makeSound() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return "Birds making noise";
}
};
System.out.println(b.makeSound());
//Lambda Exp.
Animal birds = () -> {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return "Birds making noise";
};
Animal dogs = () -> {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return "Bow BOw BOw Bow";
};
Animal cats = () -> {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return "meow meow meow meow";
};
System.out.println(cats.makeSound());
System.out.println(dogs.makeSound());
System.out.println(birds.makeSound());
}
}
|
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
Code1interface Animal {
String makeSound();
}
class Dog implements Animal {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Bow";
}
}
class Cat implements Animal {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Meow";
}
}
class Birds implements Animal {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "koko";
}
}
class Horse implements Animal {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "neigh";
}
}
class Monkey implements Animal{
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "giber";
}
}
class Lion implements Animal{
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "roar";
}
}
class Elephants implements Animal {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "trumpet";
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal a1 = new Birds();
Animal a2 = new Cat();
Animal a3 = new Dog();
System.out.println("Birds :"+a1.makeSound());
System.out.println("Cat :"+a2.makeSound());
System.out.println("Dog :"+a3.makeSound());
Animal a4 = new Animal() {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Roar";
}
};
System.out.println("Lion :"+a4.makeSound());
Animal a5 = new Animal() {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Trumpet";
}
};
System.out.println("Elephant :"+a5.makeSound());
Animal a6 = () -> "neigh";
System.out.println("Horse :"+a6.makeSound());
Animal a7 = () -> "giber";
System.out.println("Monkey :"+a7.makeSound());
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
codepublic interface Animal {
void sound();
}
package assignment68;
public class Dog implements Animal {
@Override
public void sound() {
System.out.println("Bow Bow");
}
}
package assignment68;
public class Cats implements Animal{
@Override
public void sound() {
System.out.println("Meow meow");
}
}
package assignment68;
public class Lion implements Animal {
@Override
public void sound() {
System.out.println("Roar");
}
}
package assignment68;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal an = new Dog();
an.sound();
Animal an1 = new Cats();
an1.sound();
Animal an2 = new Lion();
an2.sound();
}
}
//Anonumous class
Animal andog = new Animal() {
@Override
public void sound() {
dogs.sound();
}
};
Animal ancats = new Animal() {
@Override
public void sound() {
cat.sound();
}
Animal anlion = new Animal() {
@Override
public void sound() {
lion.sound();
}
};
};
}
}
Lambda Expression
andog.sound();
Animal andog1 = ()->System.out.println("Bow Bow");
ancats.sound();
Animal ancats1 = () ->System.out.println("Meow Meow");
anlion1.sound();
Animal anlion2 = () ->System.out.println("Roar");
System.out.println(andog1+" "+ancats1+" "+anlion2); |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
codepackage assignement21;
interface Animal{
void makesound();
}
class Dog implements Animal {
@Override
public void makesound() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Bow Bow");
}
}
class Bird implements Animal{
@Override
public void makesound() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Kichh Kichhhhh");
}
}
class Cat implements Animal {
@Override
public void makesound() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Meow Meow");
}
}
class Horse implements Animal{
@Override
public void makesound() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Neigh Neigh");
}
}
class Monkey implements Animal{
@Override
public void makesound() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("screech");
}
}
class Lion implements Animal{
@Override
public void makesound() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Roar");
}
}
class Elephant implements Animal{
@Override
public void makesound() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Trumpet");
}
}
public class Animalclass{
//Traditional classes
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
public static void main (String[]args) {
Animal Dog = new Dog();
Dog.makesound();
Animal Bird = new Bird();
Bird.makesound();
Animal Cat = new Cat();
Cat.makesound();
Animal Horse = new Horse();
Horse.makesound();
Animal Monkey = new Monkey();
Monkey.makesound();
Animal Lion = new Lion();
Lion.makesound();
Animal Elephant = new Elephant();
Elephant.makesound();
//Anonymous classes
Animal anonymousDog = new Animal() {
@Override
public void makesound() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Bow Bow");
}
};
anonymousDog.makesound();
Animal anonymousBird = new Animal() {
@Override
public void makesound() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Kichh Kichhhhh");
}
};
anonymousBird.makesound();
Animal anonymousCat = new Animal() {
@Override
public void makesound() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Meow Meow");
}
};
anonymousCat.makesound();
Animal anonymousHorse = new Animal() {
@Override
public void makesound() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Neigh Neigh");
}
};
anonymousHorse.makesound();
Animal anonymousMonkey = new Animal() {
@Override
public void makesound() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("screech");
}
};
anonymousMonkey.makesound();
Animal anonymousLion = new Animal() {
@Override
public void makesound() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Roar");
}
};
anonymousLion.makesound();
Animal anonymousElephant = new Animal() {
@Override
public void makesound() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Trumpet");
}
};
anonymousElephant.makesound();
//Lambda Expression
Animal lambdaDog = () -> {
System.out.println("Bow Bow");
};
Animal lambdaBird = ()-> {
System.out.println("Kichh Kichhhhh");
};
Animal lambdaHorse = ()-> {
System.out.println("Neigh Neigh");
};
Animal lambdaMonkey = ()-> {
System.out.println("screech");
};
Animal lambdaLion = ()-> {
System.out.println("Roar");
};
Animal lambdaElephant = ()-> {
System.out.println("Trumpet");
};
}}
|
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
interface Animal {
String makeSound();
}
class Dog implements Animal {
public String makeSound() {
return "Bow Bow....";
}
}
class Birds implements Animal {
public String makeSound() {
return "Chirp Chirp....";
}
}
class Cats implements Animal {
public String makeSound() {
return "Meow Meow....";
}
}
class Horses implements Animal {
public String makeSound() {
return "Neigh Neigh....";
}
}
class Monkeys implements Animal {
public String makeSound() {
return "ohh ohh....";
}
}
class Lions implements Animal {
public String makeSound() {
return "Roar Roar....";
}
}
class Elephants implements Animal {
public String makeSound() {
return "Trumpeting Trumpeting....";
}
}
public class Discussion68 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Normal Way Of Printing:");
Animal dog = new Dog();
System.out.println(dog.makeSound());
Animal cat = new Cats();
System.out.println(cat.makeSound());
Animal horses = new Horses();
System.out.println(horses.makeSound());
Animal monkeys = new Monkeys();
System.out.println(monkeys.makeSound());
Animal lions = new Lions();
System.out.println(lions.makeSound());
Animal elephants = new Elephants();
System.out.println(elephants.makeSound());
System.out.println("Using Anonymous Class:");
Animal anonDog = new Animal(){
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Bow Bow...";
}
};
System.out.println(anonDog.makeSound());
Animal anonCats = new Animal()
{
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Meow Meow...";
}
};
System.out.println(anonCats.makeSound());
Animal anonHorses = new Animal(){
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Neigh Neigh...";
}
};
System.out.println(anonHorses.makeSound());
Animal anonMonkeys = new Animal(){
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "ohh ohh ohh ohh...";
}
};
System.out.println(anonMonkeys.makeSound());
Animal anonLions = new Animal(){
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Roar Roar...";
}
};
System.out.println(anonLions.makeSound());
Animal anonElephants = new Animal(){
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Trumpeting Trumpeting...";
}
};
System.out.println(anonElephants.makeSound());
System.out.println("Using Lambda Expression");
Animal lambdaDog =() ->"Bow Bow";
System.out.println(lambdaDog.makeSound());
Animal lambdaCats =()->"Chirp Chirp";
System.out.println(lambdaCats.makeSound());
Animal lambdaHorses =()->"Neigh Neigh";
System.out.println(lambdaHorses.makeSound());
Animal lambdaMonkeys =()->"ohh ohh ohh ohh";
System.out.println(lambdaMonkeys.makeSound());
Animal lambdaLions =()->"Roar Roar";
System.out.println(lambdaLions.makeSound());
Animal lambdaElephants =()->"Trumpeting Trumpeting";
System.out.println(lambdaElephants.makeSound());
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
interface Animal {
String makeSound();
}
class Dog implements Animal {
public String makeSound() {
return "Bow Bow....";
}
}
class Birds implements Animal {
public String makeSound() {
return "Chirp Chirp....";
}
}
class Cats implements Animal {
public String makeSound() {
return "Meow Meow....";
}
}
class Horses implements Animal {
public String makeSound() {
return "Neigh Neigh....";
}
}
class Monkeys implements Animal {
public String makeSound() {
return "ohh ohh....";
}
}
class Lions implements Animal {
public String makeSound() {
return "Roar Roar....";
}
}
class Elephants implements Animal {
public String makeSound() {
return "Trumpeting Trumpeting....";
}
}
public class Discussion68 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Normal Way Of Printing:");
Animal dog = new Dog();
System.out.println(dog.makeSound());
Animal cat = new Cats();
System.out.println(cat.makeSound());
Animal horses = new Horses();
System.out.println(horses.makeSound());
Animal monkeys = new Monkeys();
System.out.println(monkeys.makeSound());
Animal lions = new Lions();
System.out.println(lions.makeSound());
Animal elephants = new Elephants();
System.out.println(elephants.makeSound());
System.out.println("Using Anonymous Class:");
Animal anonDog = new Animal(){
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Bow Bow...";
}
};
System.out.println(anonDog.makeSound());
Animal anonCats = new Animal()
{
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Meow Meow...";
}
};
System.out.println(anonCats.makeSound());
Animal anonHorses = new Animal(){
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Neigh Neigh...";
}
};
System.out.println(anonHorses.makeSound());
Animal anonMonkeys = new Animal(){
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "ohh ohh ohh ohh...";
}
};
System.out.println(anonMonkeys.makeSound());
Animal anonLions = new Animal(){
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Roar Roar...";
}
};
System.out.println(anonLions.makeSound());
Animal anonElephants = new Animal(){
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Trumpeting Trumpeting...";
}
};
System.out.println(anonElephants.makeSound());
System.out.println("Using Lambda Expression");
Animal lambdaDog =() ->"Bow Bow";
System.out.println(lambdaDog.makeSound());
Animal lambdaCats =()->"Chirp Chirp";
System.out.println(lambdaCats.makeSound());
Animal lambdaHorses =()->"Neigh Neigh";
System.out.println(lambdaHorses.makeSound());
Animal lambdaMonkeys =()->"ohh ohh ohh ohh";
System.out.println(lambdaMonkeys.makeSound());
Animal lambdaLions =()->"Roar Roar";
System.out.println(lambdaLions.makeSound());
Animal lambdaElephants =()->"Trumpeting Trumpeting";
System.out.println(lambdaElephants.makeSound());
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
PRASETHA N package com.practice.problems.java;
public class AnimalNoiseUsingClasses {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal dog = new Dog();
Animal bird = new Bird();
Animal cat = new Cat();
Animal horse = new Horse();
Animal monkey = new Monkey();
Animal lion = new Lion();
Animal elephant = new Elephant();
System.out.println("Dog: " + dog.makeSound());
System.out.println("Bird: " + bird.makeSound());
System.out.println("Cat: " + cat.makeSound());
System.out.println("Horse: " + horse.makeSound());
System.out.println("Monkey: " + monkey.makeSound());
System.out.println("Lion: " + lion.makeSound());
System.out.println("Elephant: " + elephant.makeSound());
}
}
@FunctionalInterface
interface Animal {
String makeSound();
}
/*
* Implement the interface using traditional classes to return the noise made by
* dogs, birds, cats, horses, monkeys, lions, and elephants.
*/
class Dog implements Animal {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Bow Bow";
}
}
class Bird implements Animal {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Tweet";
}
}
class Cat implements Animal {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Meow Meow";
}
}
class Horse implements Animal {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Neigh";
}
}
class Monkey implements Animal {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Ooh ooh aah aah";
}
}
class Lion implements Animal {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Roar";
}
}
class Elephant implements Animal {
@Override
public String makeSound() {
return "Trumpet";
}
}TASK-2 package com.practice.problems.java;
public class AnimalNoiseUsingAnonymousClasses {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal dog = new Animal() {
public String makeSound() {
return "Bow Bow";
}
};
Animal bird = new Animal() {
public String makeSound() {
return "Tweet";
}
};
Animal cat = new Animal() {
public String makeSound() {
return "Meow Meow";
}
};
Animal horse = new Animal() {
public String makeSound() {
return "Neigh";
}
};
Animal monkey = new Animal() {
public String makeSound() {
return "Ooh ooh aah aah";
}
};
Animal lion = new Animal() {
public String makeSound() {
return "Roar";
}
};
Animal elephant = new Animal() {
public String makeSound() {
return "Trumpet";
}
};
System.out.println("Dog: " + dog.makeSound());
System.out.println("Bird: " + bird.makeSound());
System.out.println("Cat: " + cat.makeSound());
System.out.println("Horse: " + horse.makeSound());
System.out.println("Monkey: " + monkey.makeSound());
System.out.println("Lion: " + lion.makeSound());
System.out.println("Elephant: " + elephant.makeSound());
}
}TASK-3 package com.practice.problems.java;
public class AnimalNoiseInterface {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal dog = () -> "Bow Bow";
Animal bird = () -> "Tweet";
Animal cat = () -> "Meow Meow";
Animal horse = () -> "Neigh";
Animal monkey = () -> "Ooh ooh aah aah";
Animal lion = () -> "Roar";
Animal elephant = () -> "Trumpet";
System.out.println("Dog: " + dog.makeSound());
System.out.println("Bird: " + bird.makeSound());
System.out.println("Cat: " + cat.makeSound());
System.out.println("Horse: " + horse.makeSound());
System.out.println("Monkey: " + monkey.makeSound());
System.out.println("Lion: " + lion.makeSound());
System.out.println("Elephant: " + elephant.makeSound());
}
} |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
*Task 1 Lamda Expression_Sayan Dey_Completed_1. Using Traditional Classes interface Animal { // Traditional Classes class Bird implements Animal { class Cat implements Animal { class Horse implements Animal { class Monkey implements Animal { class Lion implements Animal { class Elephant implements Animal { public class TraditionalClass { } 2. Using Anonymous Classespublic class AnonymousClass { } 3. Using Lamda Expressionpublic class LamdaExpression { } |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
Bhavana // Traditional classes for each animal class Bird implements Animal { class Cat implements Animal { class Horse implements Animal { class Monkey implements Animal { class Lion implements Animal { class Elephant implements Animal { public class AnimalSoundsAnonymous { } } |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
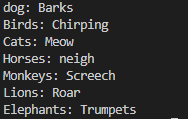
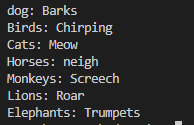
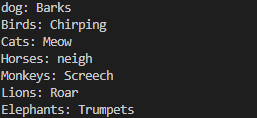

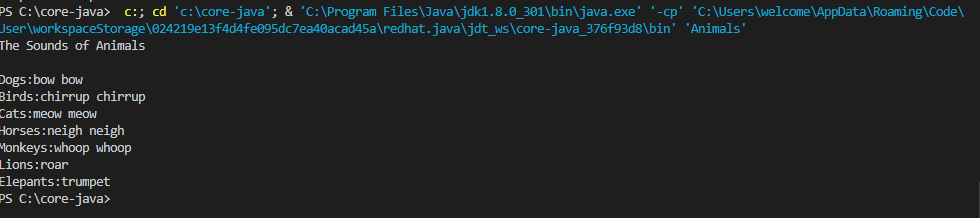
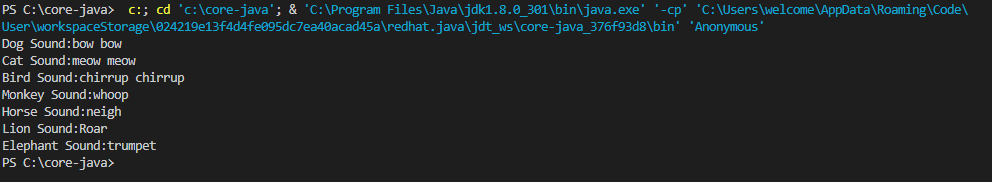
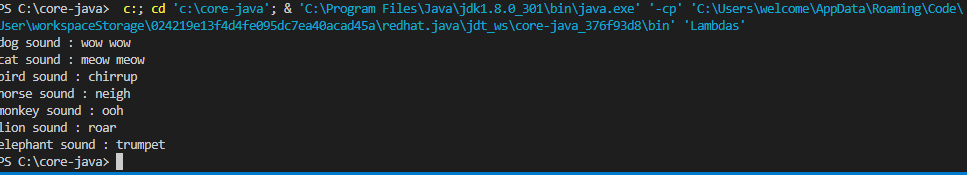
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading. Please reload this page.
-
Given a functional interface
Animal:Implement the interface using traditional classes to return the noise made by
dogs,birds,cats,horses,monkeys,lions, andelephants.Implement the interface using anonymous classes to return the noise made by
dogs,birds,cats,horses,monkeys,lions, andelephants.Implement the interface using lambda expressions to return the noise made by
dogs,birds,cats,horses,monkeys,lions, andelephants.Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
All reactions